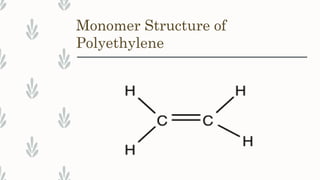
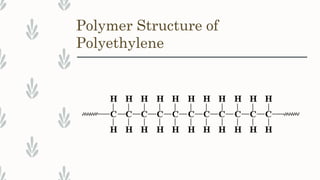
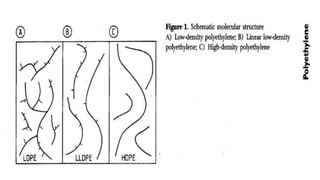
Polyethylene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer made from ethylene, first synthesized by Hans von Pechmann. It comes in several types, including low-density, high-density, linear low-density, and ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene, each with distinct properties and applications. Polyethylene is widely used in packaging and construction, offering various mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance properties.