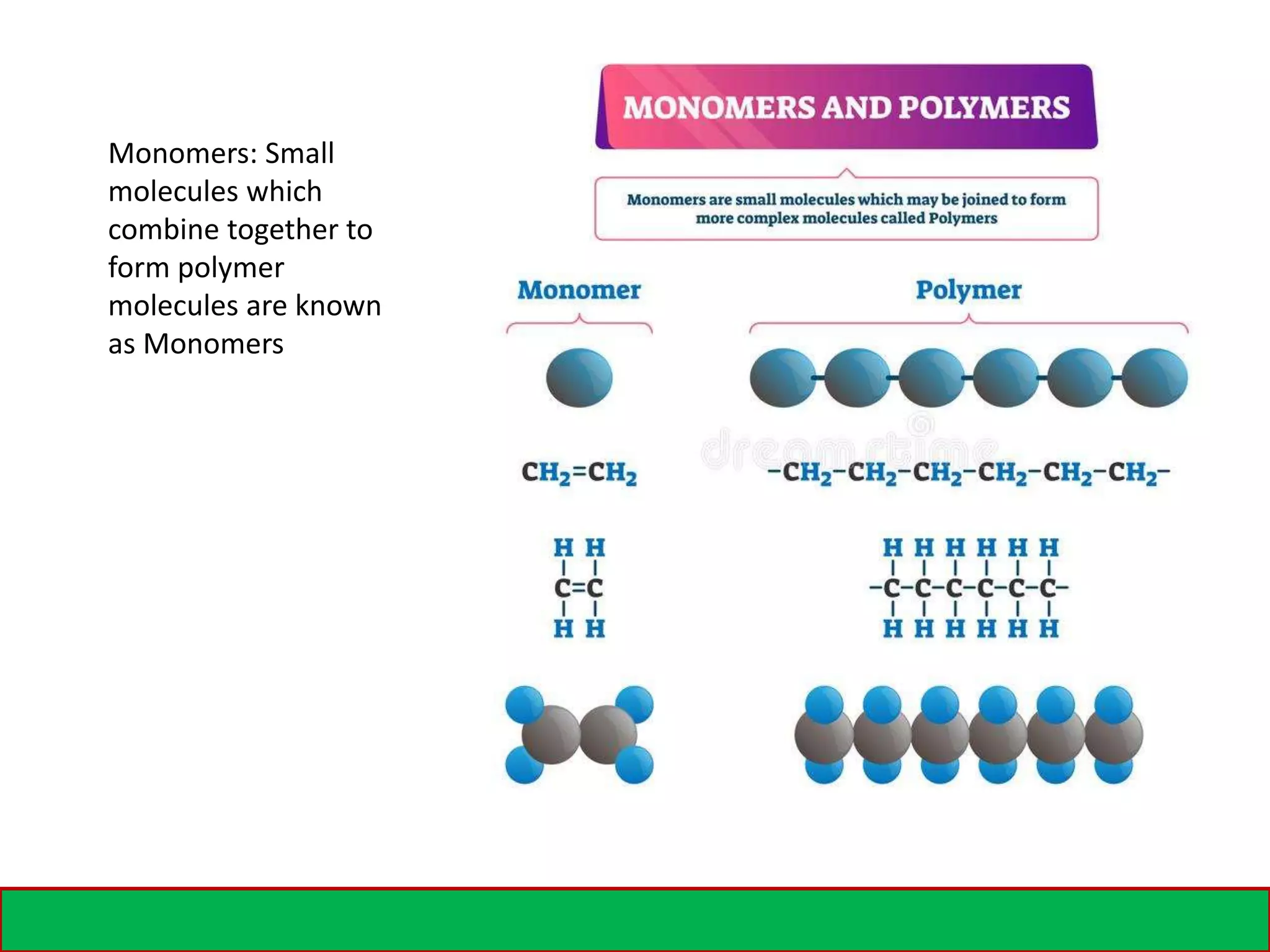
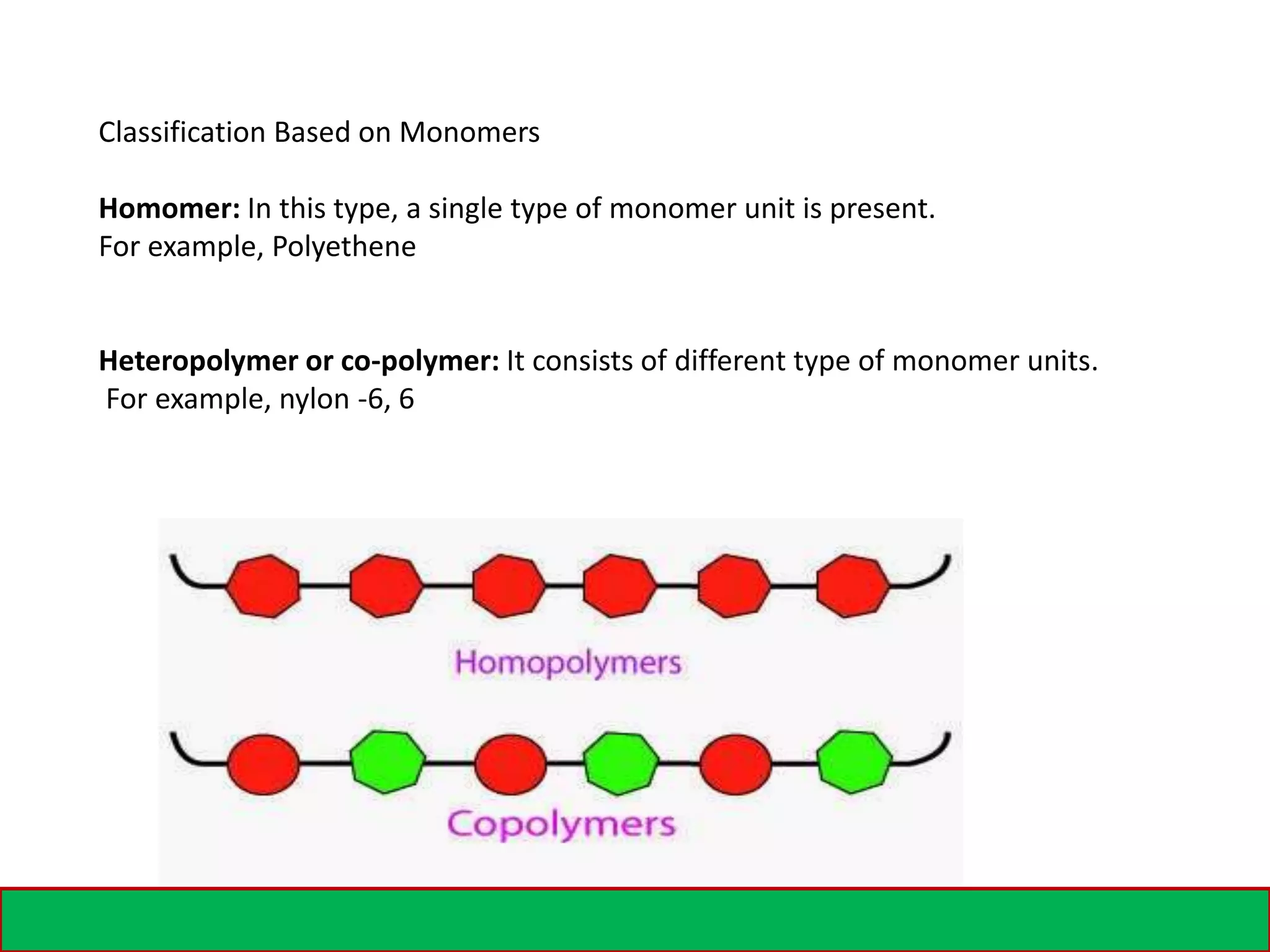
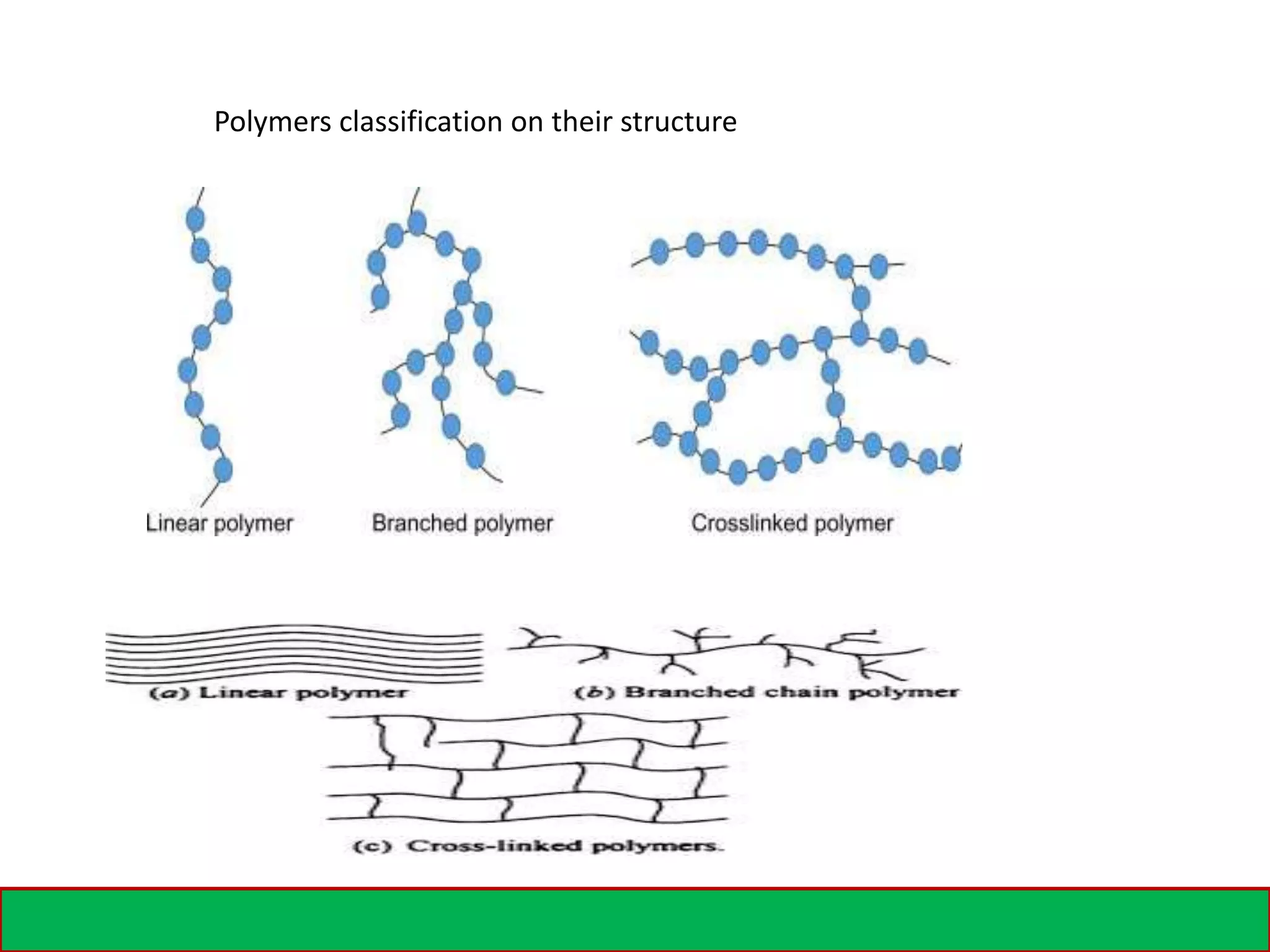
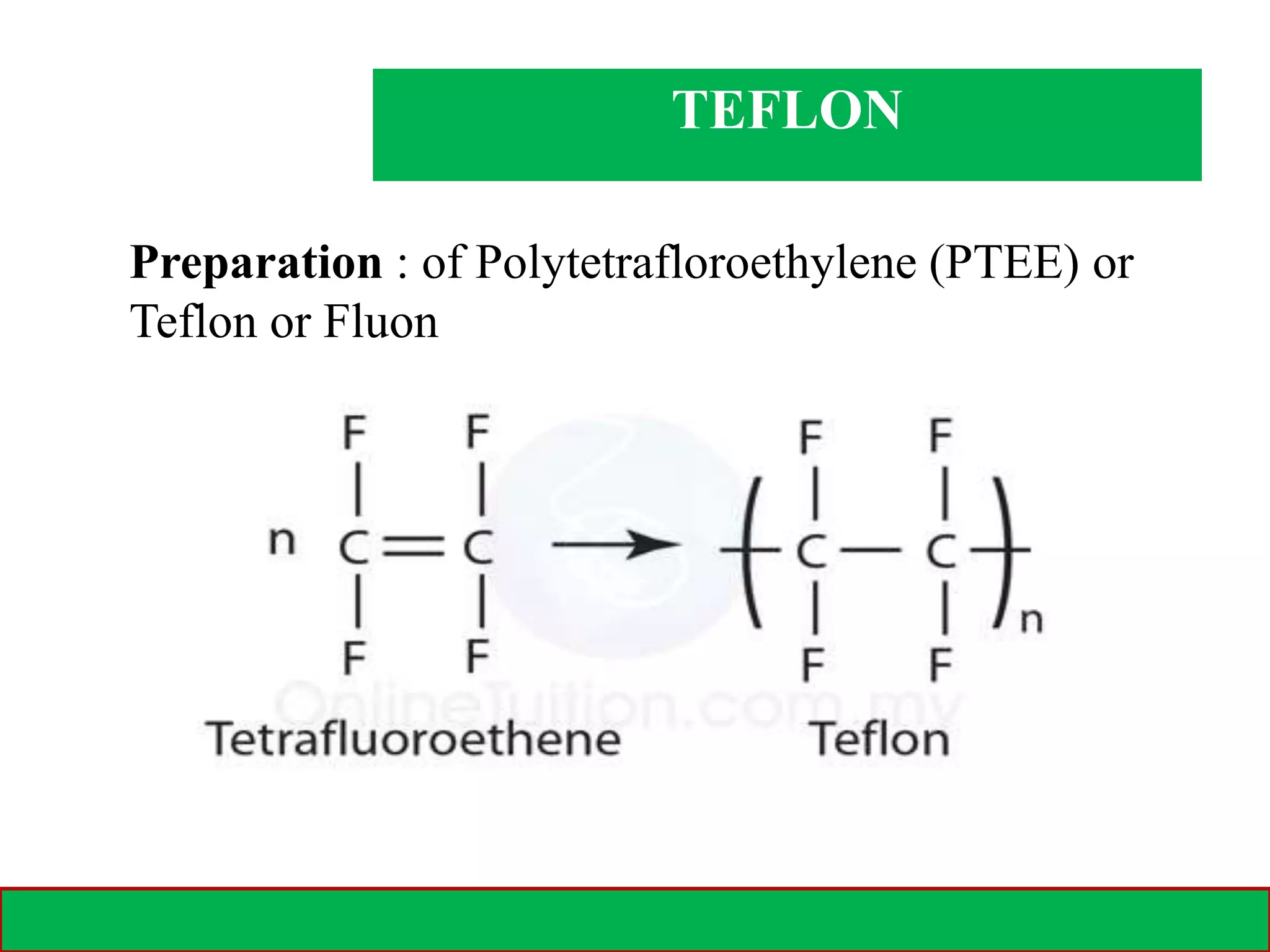
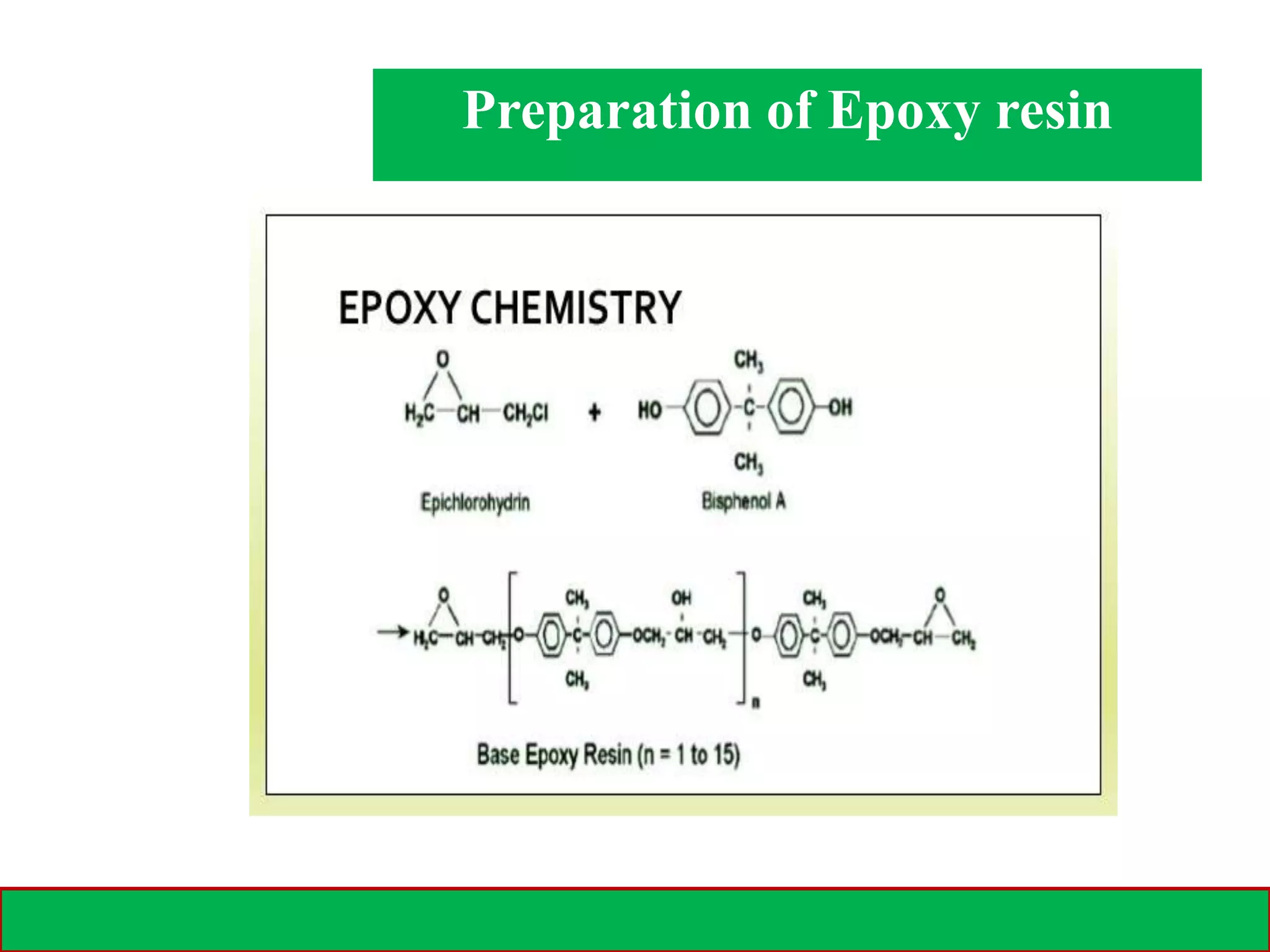
A polymer is formed from small molecular units called monomers that join together in long chains through chemical bonds. There are different types of polymers classified by their monomer structure and occurrence. Common synthetic polymers include plastics like polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, and epoxy resin. These polymers have various applications due to their properties such as corrosion resistance, low cost, and ability to be molded into complex shapes.