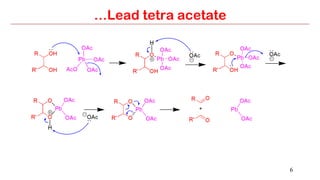
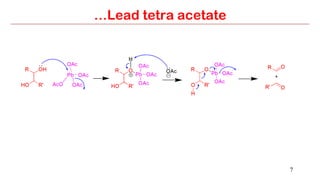
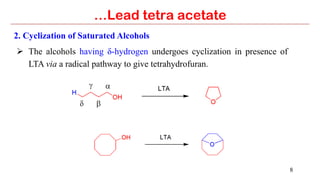
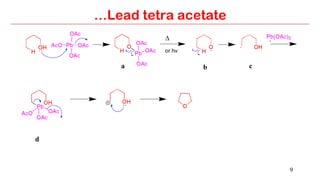
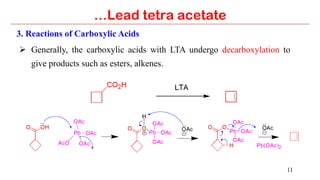
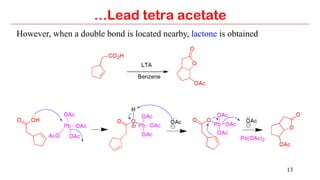
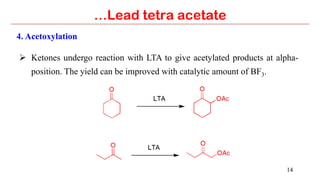
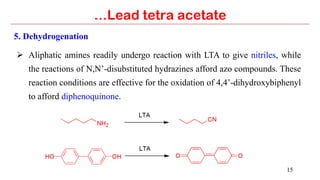
Lead tetra acetate is a powerful oxidizing reagent that can oxidize alcohols to aldehydes and ketones, induce cyclization of saturated alcohols, and undergo decarboxylation or lactonization with carboxylic acids. It is also used for acetoxylation of ketones and dehydrogenation of amines and hydrazines. However, lead tetra acetate is toxic, hygroscopic, and turns brown upon exposure to air, so it must be handled with extreme care in a chemical hood.