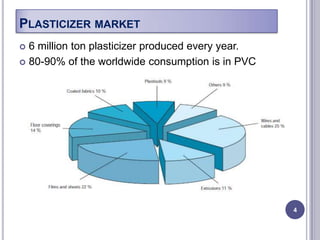
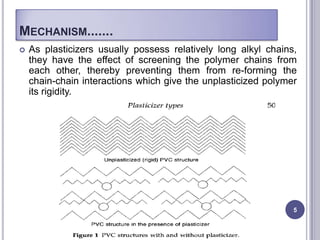
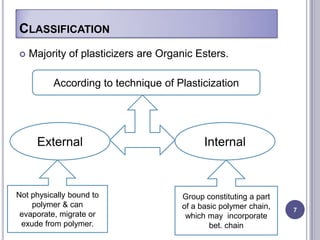
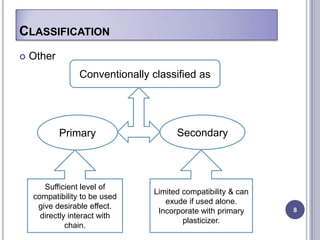
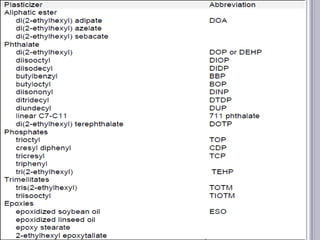
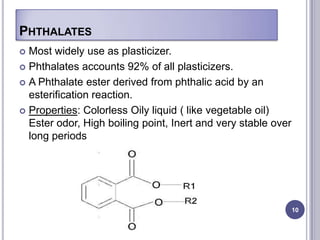
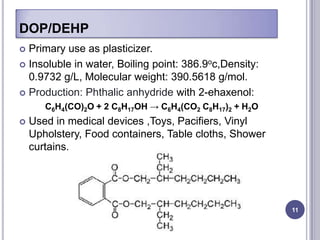
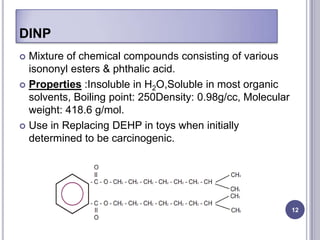
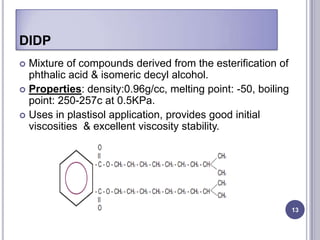
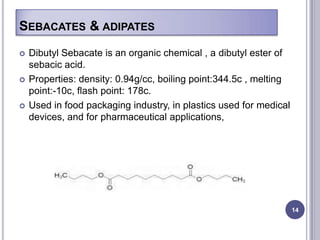
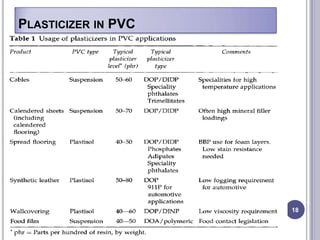
Plasticizers are chemicals added to polymers to improve flexibility and processing. They work by spacing out polymer molecules, allowing easier movement. Most plasticizers are organic esters added to PVC to make it flexible. Phthalates are the most widely used type, accounting for over 90% of plasticizers. Common phthalate plasticizers include DOP, DEHP, DINP and DIDP. Selection depends on the required properties and application. Health concerns have led to a search for safer alternatives to phthalates.