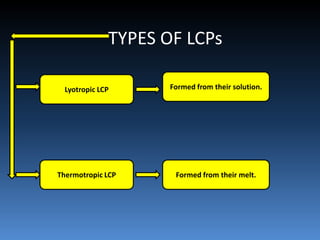
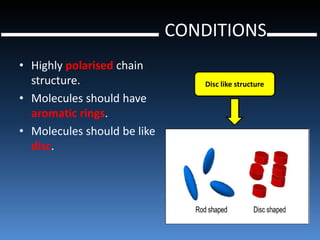
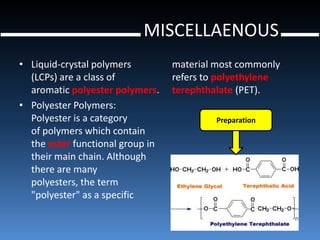
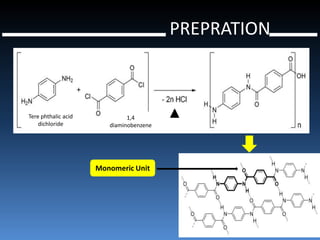
Liquid crystal polymers are polymers that align their molecular chains parallel over long distances prior to crystallizing from their melt or solution. There are two types: lyotropic LCPs formed from solution and thermotropic LCPs formed from melt. LCPs have highly polarized chain structures, aromatic rings, and disc-like molecular shapes. They have properties like high crystallinity, strength, toughness, and heat resistance. LCPs find applications in optics, electronics, transportation, aerospace, and more. Kevlar is a notable para-aramid fiber with very high tensile strength used for bulletproof vests, cables, tires, and other applications.