1. Phenol can be prepared through several methods including the Dow process involving chlorobenzene, cumene oxidation, and from coal tar.
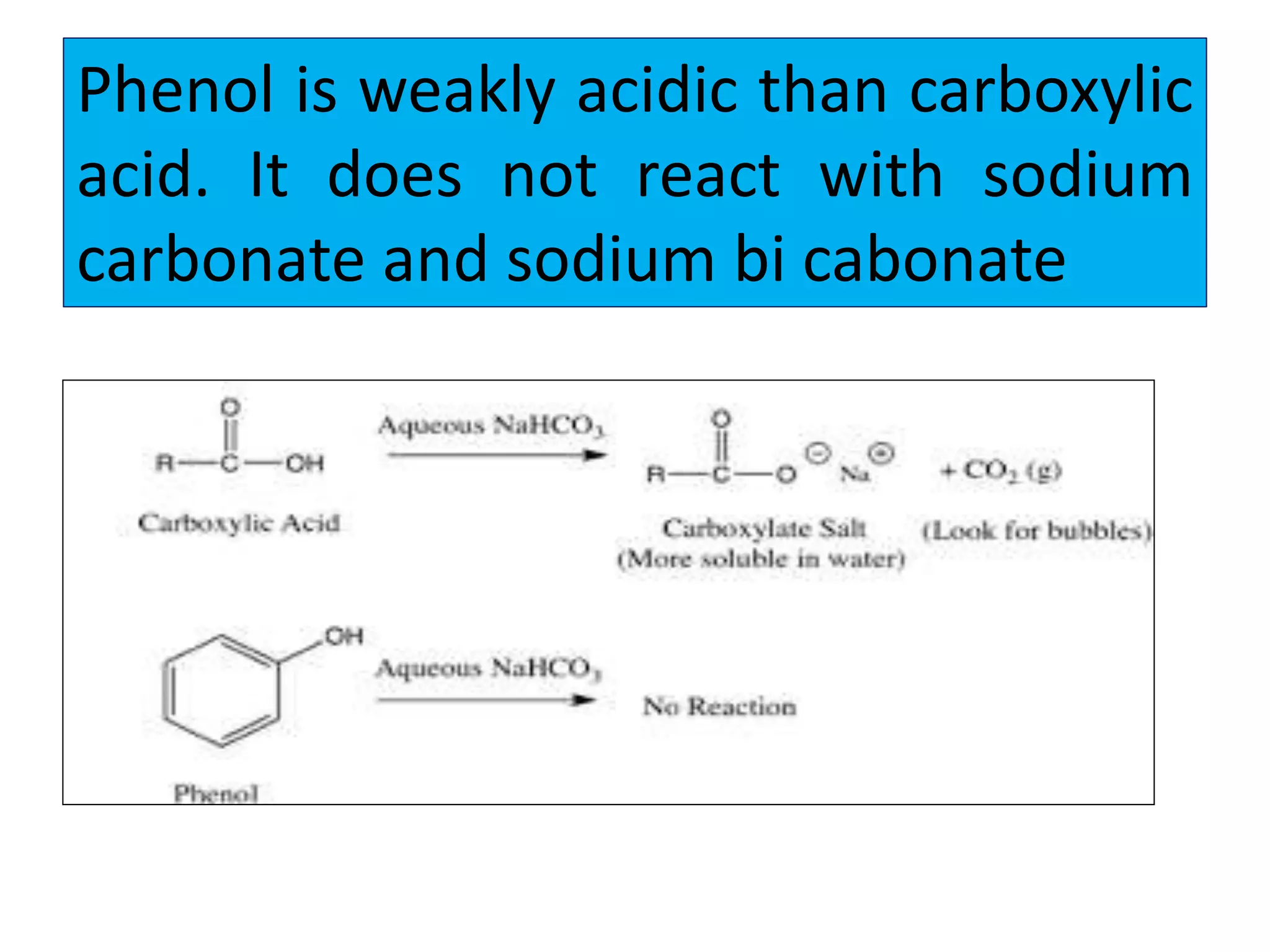
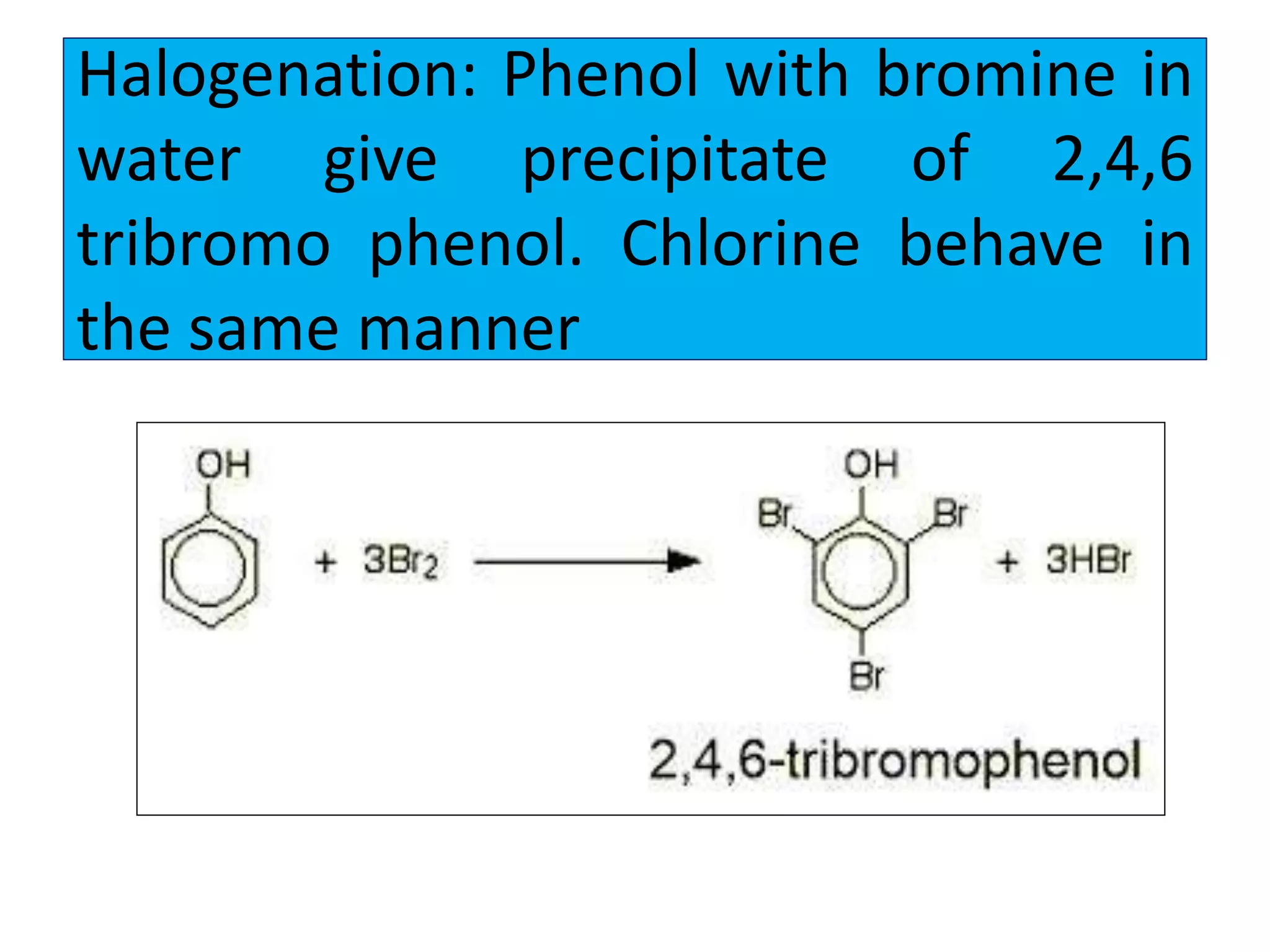
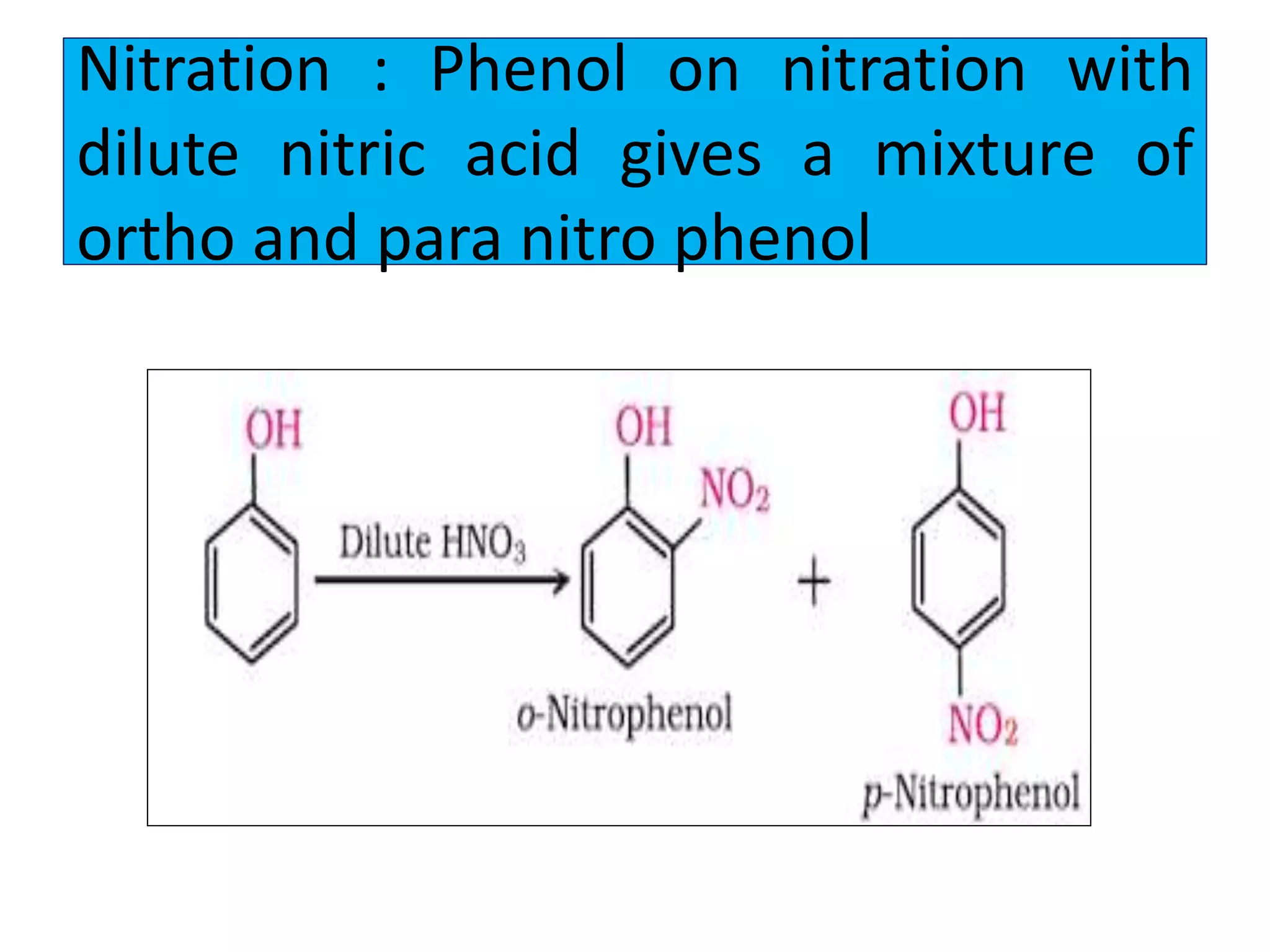
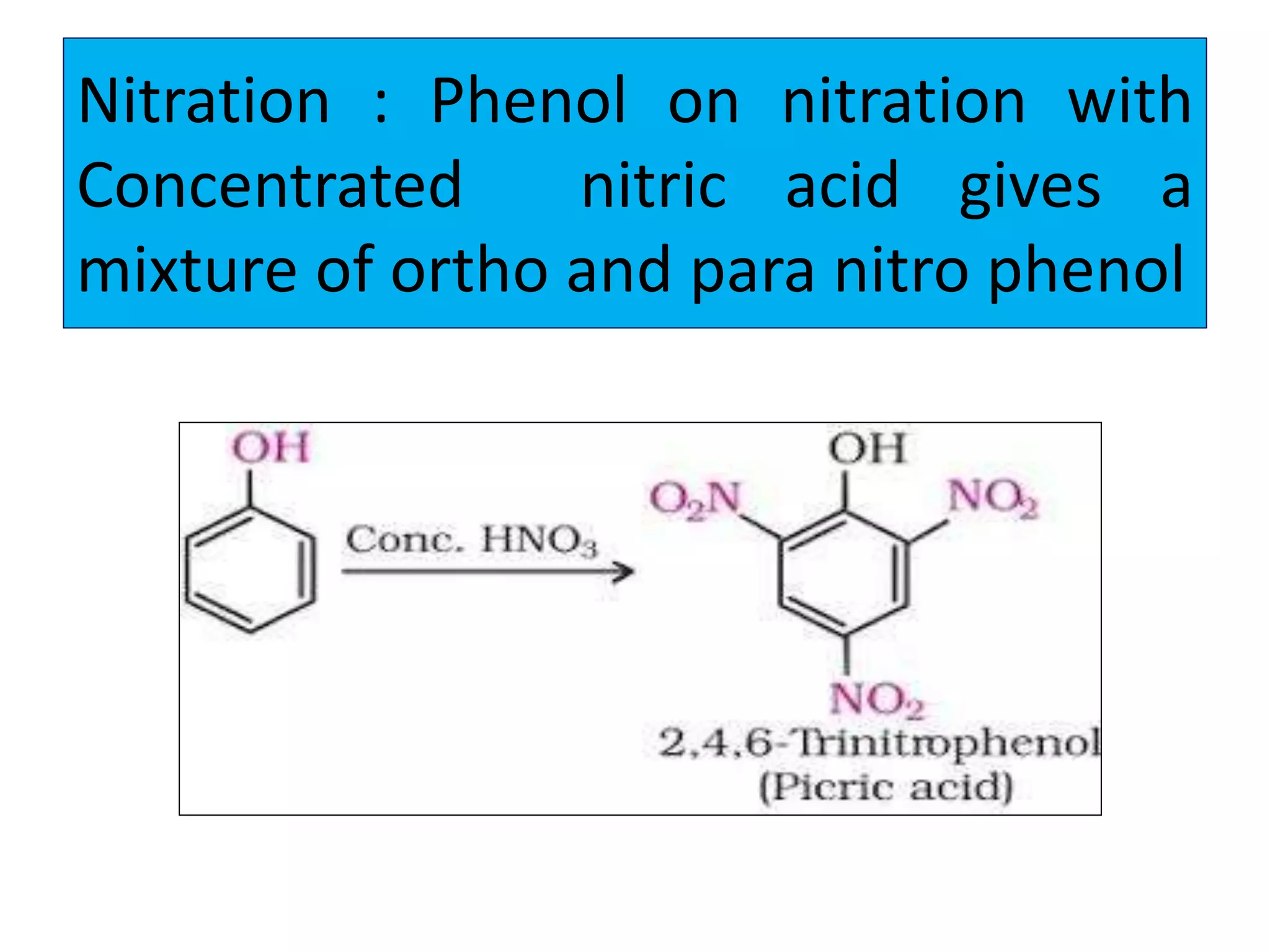
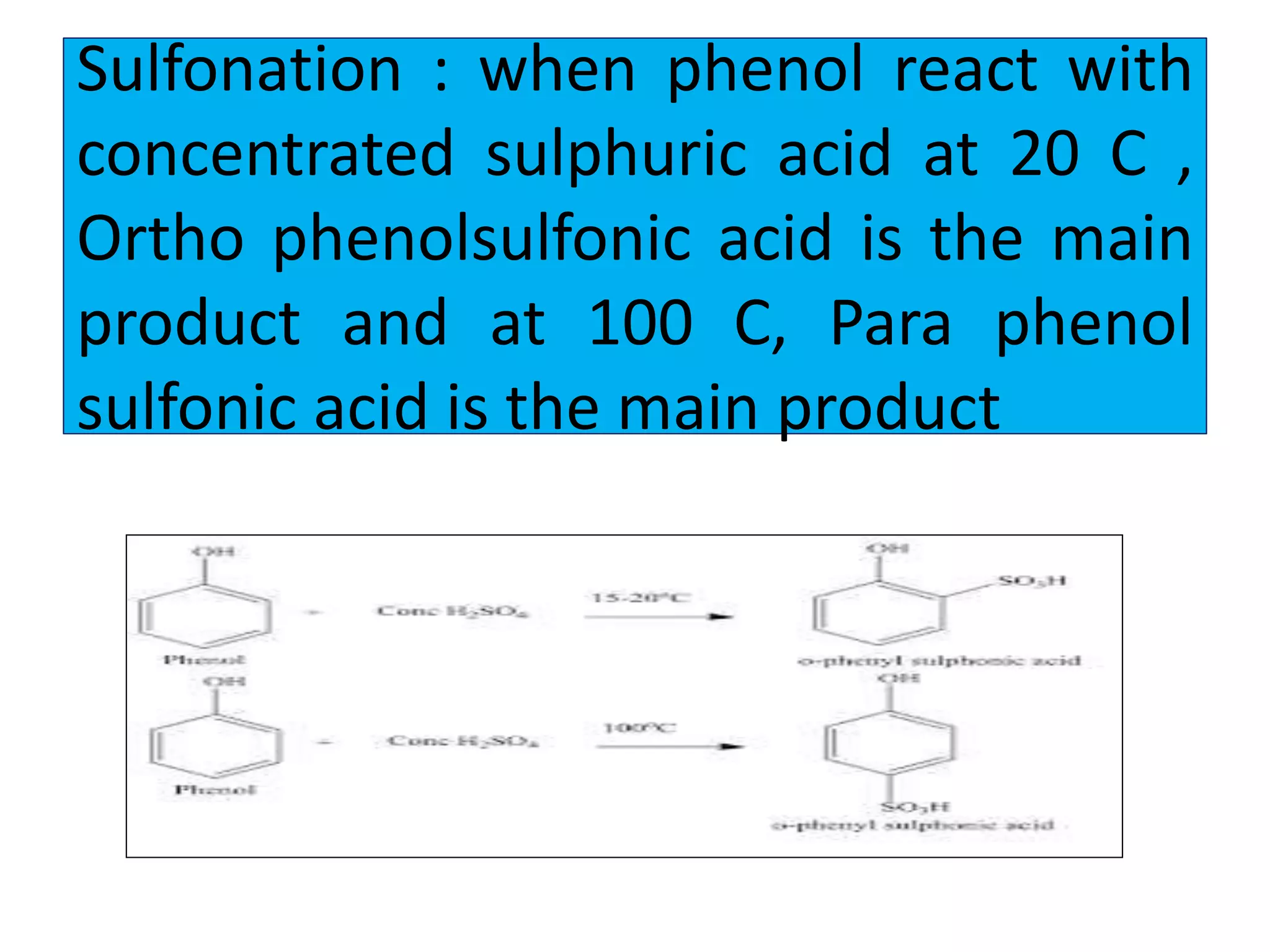
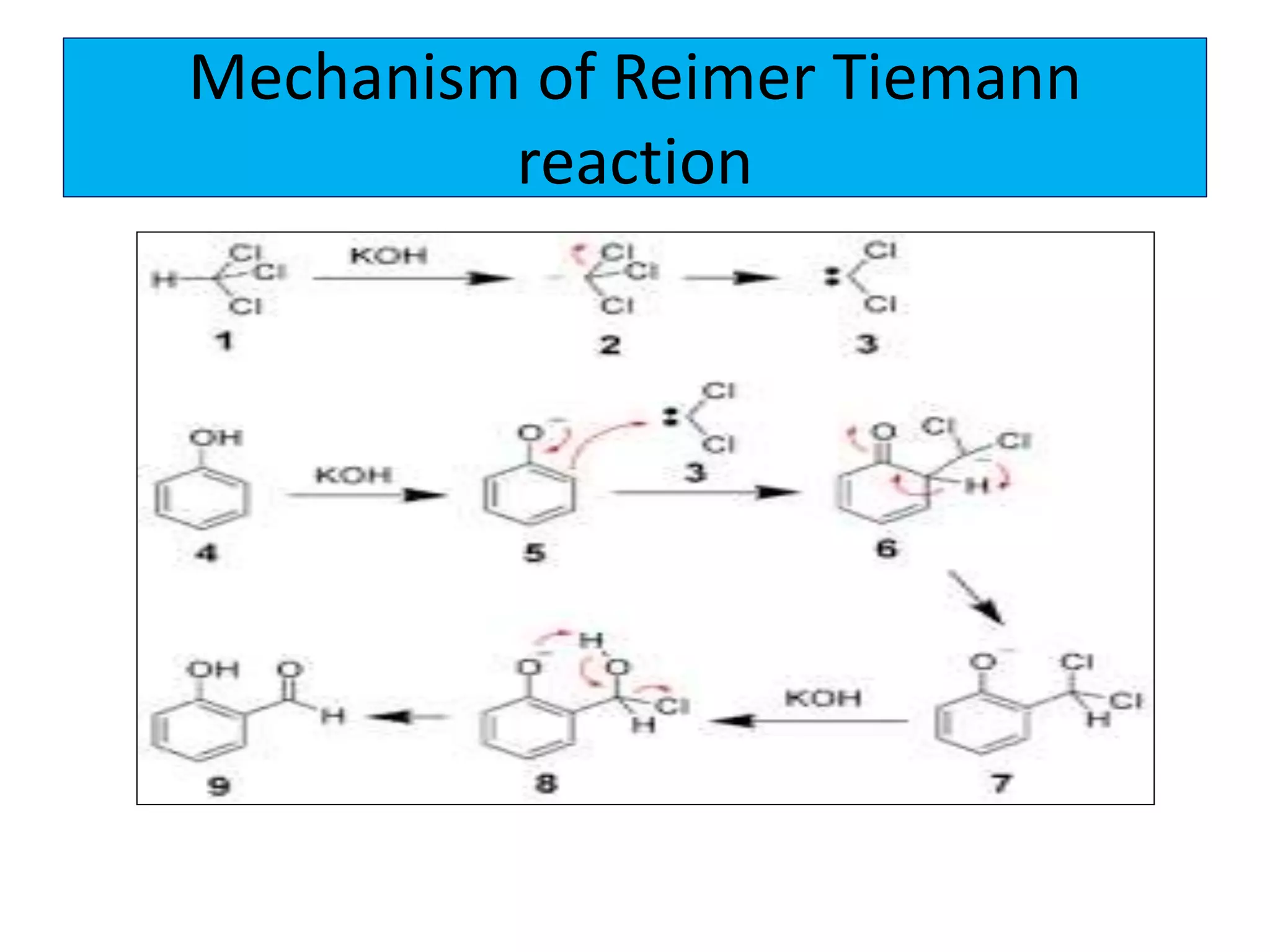
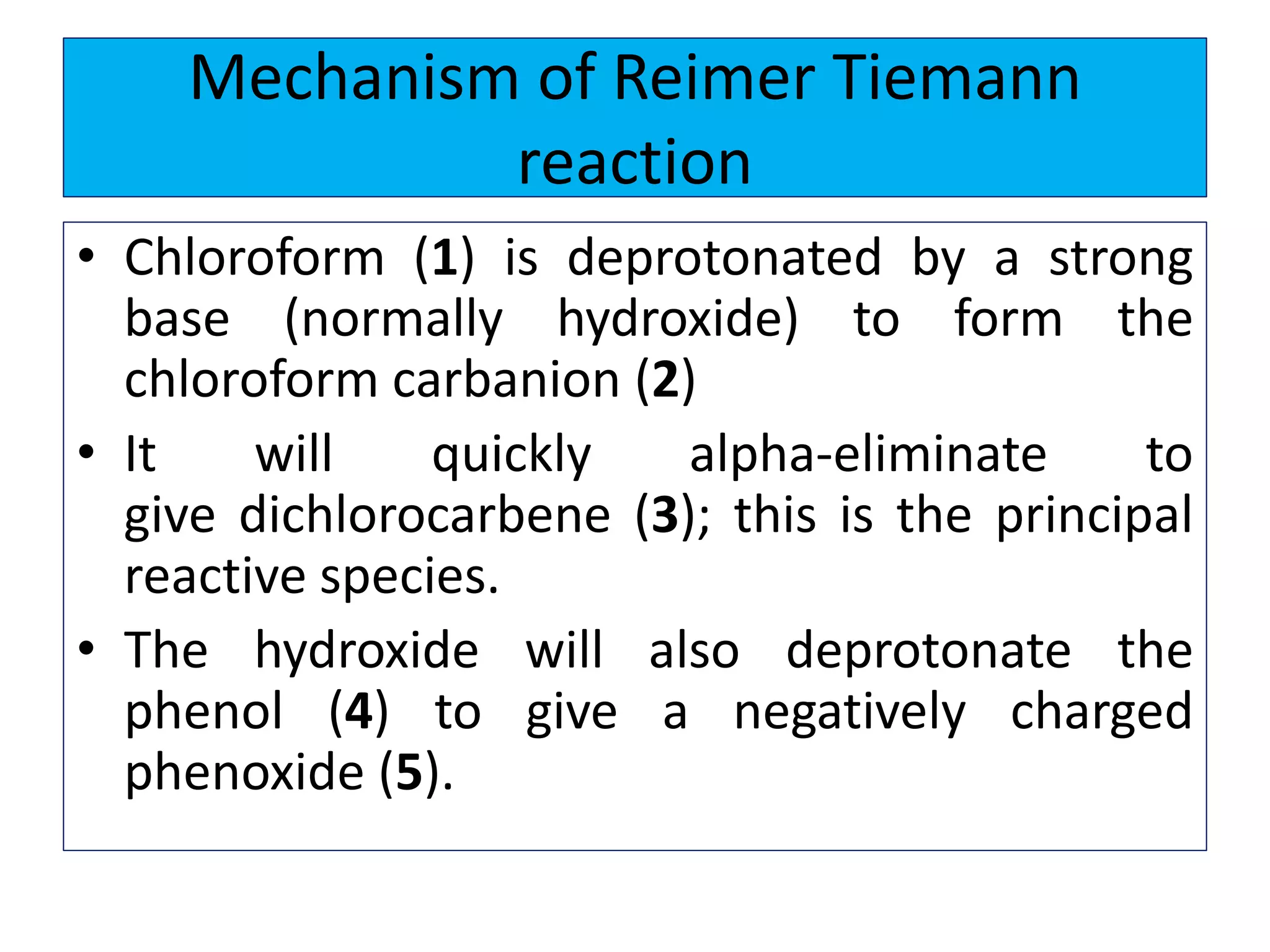
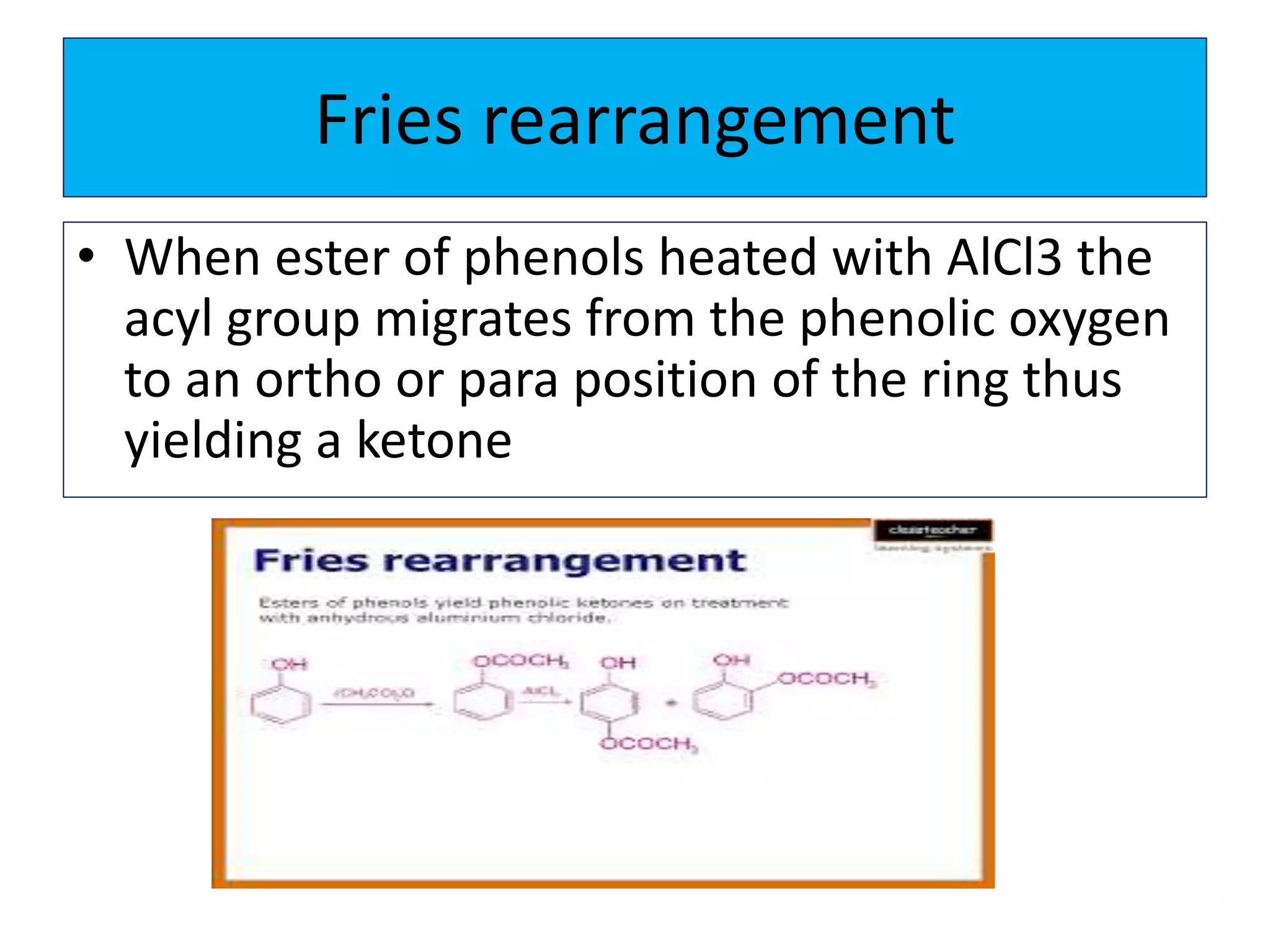
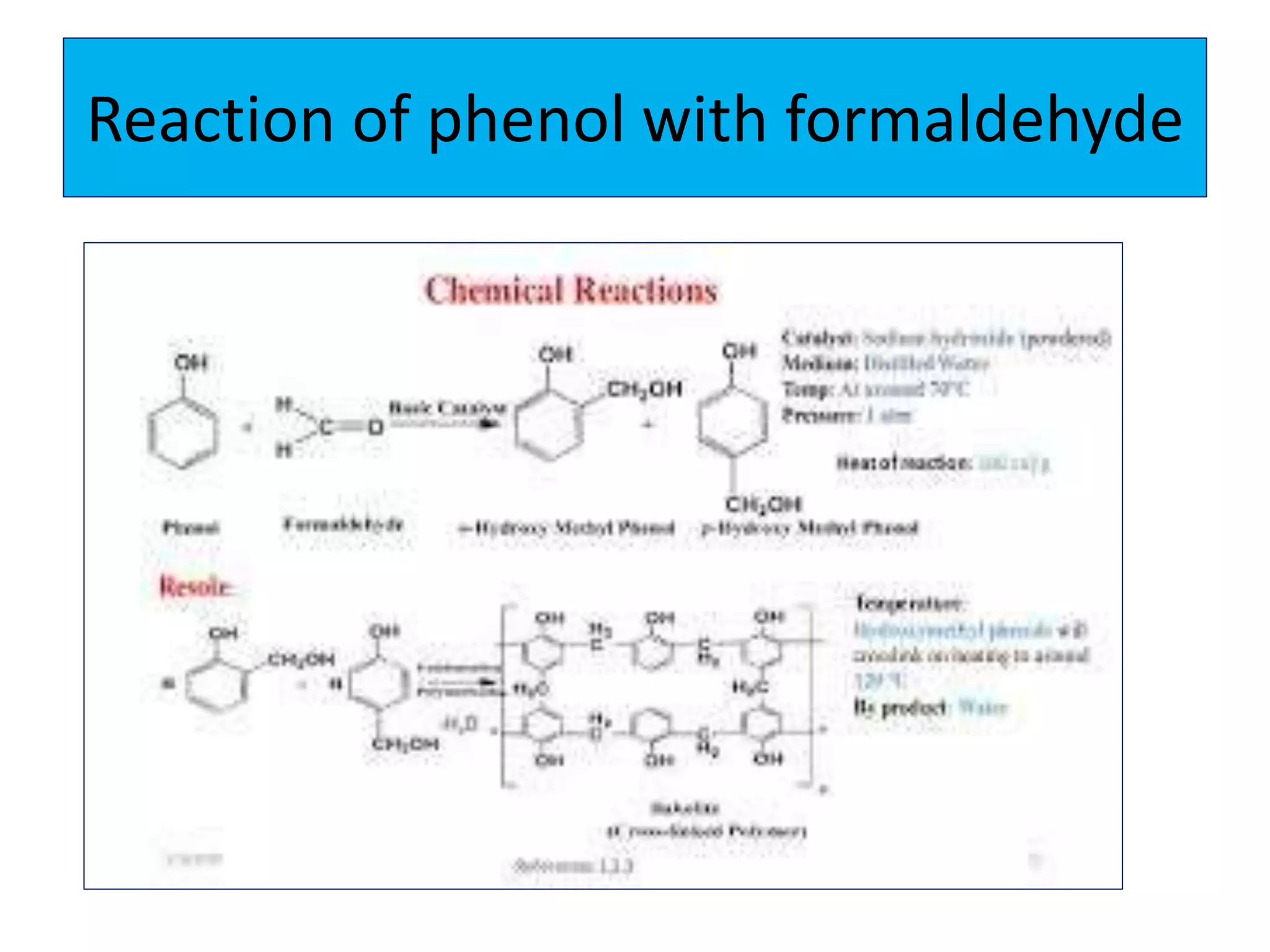
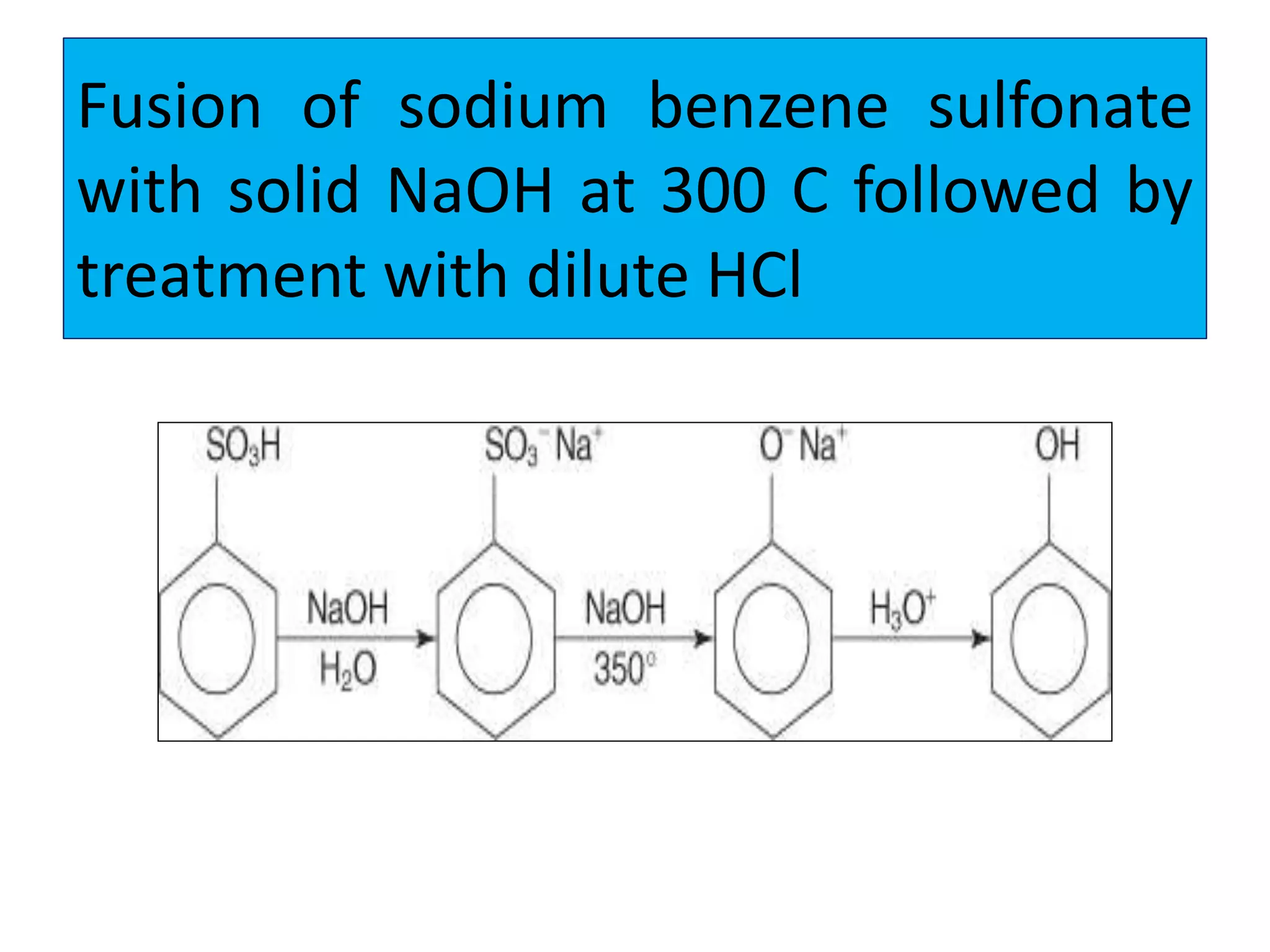
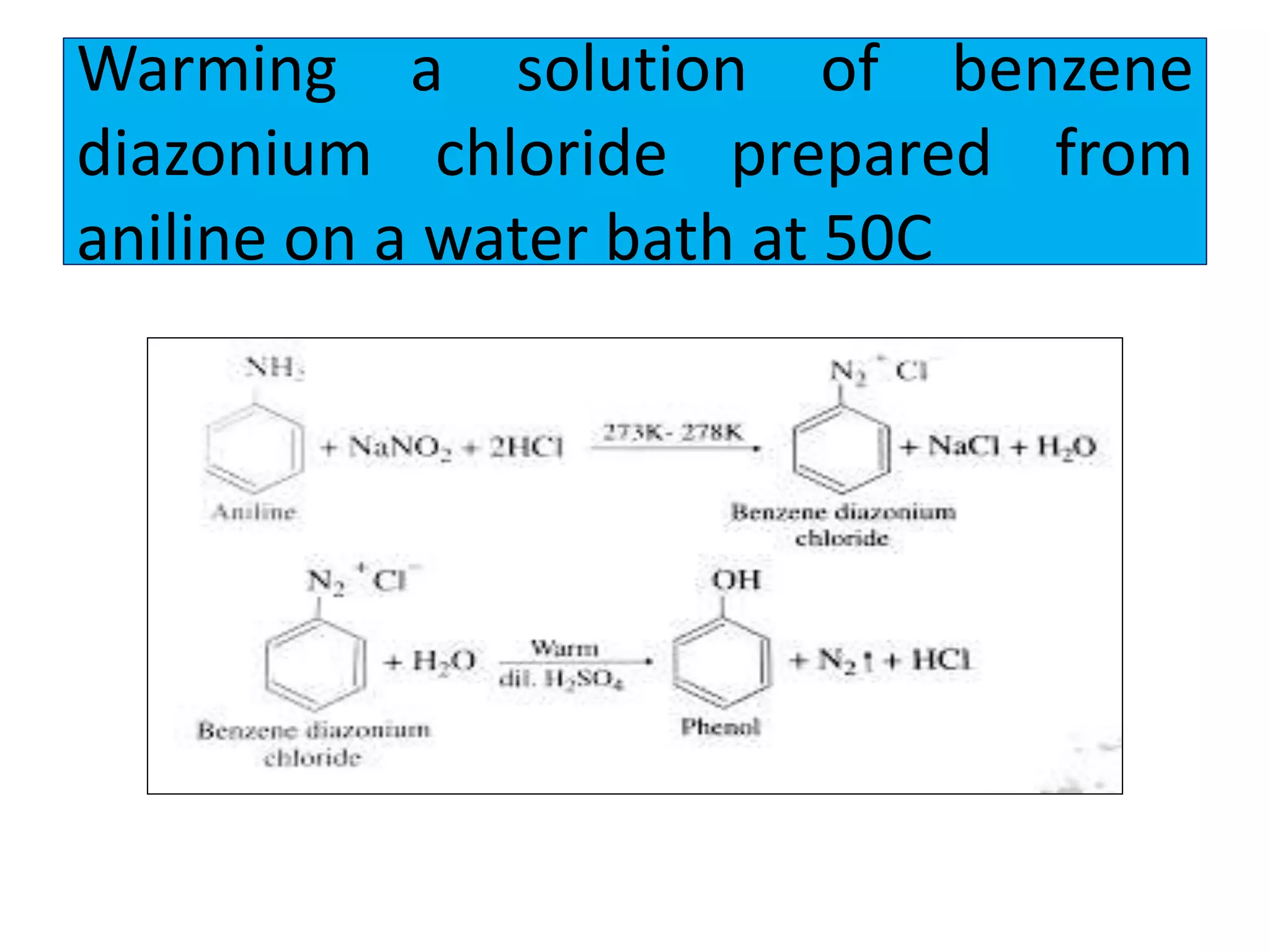
2. Phenol undergoes various reactions including forming salts with bases, esterification, ether formation, halogenation, nitration, sulfonation, and the Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
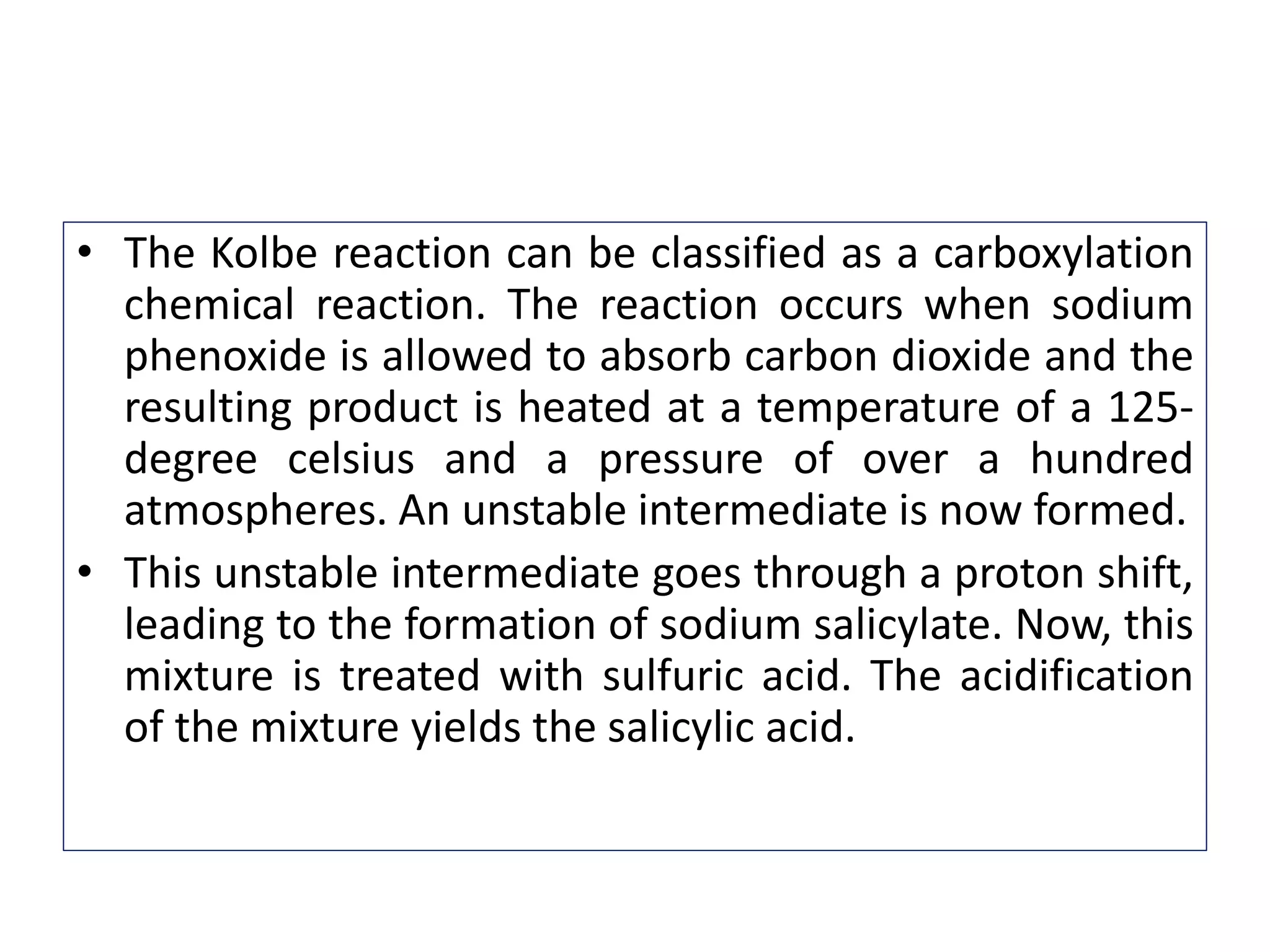
3. The Kolbe-Schmitt or Kolbe process involves heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure to form sodium salicylate, which is then acidified to form salicylic acid.




![From Coal tar
• Coal tar provides natural source of phenol and
cresol.
• The middle oil fraction of coal tar contains
phenols, cresols and naphthalene.[ 170-240 C]
• Oil when cooled solid naphthalene deposit.
• Centrifuge and the oil left out is agitated with
NaOH gives phenols and cresols.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/preparationandreactionofphenol-201209034936/75/Preparation-and-reaction-of-phenol-7-2048.jpg)