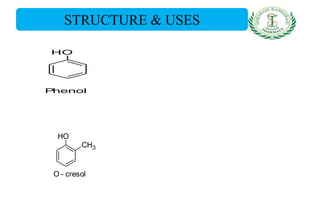
This document discusses phenols, including their:
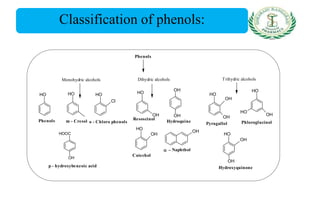
- Classification into simple phenols, monohydric phenols, dihydric phenols, and trihydric phenols
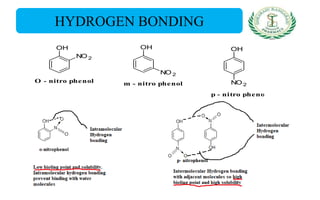
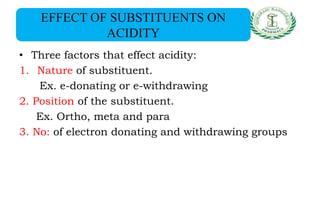
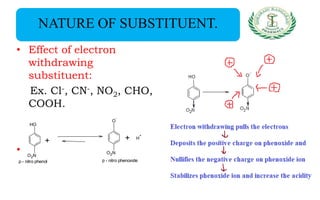
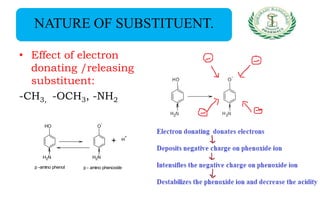
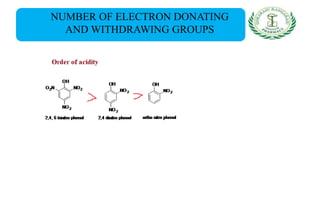
- Nomenclature and physico-chemical properties such as acidity, hydrogen bonding, and effect of substituents on acidity
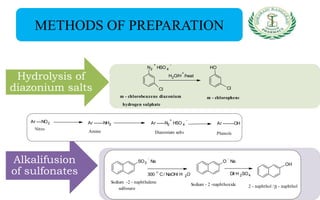
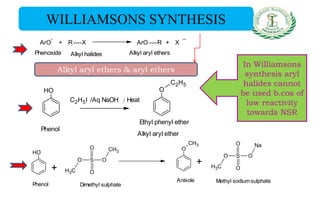
- Preparation methods like hydrolysis of diazonium salts, alkali fusion of sulfonates
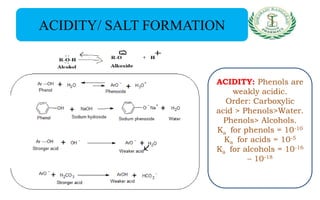
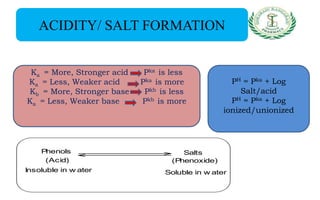
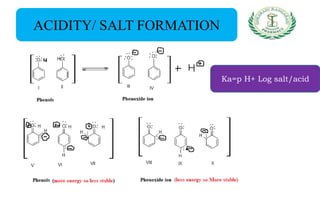
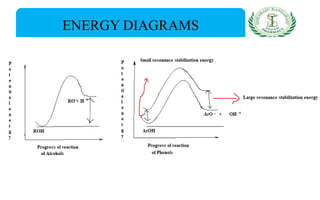
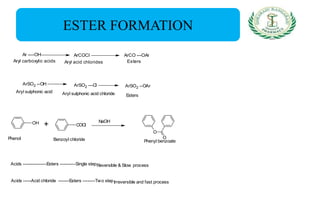
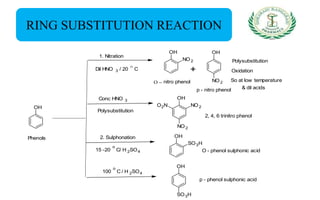
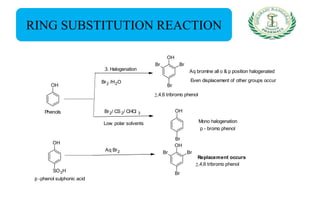
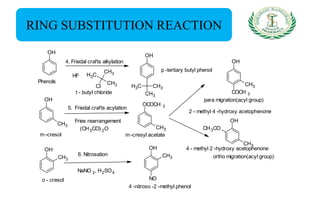
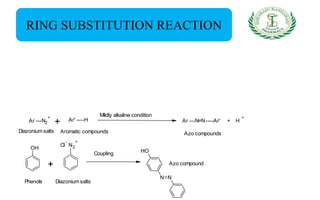
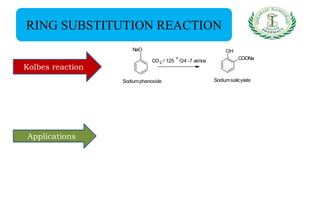
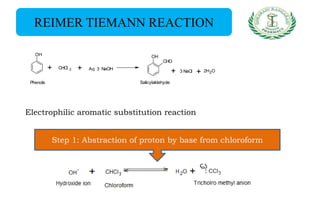
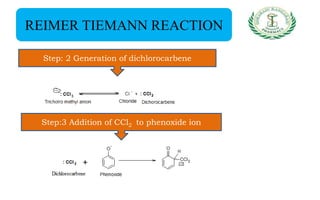
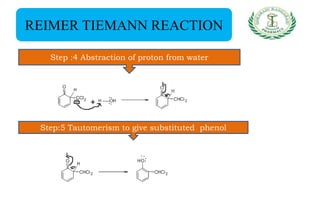
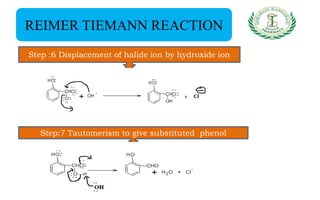
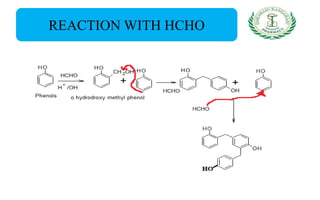
- Reactions including acidity/salt formation, ester formation, ring substitution, and reactions with formaldehyde
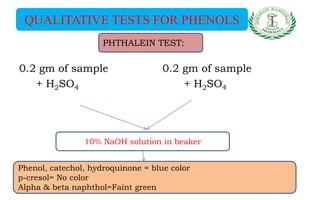
- Qualitative tests for phenols using ferric chloride and Libermann reaction
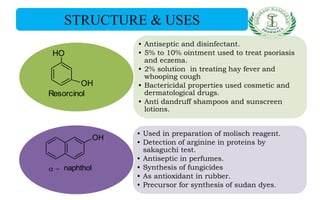
- Uses of phenol, o-cresol, resorcinol, and