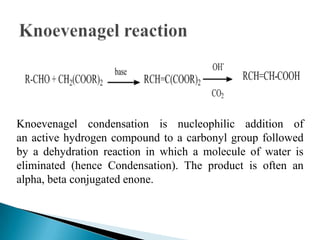
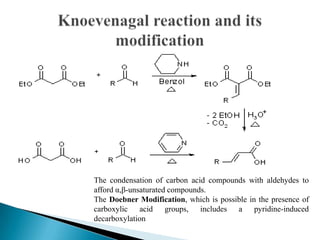
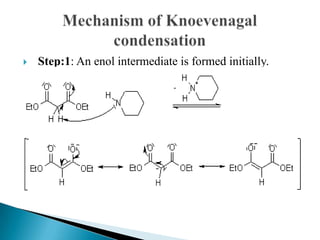
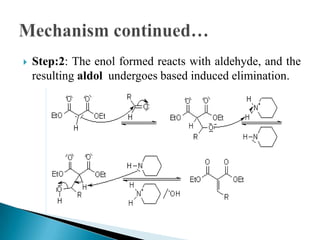
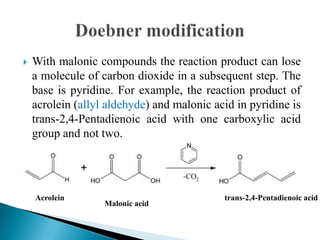
The Knoevenagel condensation reaction involves the nucleophilic addition of an active hydrogen compound to a carbonyl group, followed by a dehydration reaction to form an α,β-unsaturated enone. It is a modification of the aldol condensation and uses an active methylene compound and an aldehyde or ketone in the presence of a weak base such as pyridine. With malonic acid derivatives, the reaction product can undergo decarboxylation to form trans-2,4-pentadienoic acid. The Knoevenagel reaction is widely used in the synthesis of conjugated enones for various reactions.