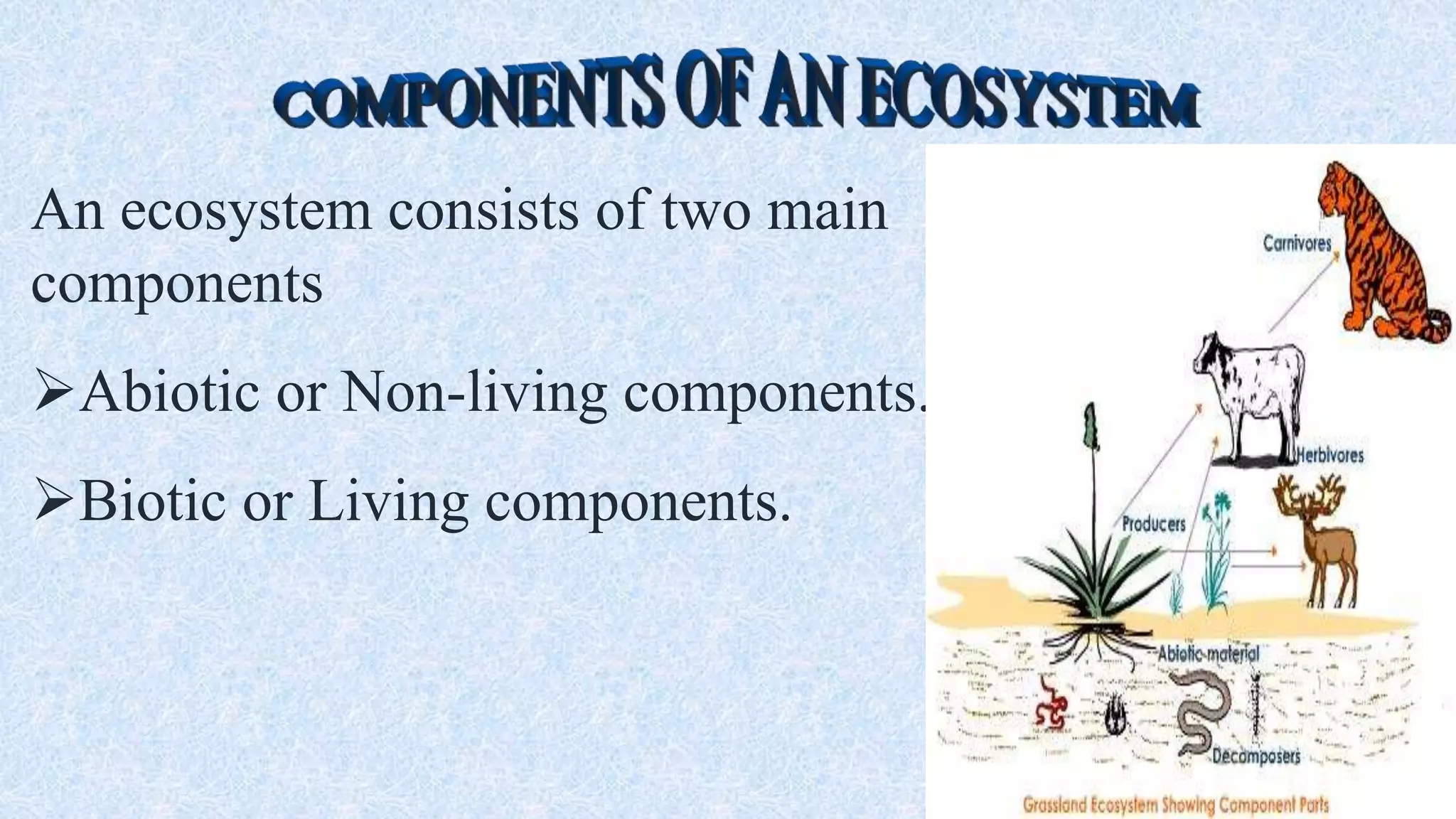
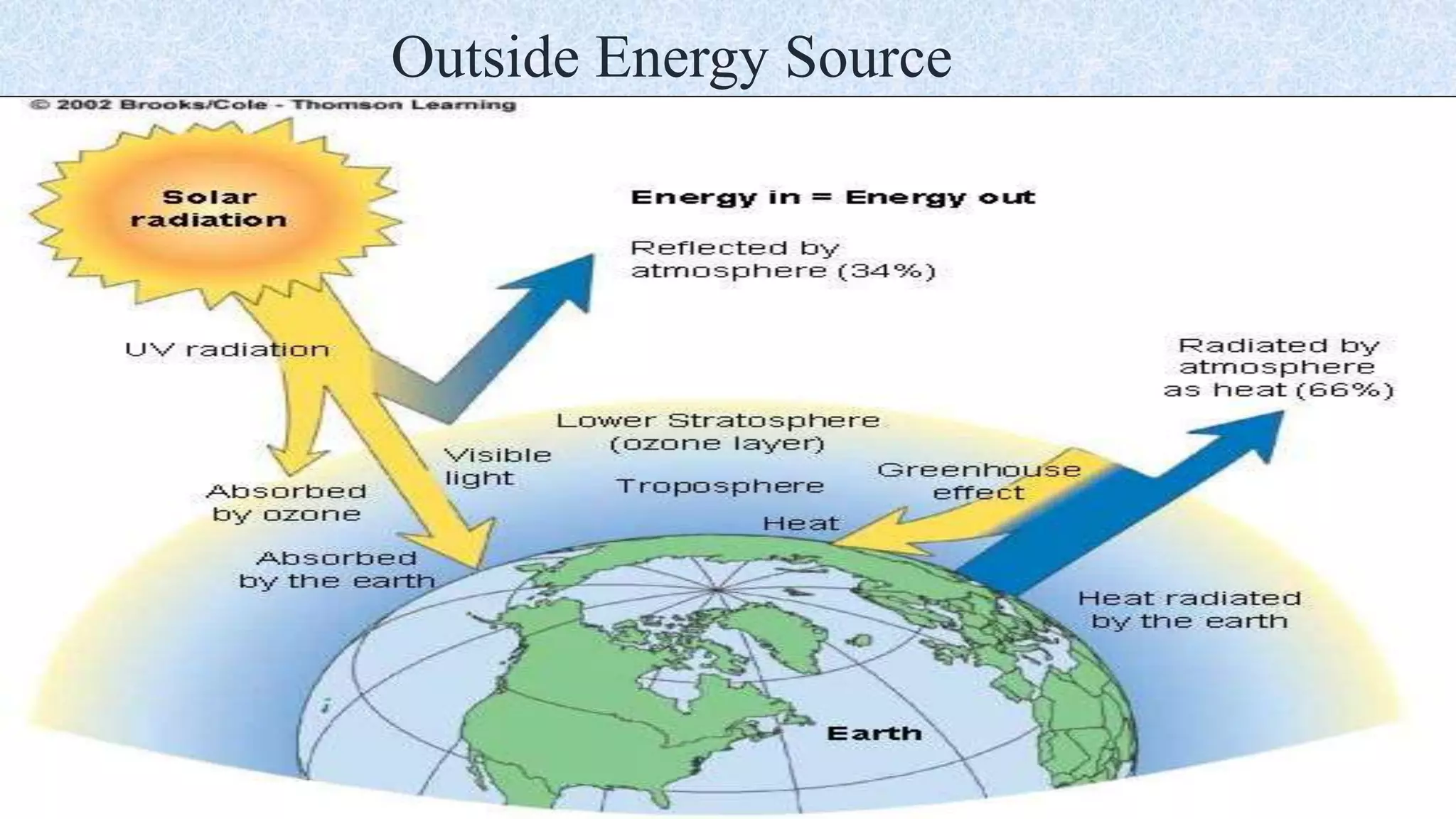
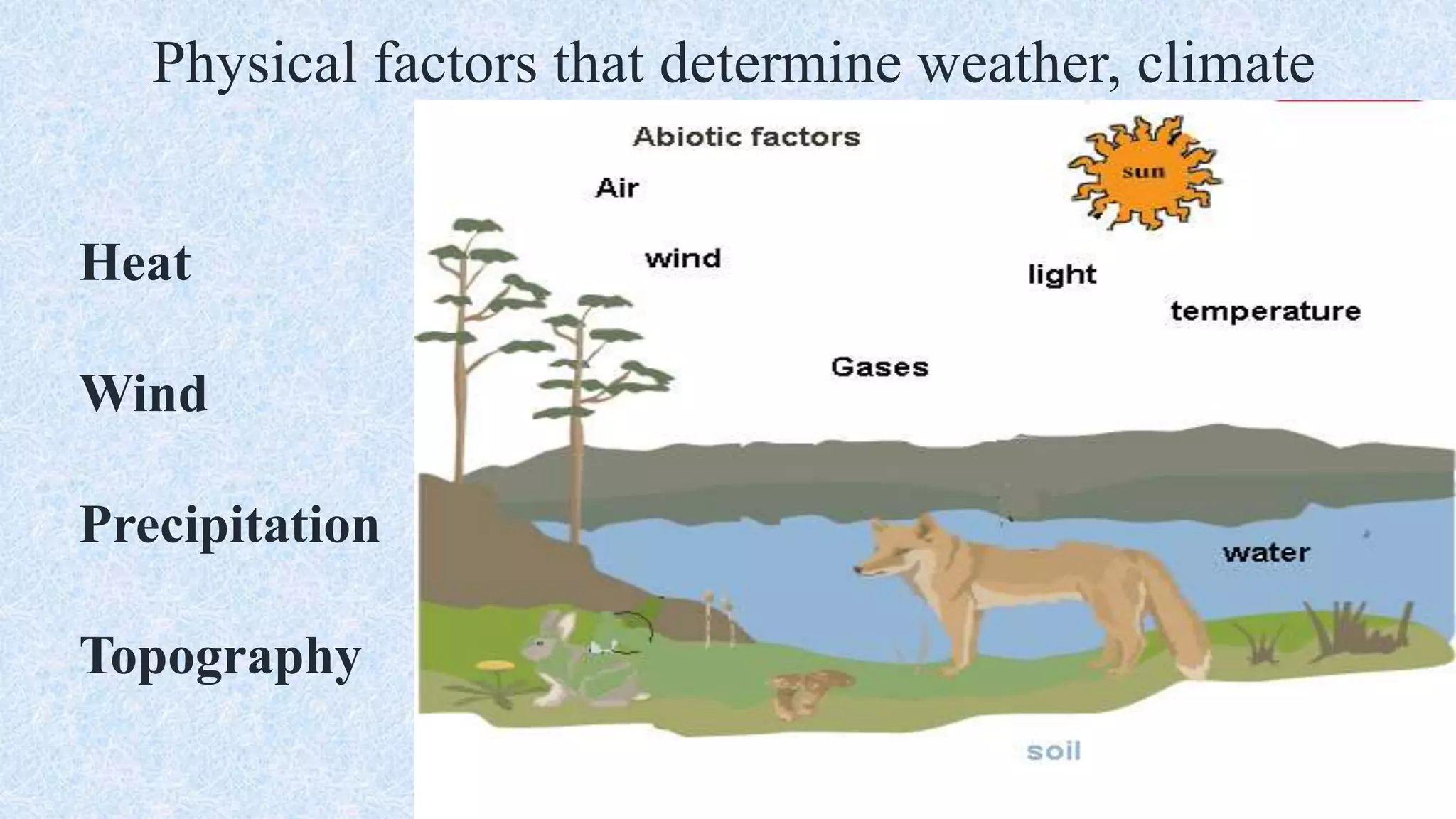
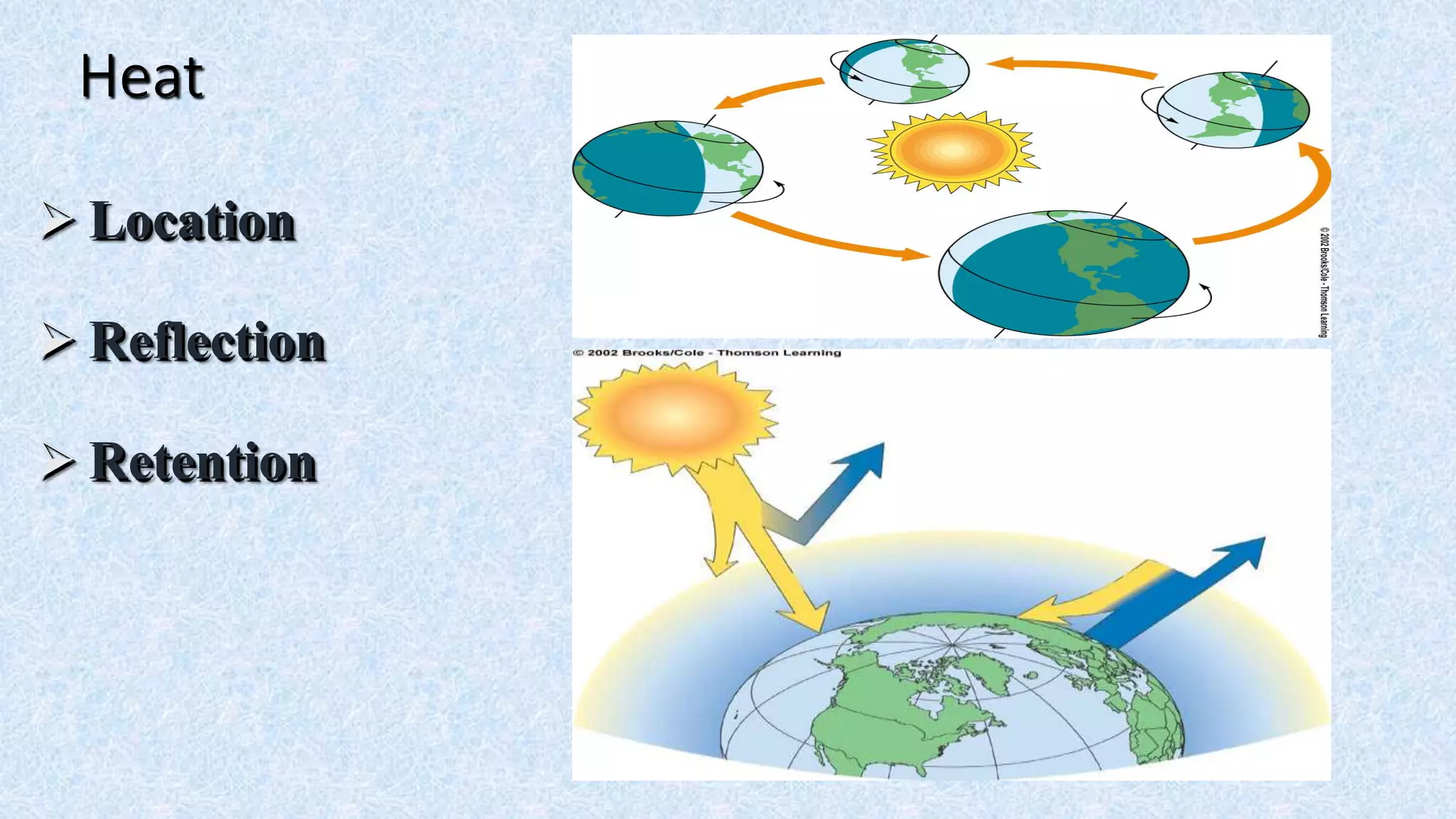
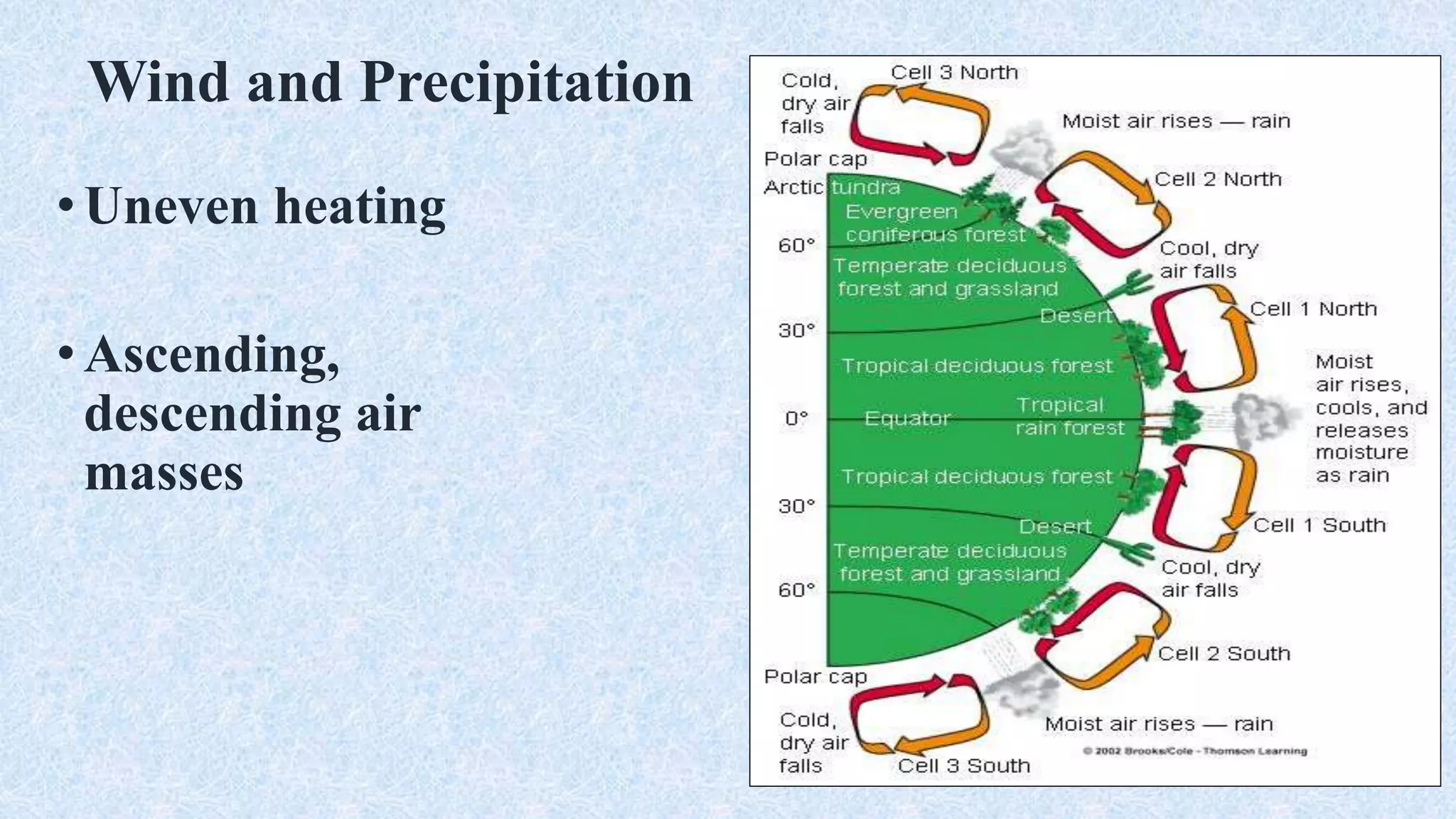
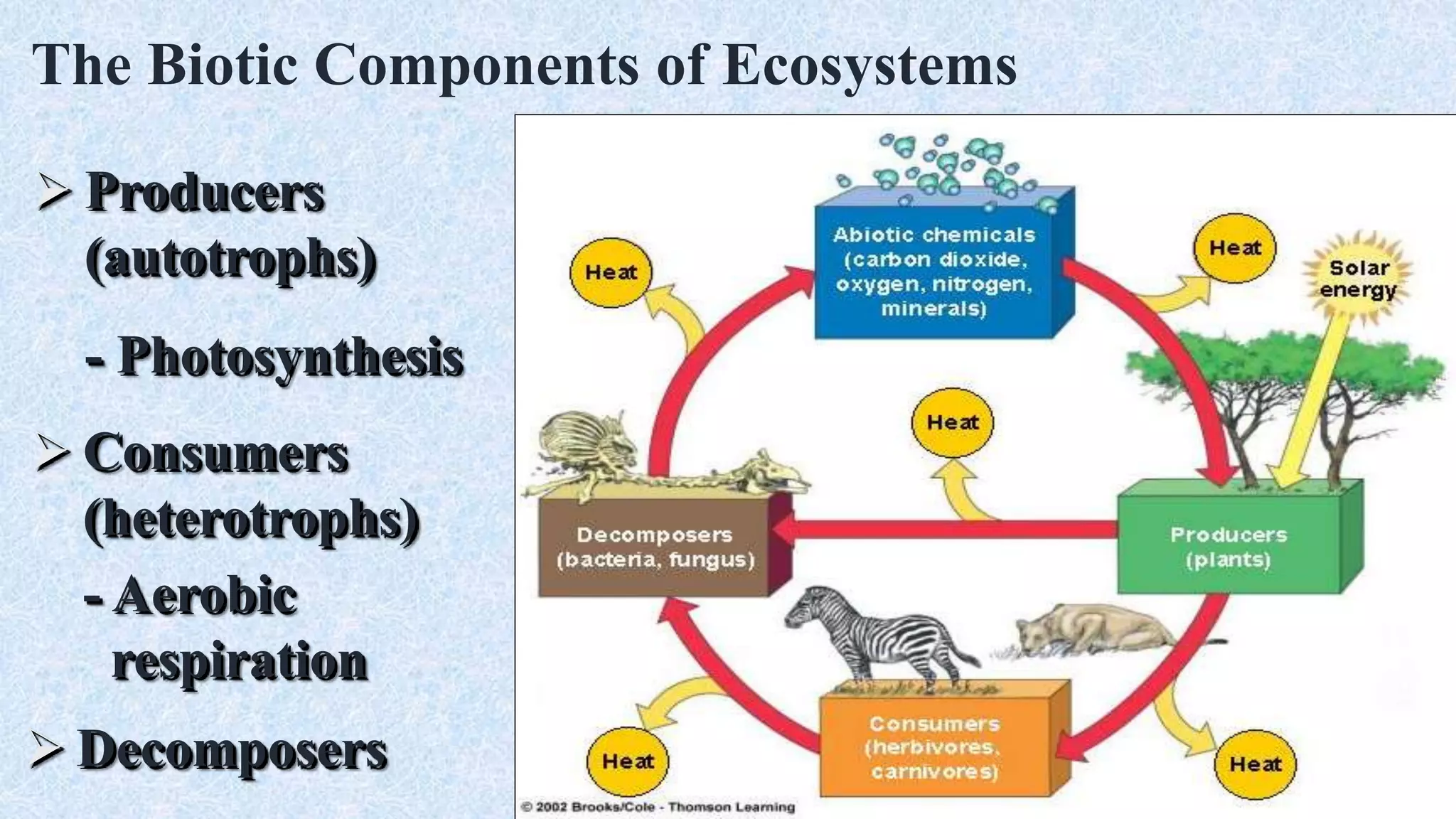
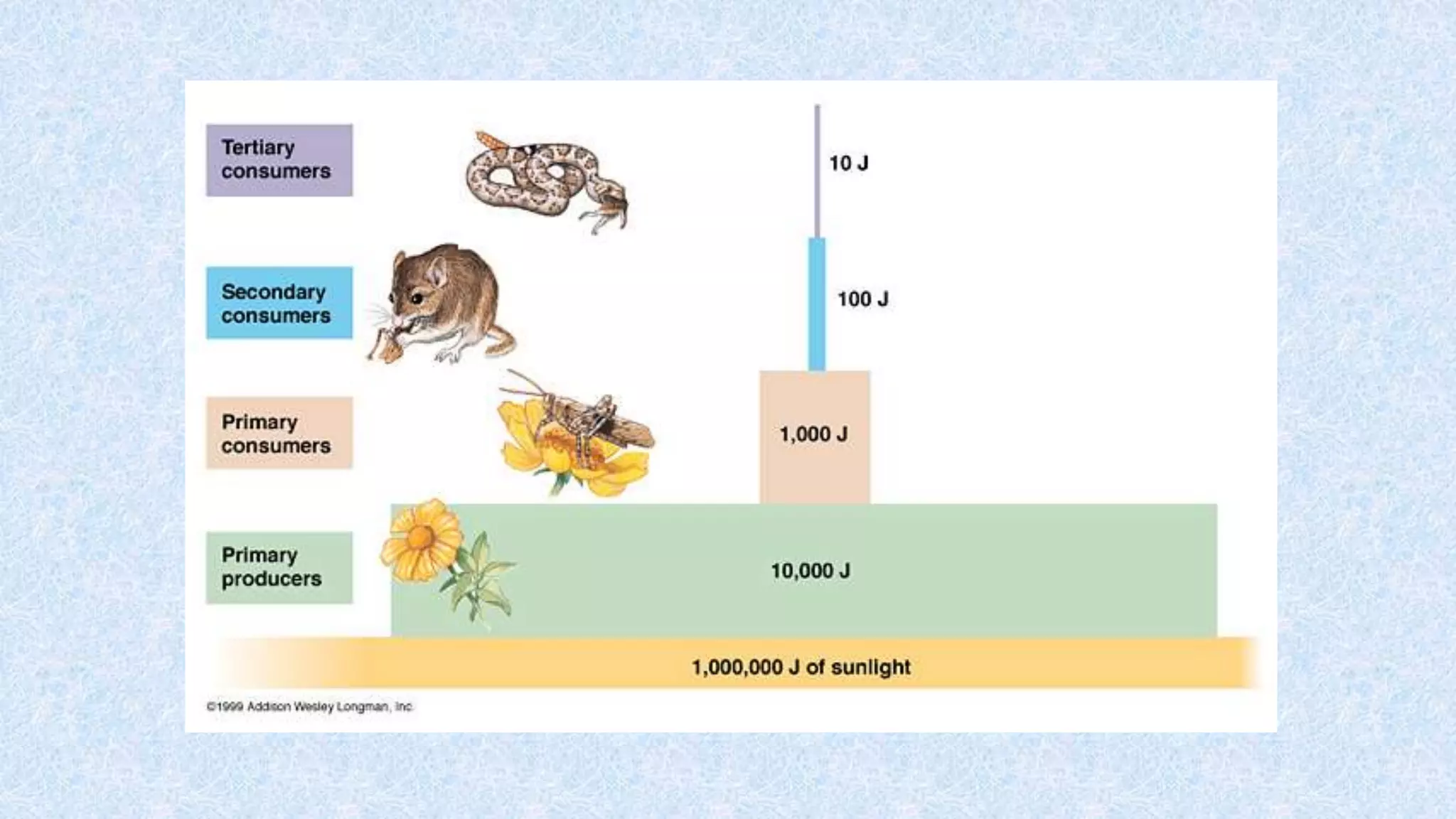
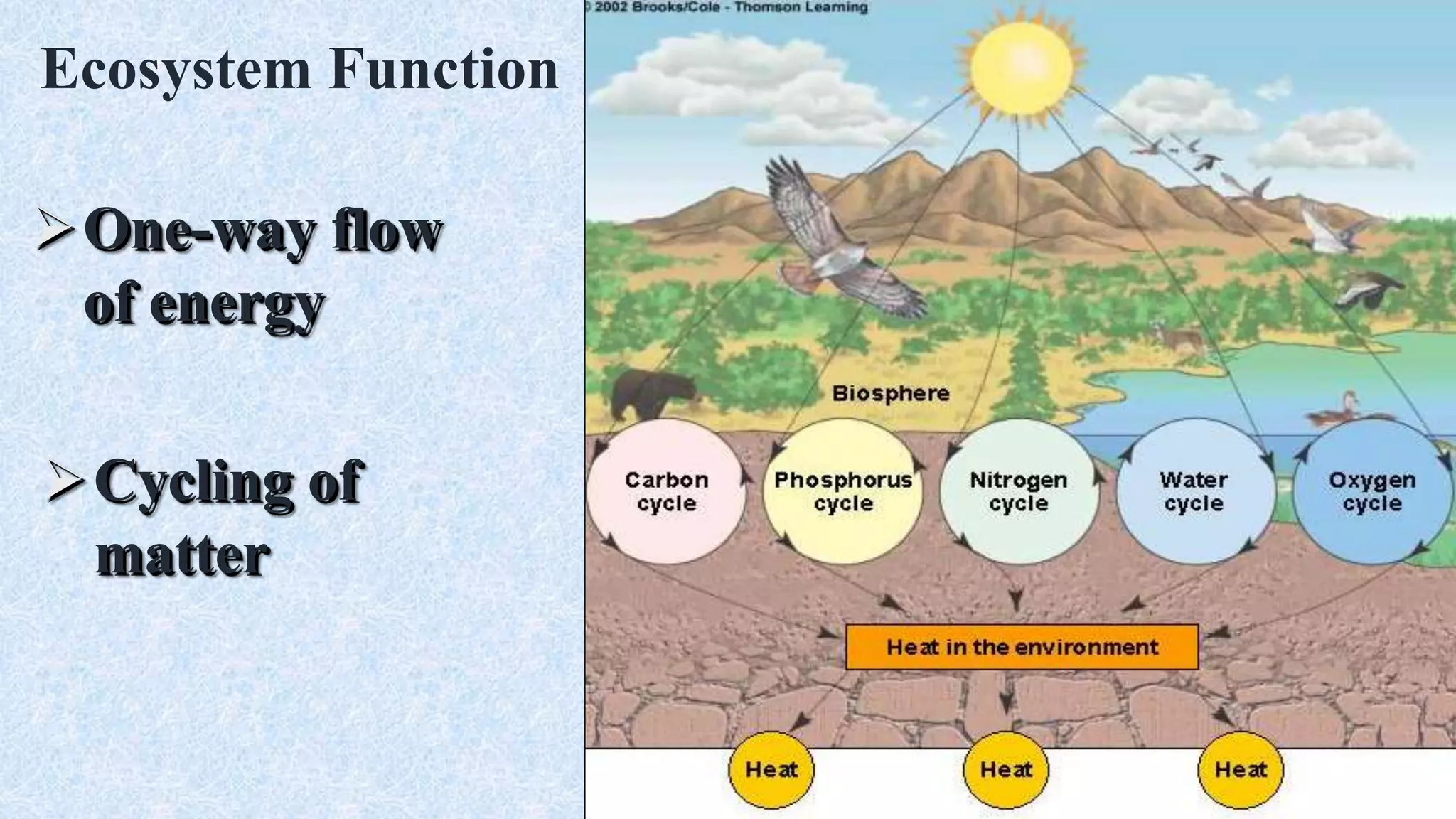
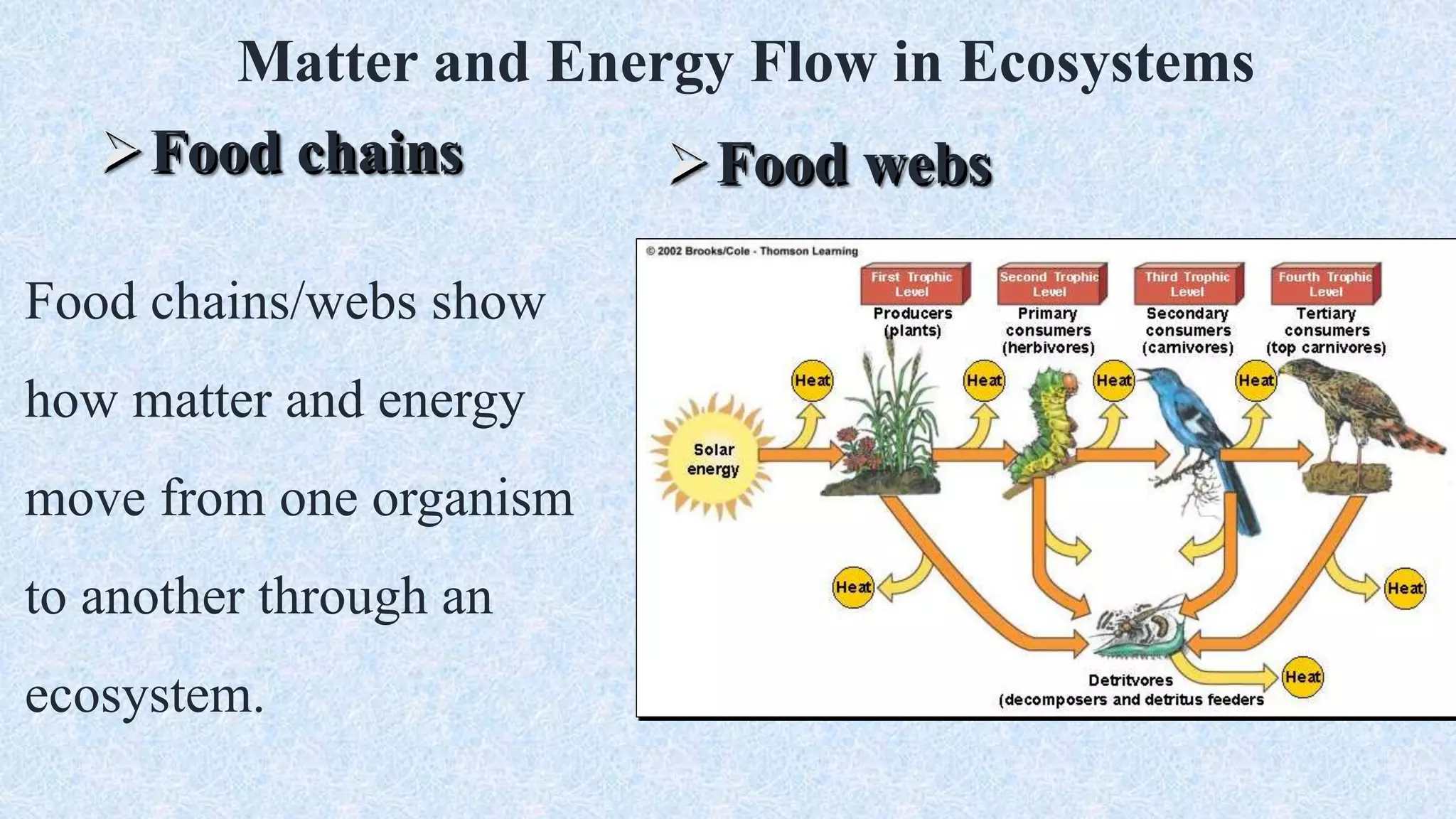
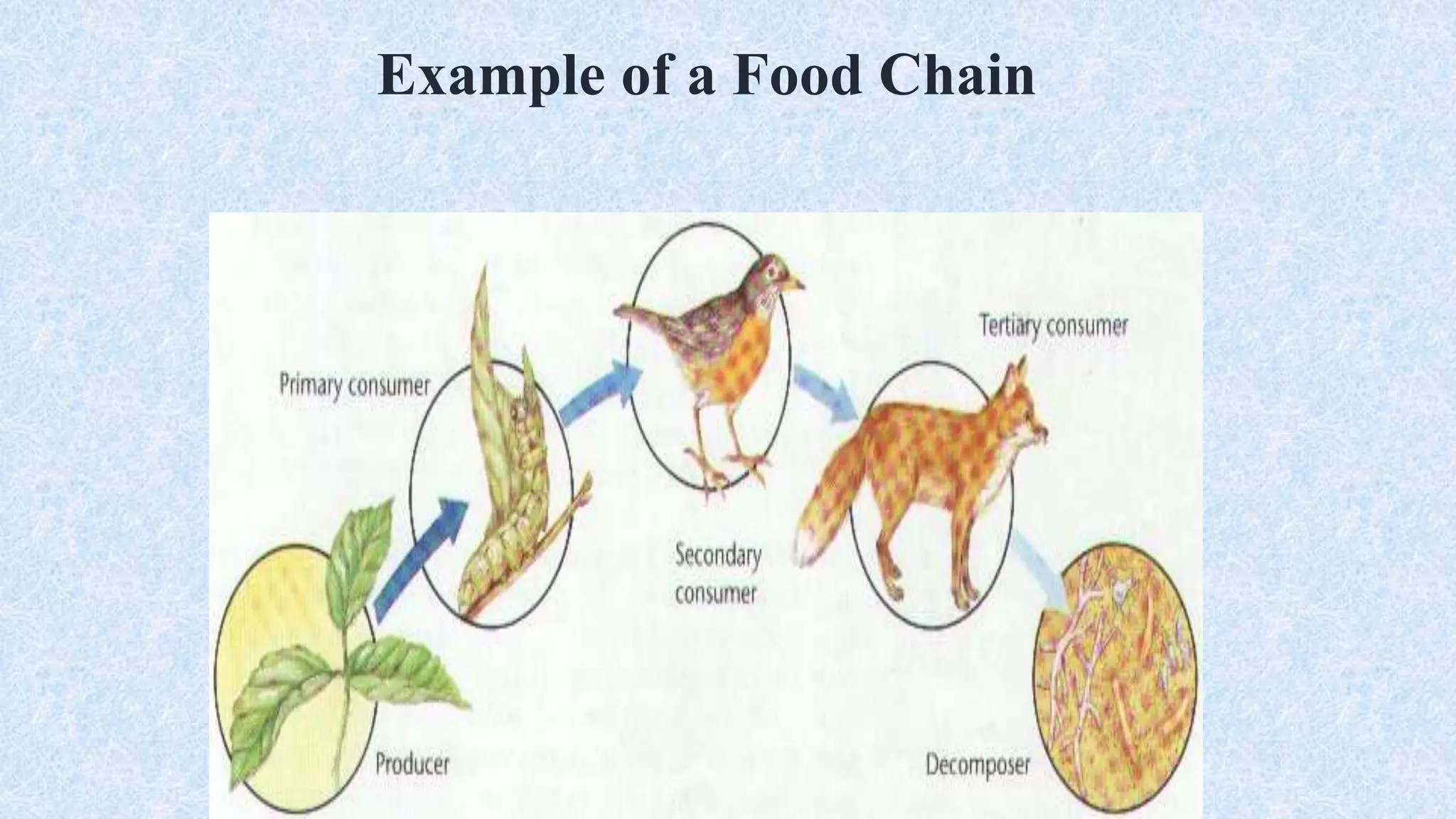
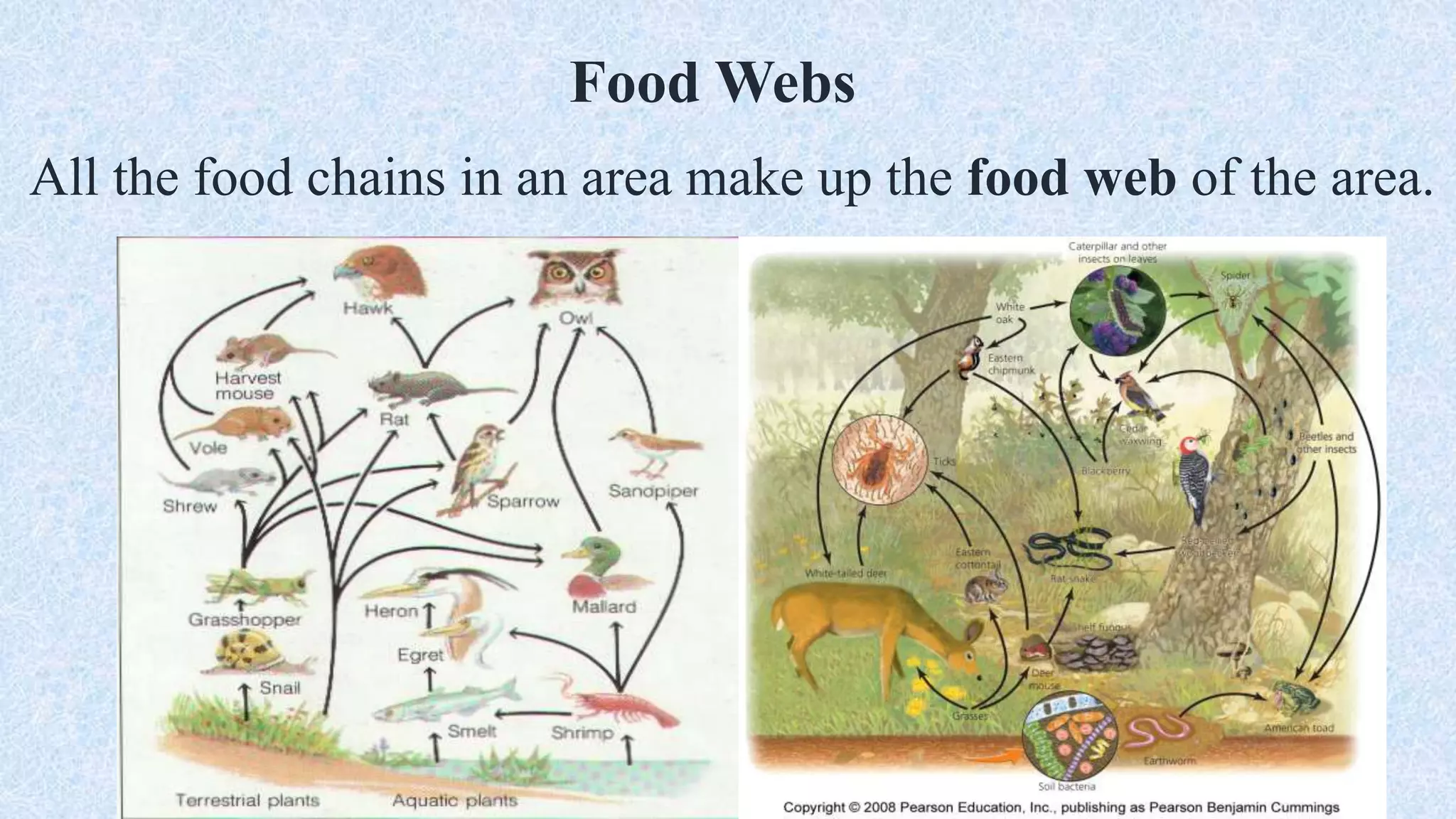
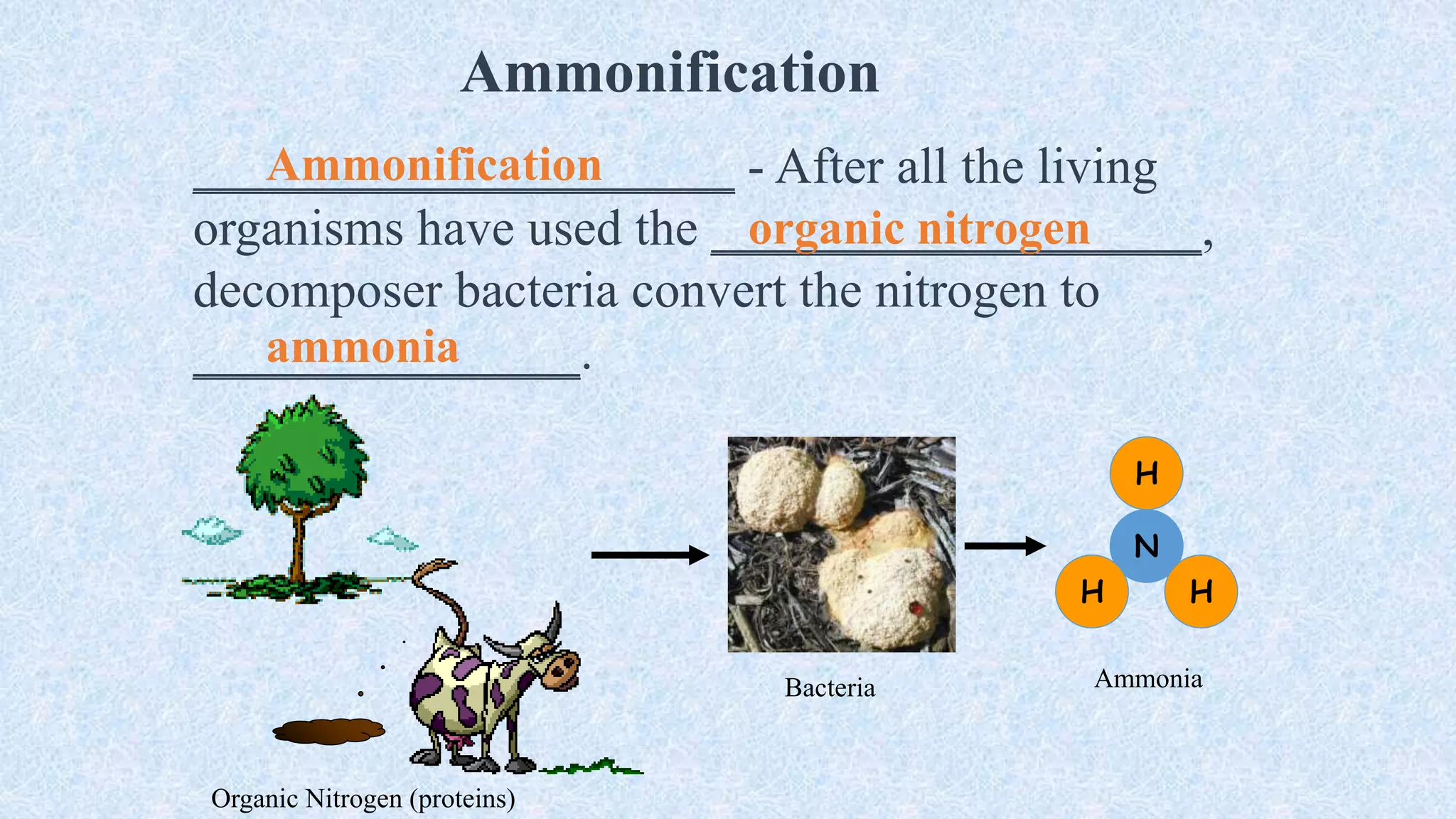
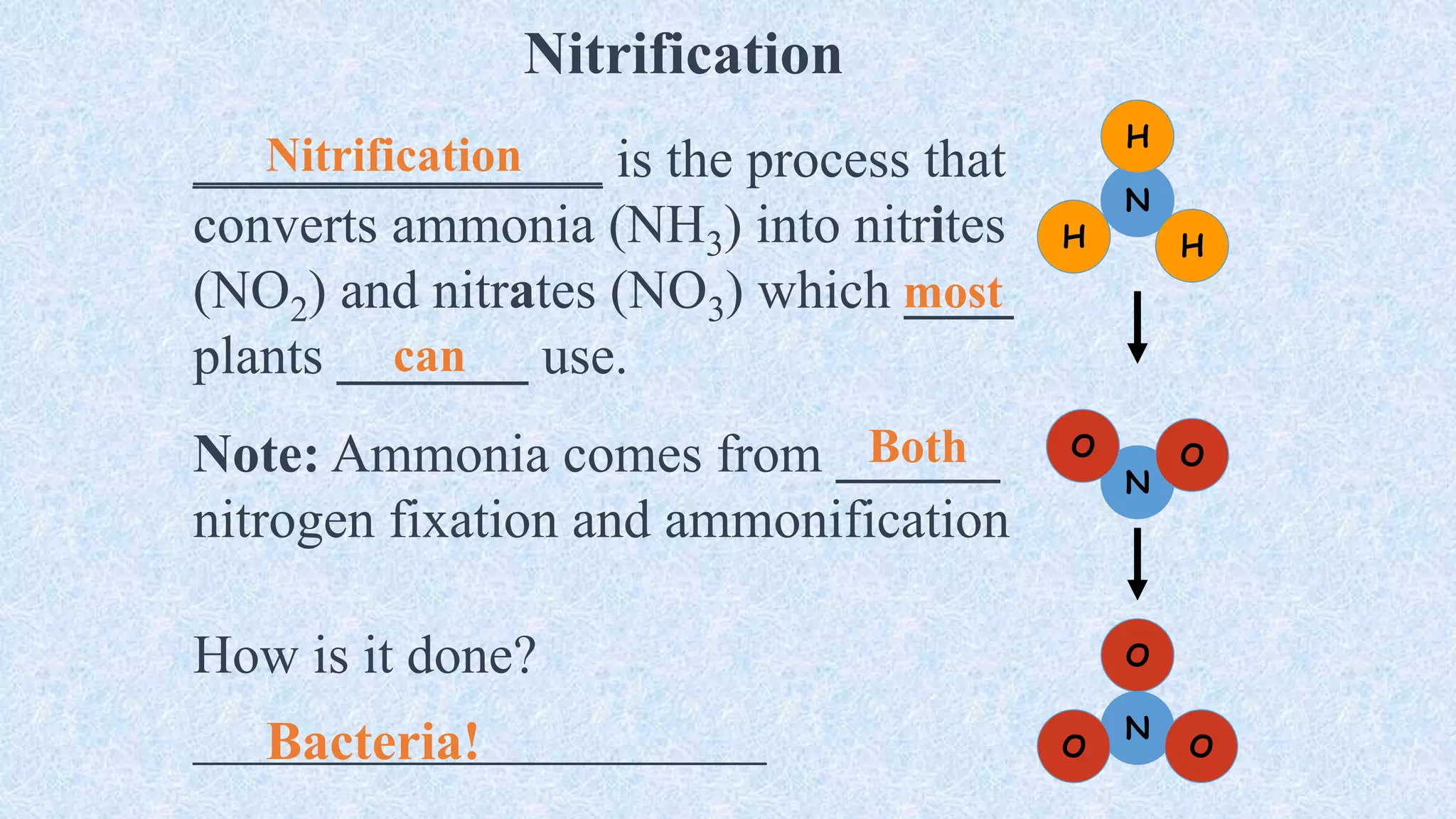
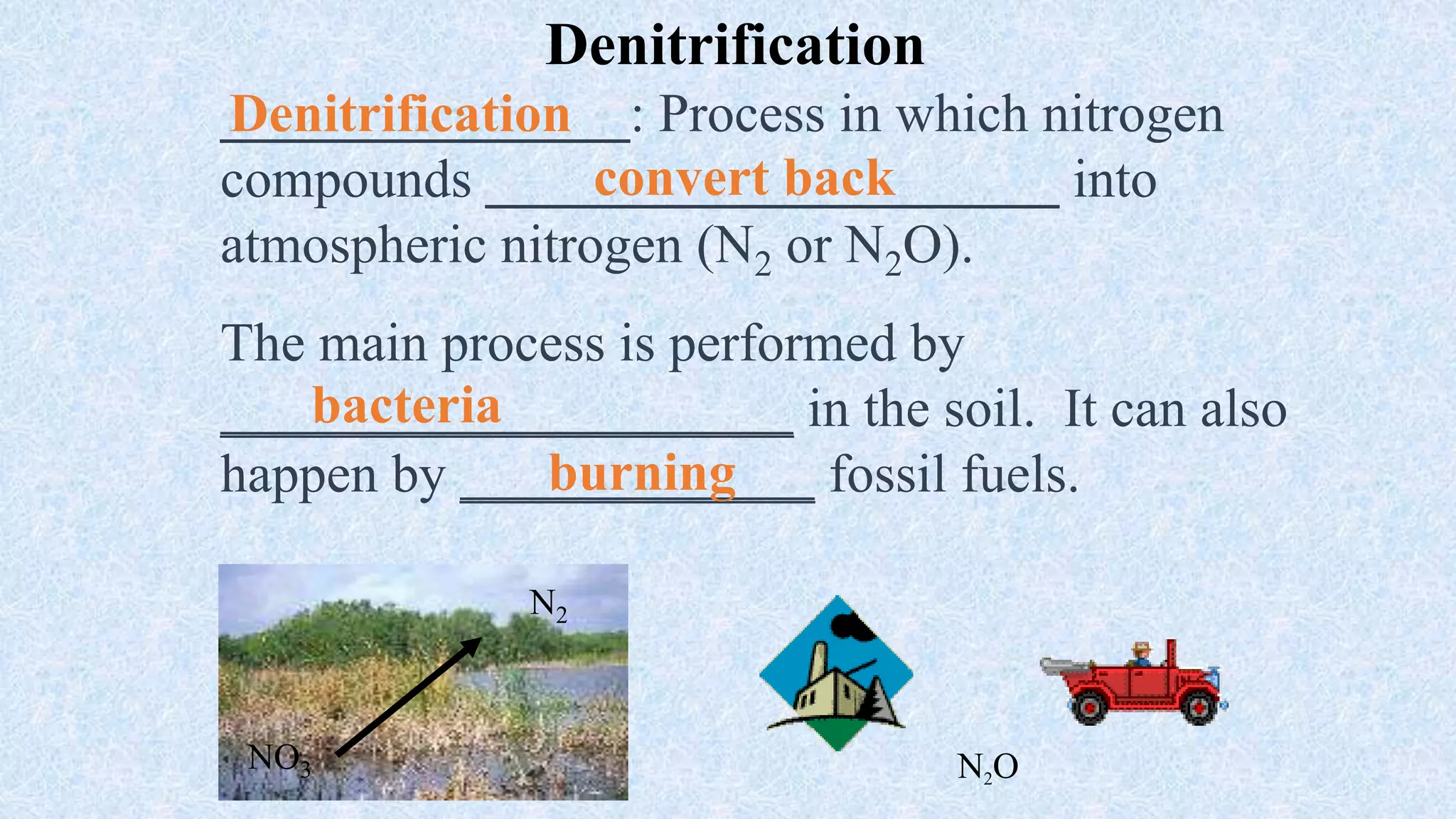
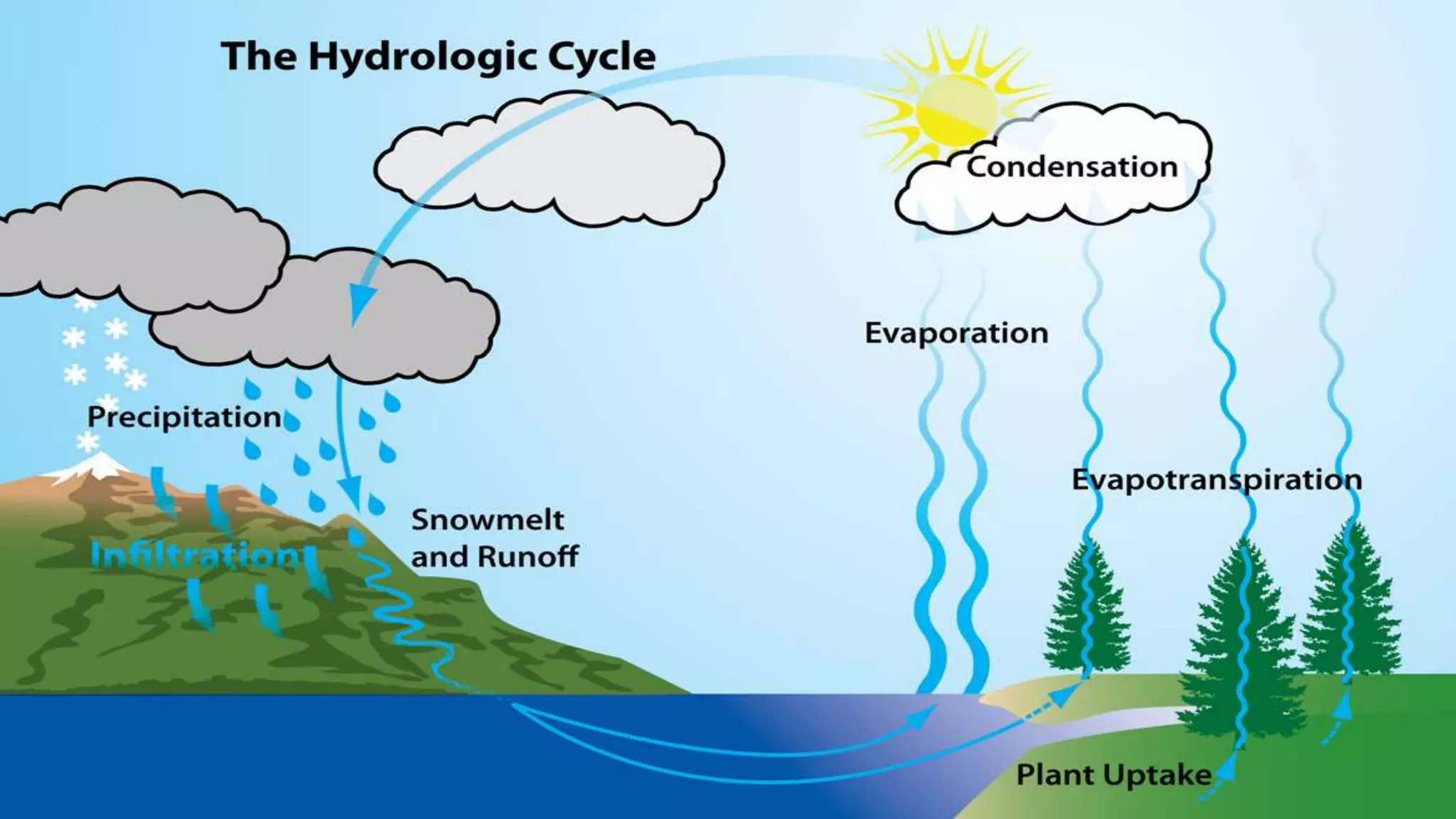
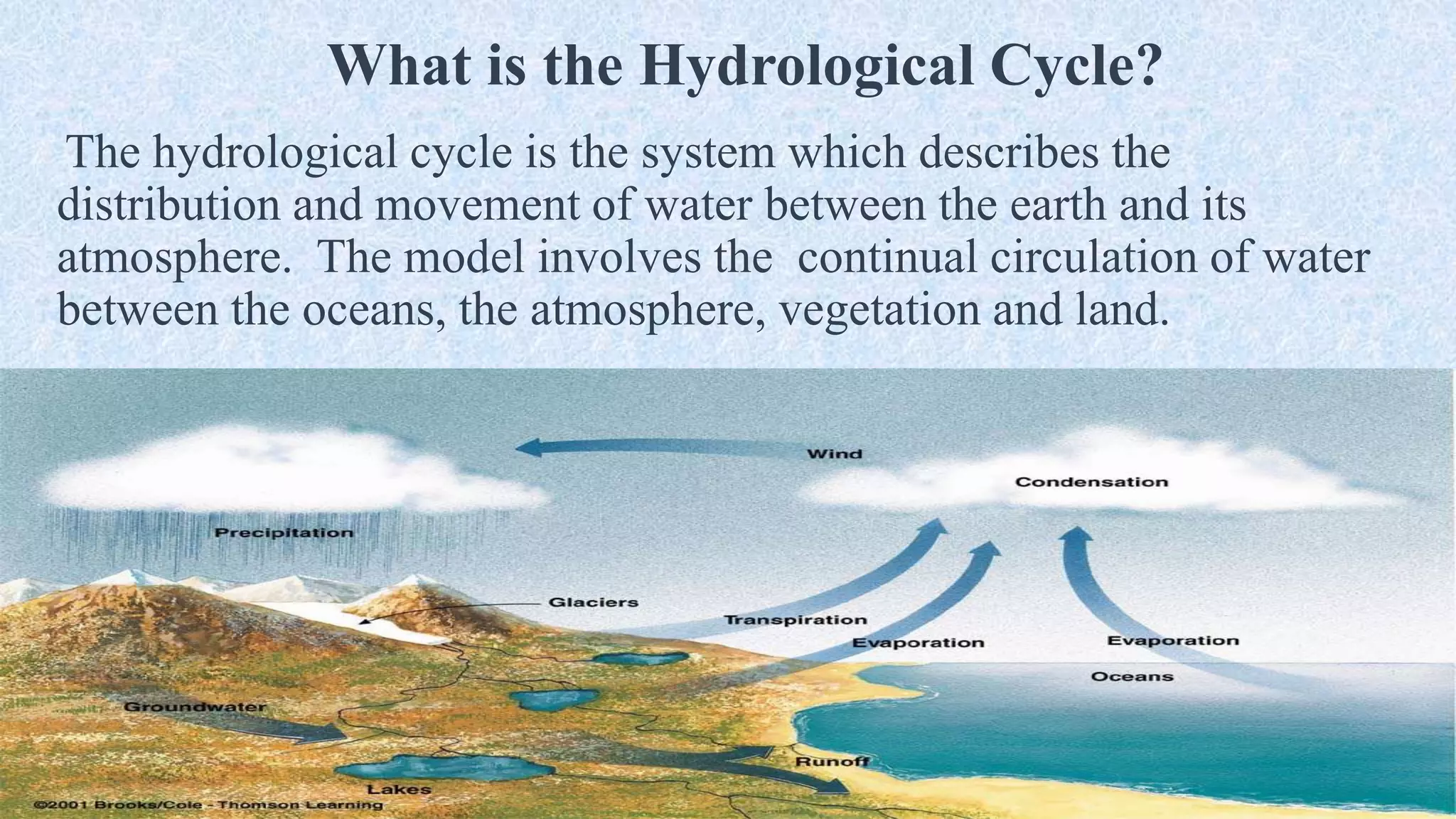
An ecosystem is defined as a community of organisms interacting with one another and their non-living environment, comprising biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components. Key processes include energy flow, matter cycling, and ecological succession, with various types of ecosystems such as terrestrial and aquatic. The document also covers biogeochemical cycles, particularly the nitrogen and hydrological cycles, highlighting the importance of nitrogen fixation and the movement of water through the Earth-atmosphere system.