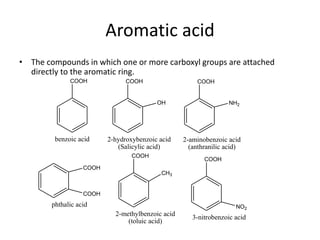
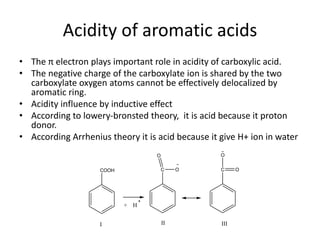
1. Aromatic acids contain one or more carboxyl groups directly attached to an aromatic ring. The acidity of aromatic acids is influenced by electron withdrawing and donating groups on the ring through inductive or resonance effects.
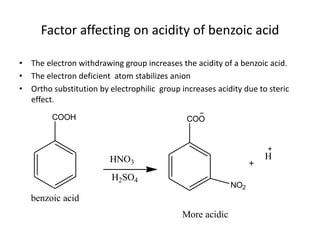
2. Electron withdrawing groups increase the acidity of benzoic acid by stabilizing the anion through resonance. Electron donating groups decrease acidity by increasing the electron density of the aromatic ring.
3. Aromatic acids undergo various reactions including salt formation, esterification, acylation, reduction, decarboxylation, and electrophilic substitution.