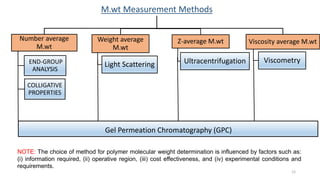
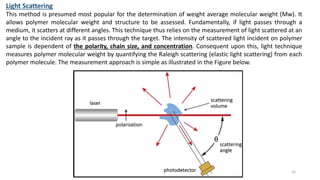
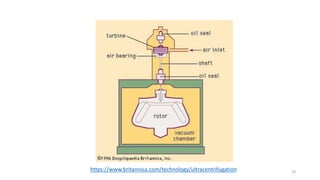
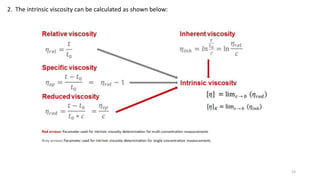
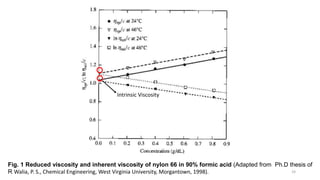
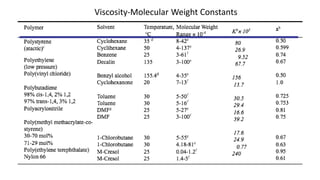
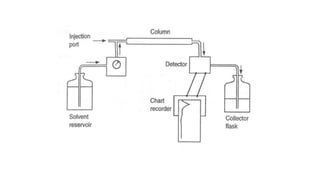
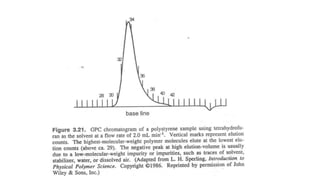
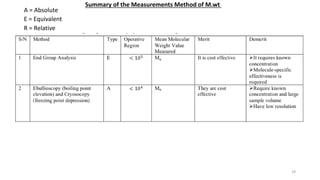
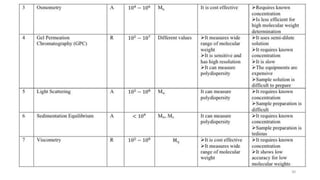
- There are several methods to measure the average molecular weight of polymers, including end-group analysis, colligative properties, light scattering, and ultracentrifugation.
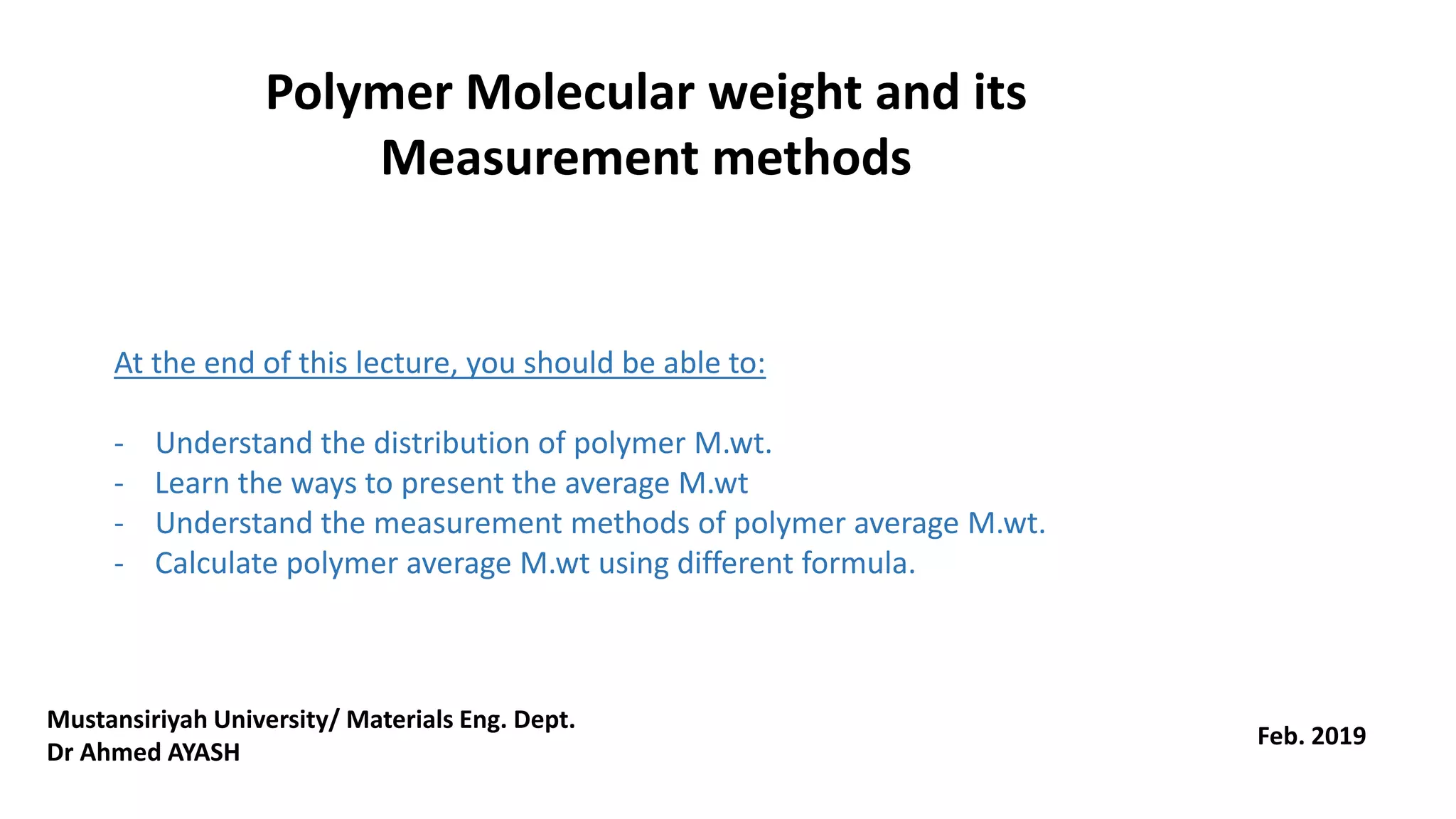
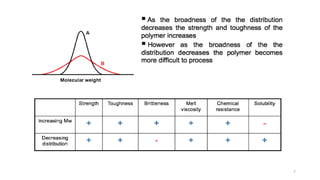
- The molecular weight distribution and average molecular weights determine important properties like viscosity and processability.
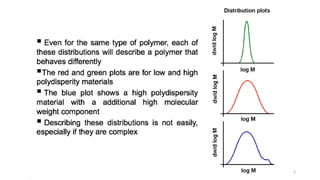
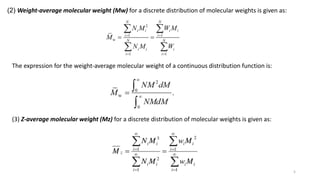
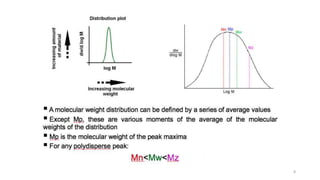
- Common averages include the number-average molecular weight (Mn), weight-average molecular weight (Mw), and viscosity-average molecular weight (Mv). The ratio of Mw/Mn is called the polydispersity index (PDI).
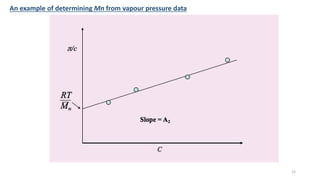
- Techniques like end-group analysis and colligative properties work best for lower molecular weights, while light scattering and ultracentrifugation can measure wider ranges up to 100,