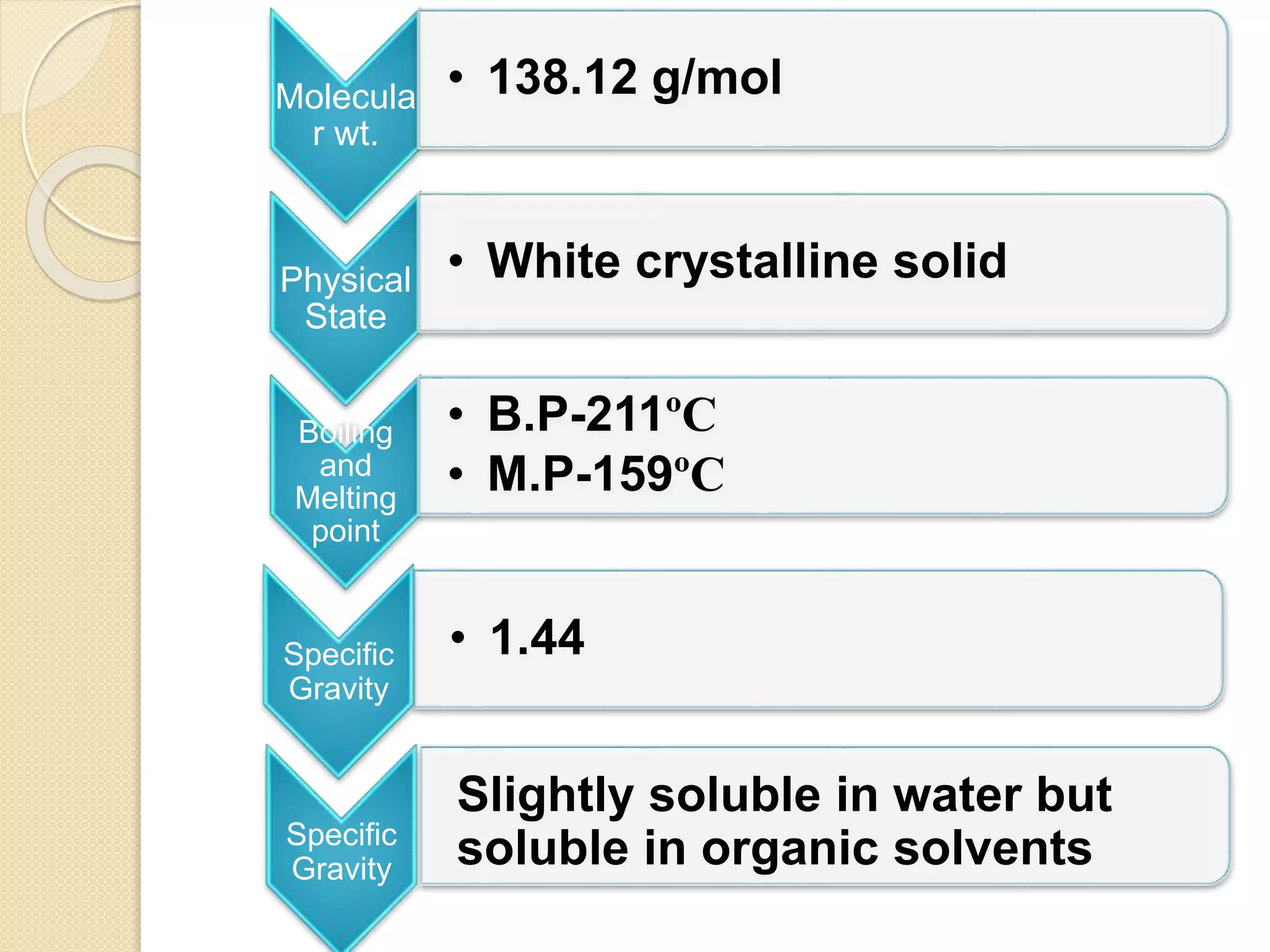
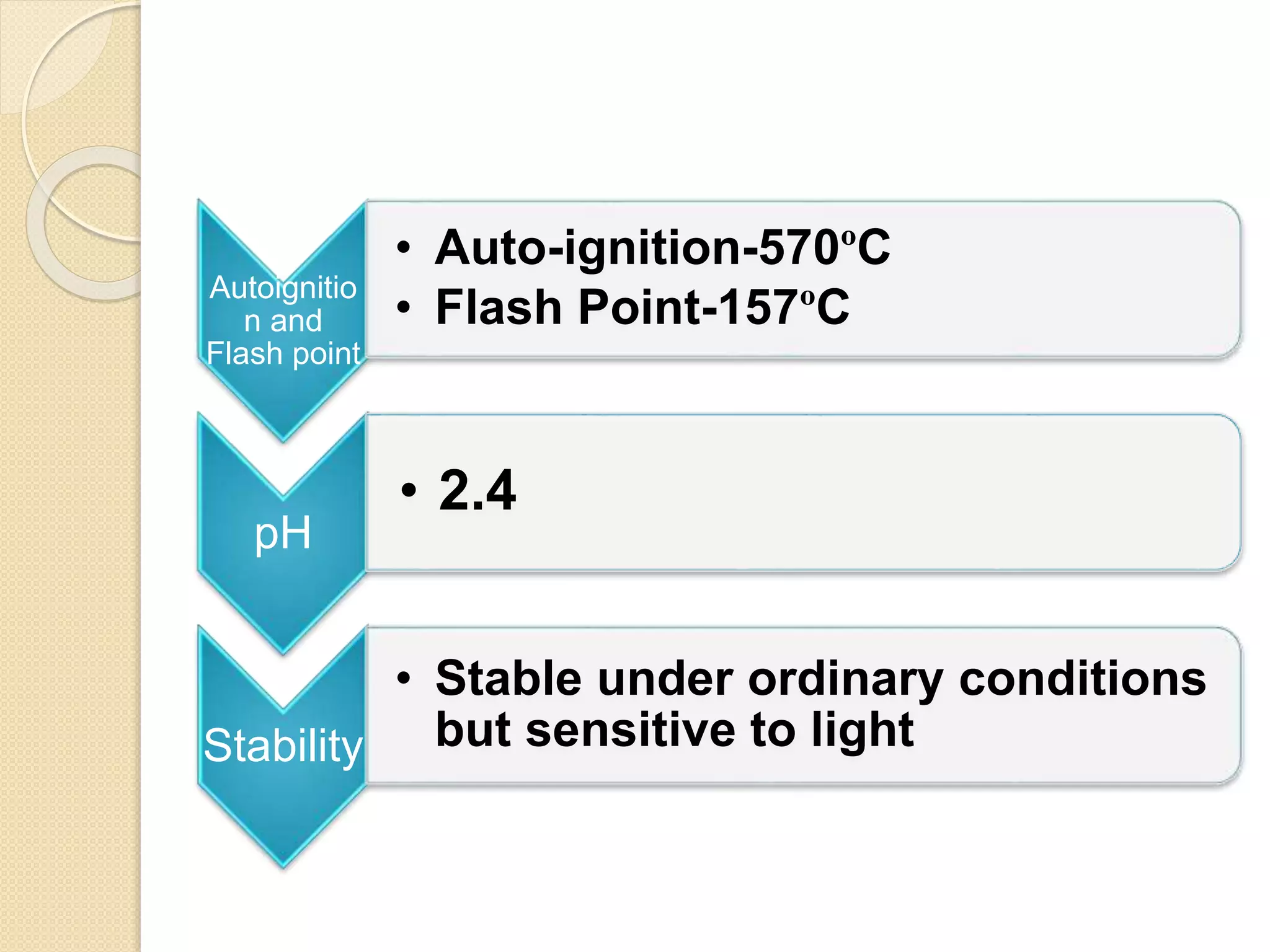
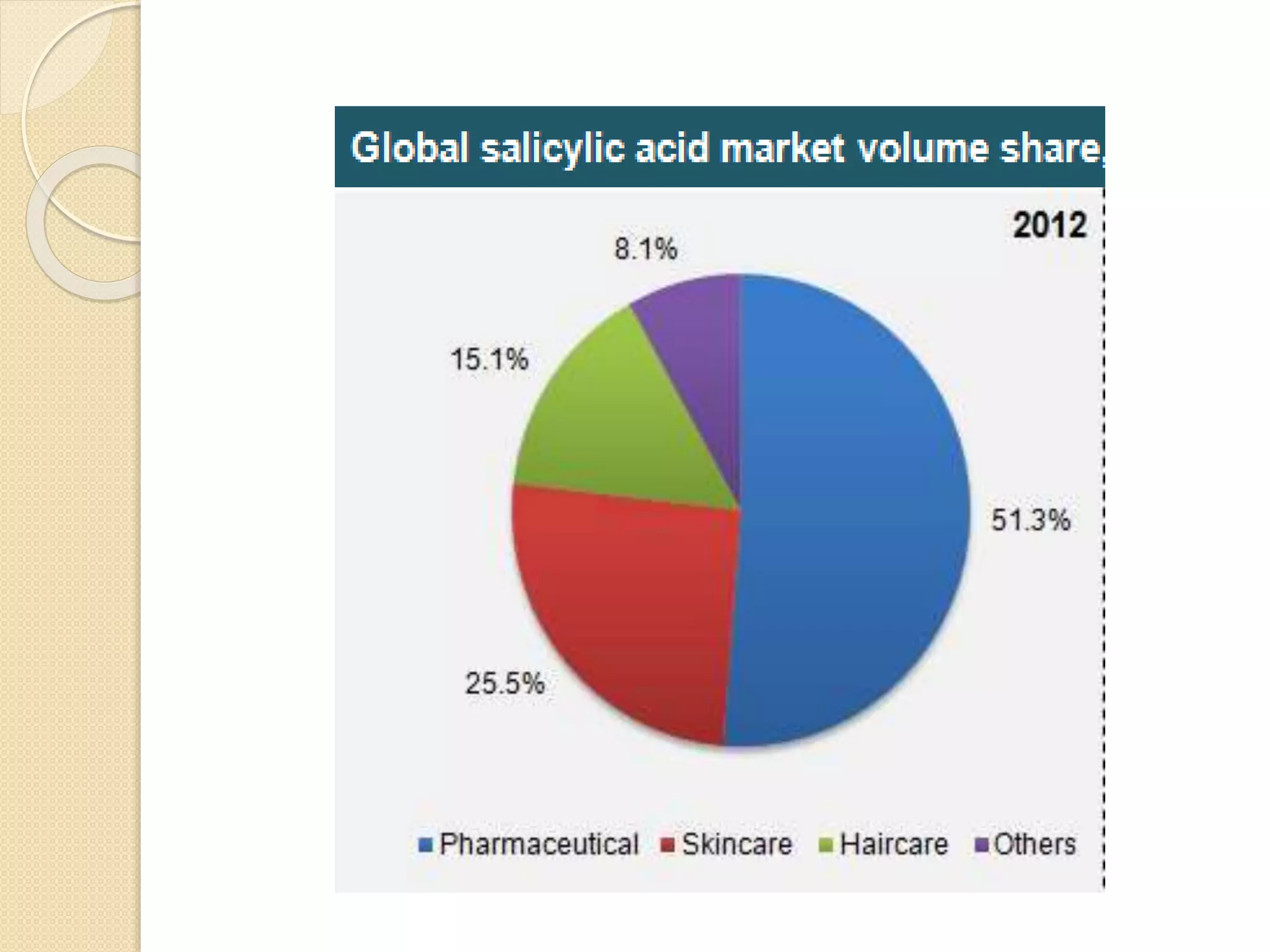
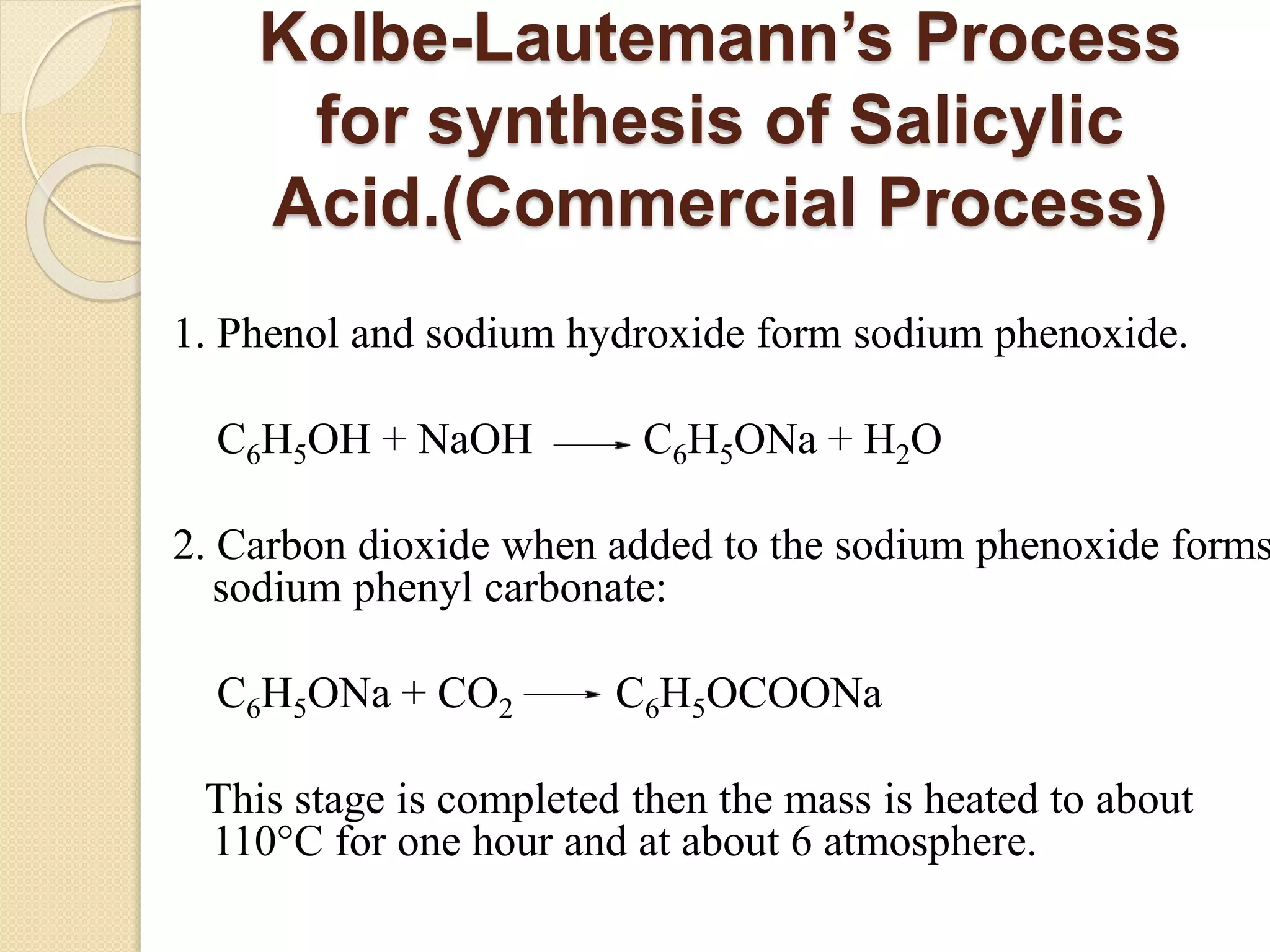
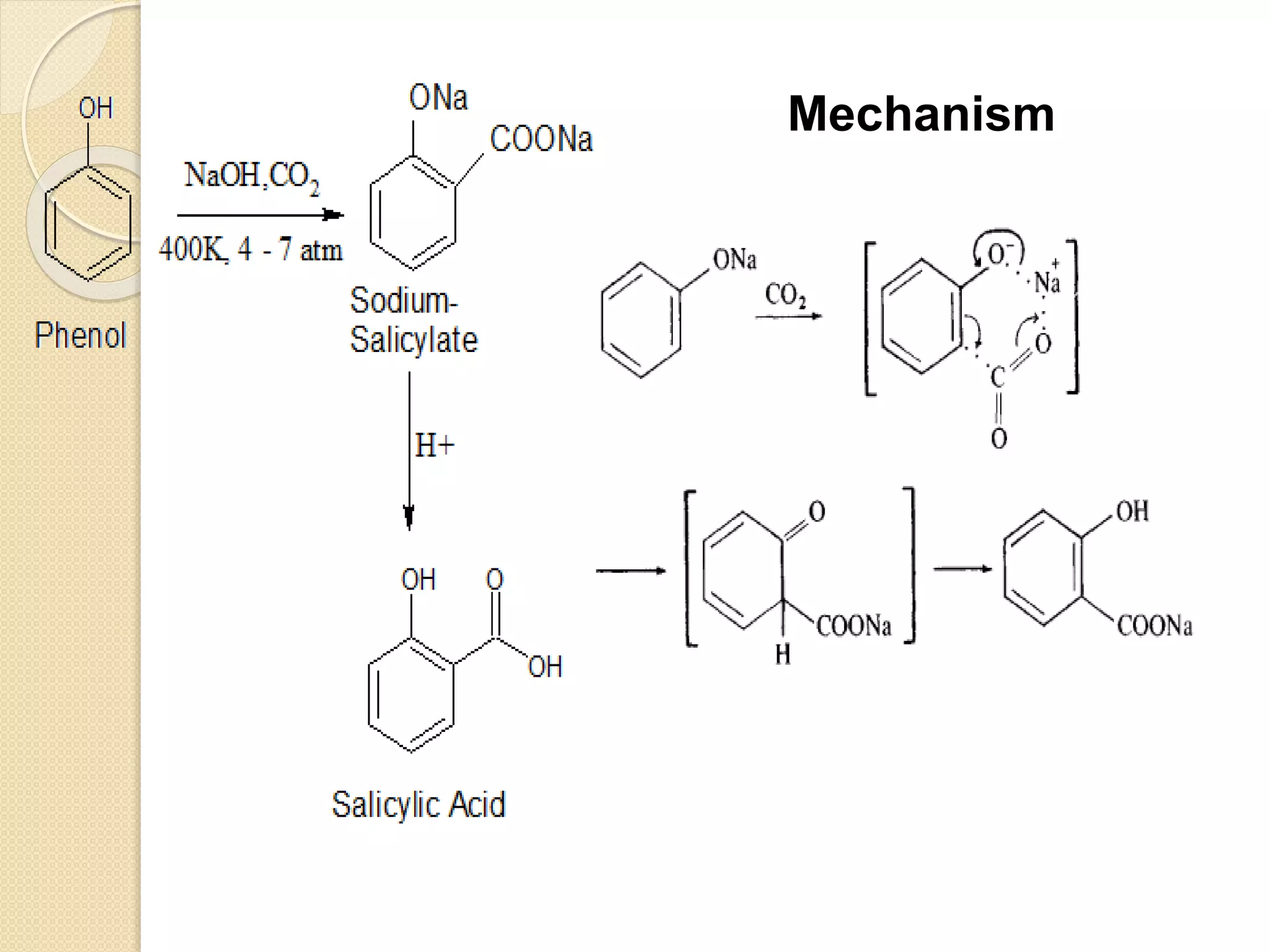
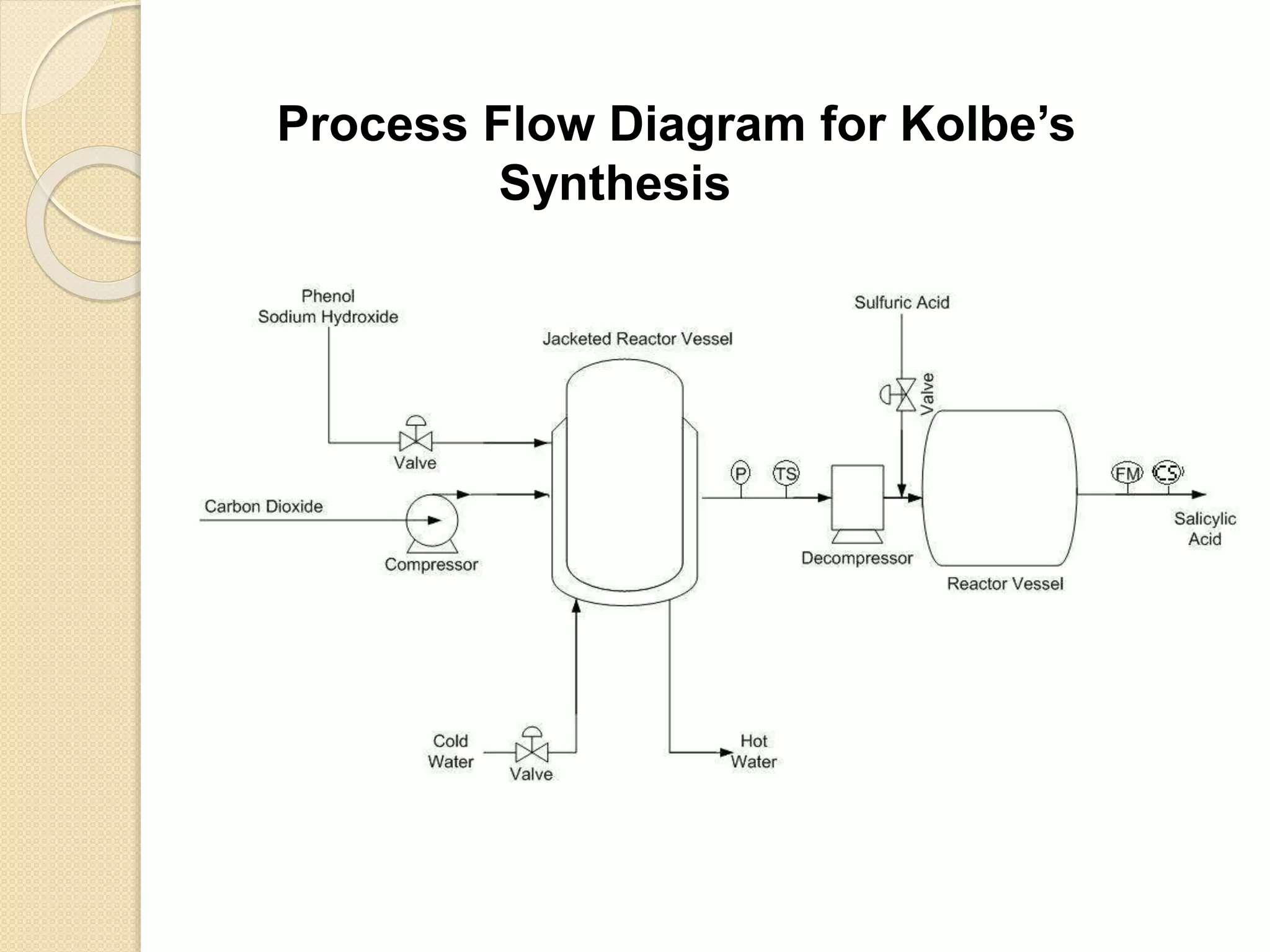
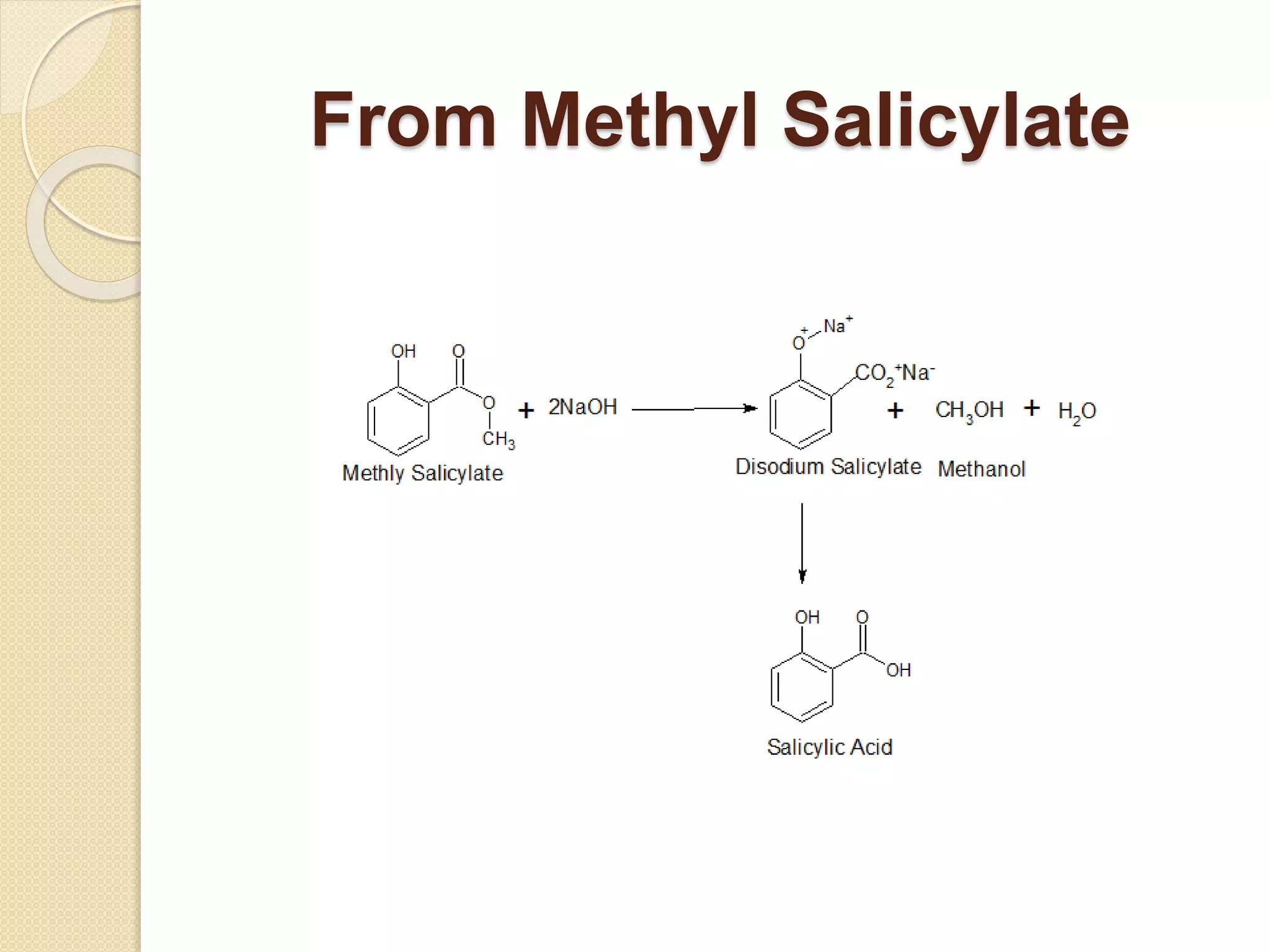
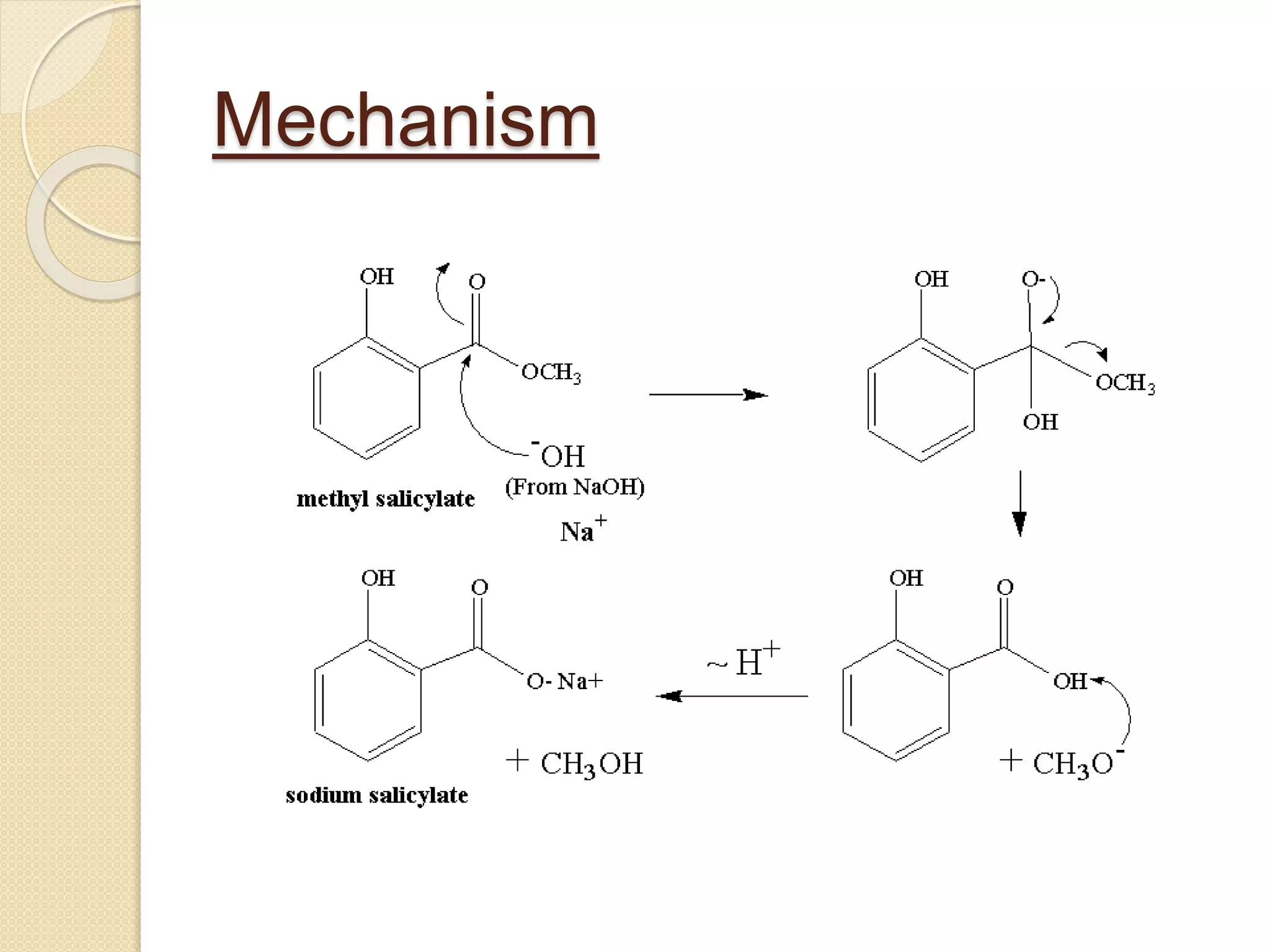
Salicylic acid is obtained from the bark of willow trees. It has the formula C7H6O3 and is a colorless crystalline organic acid. It was first discovered in 1839 by fusing salicylic aldehyde with potassium hydroxide. Salicylic acid is used externally to treat skin conditions like athlete's foot and warts, and is also used in acne treatments. It is synthesized commercially via the Kolbe-Lautemann process, which involves reacting phenol with sodium and carbon dioxide to produce sodium salicylate, then converting it to salicylic acid.