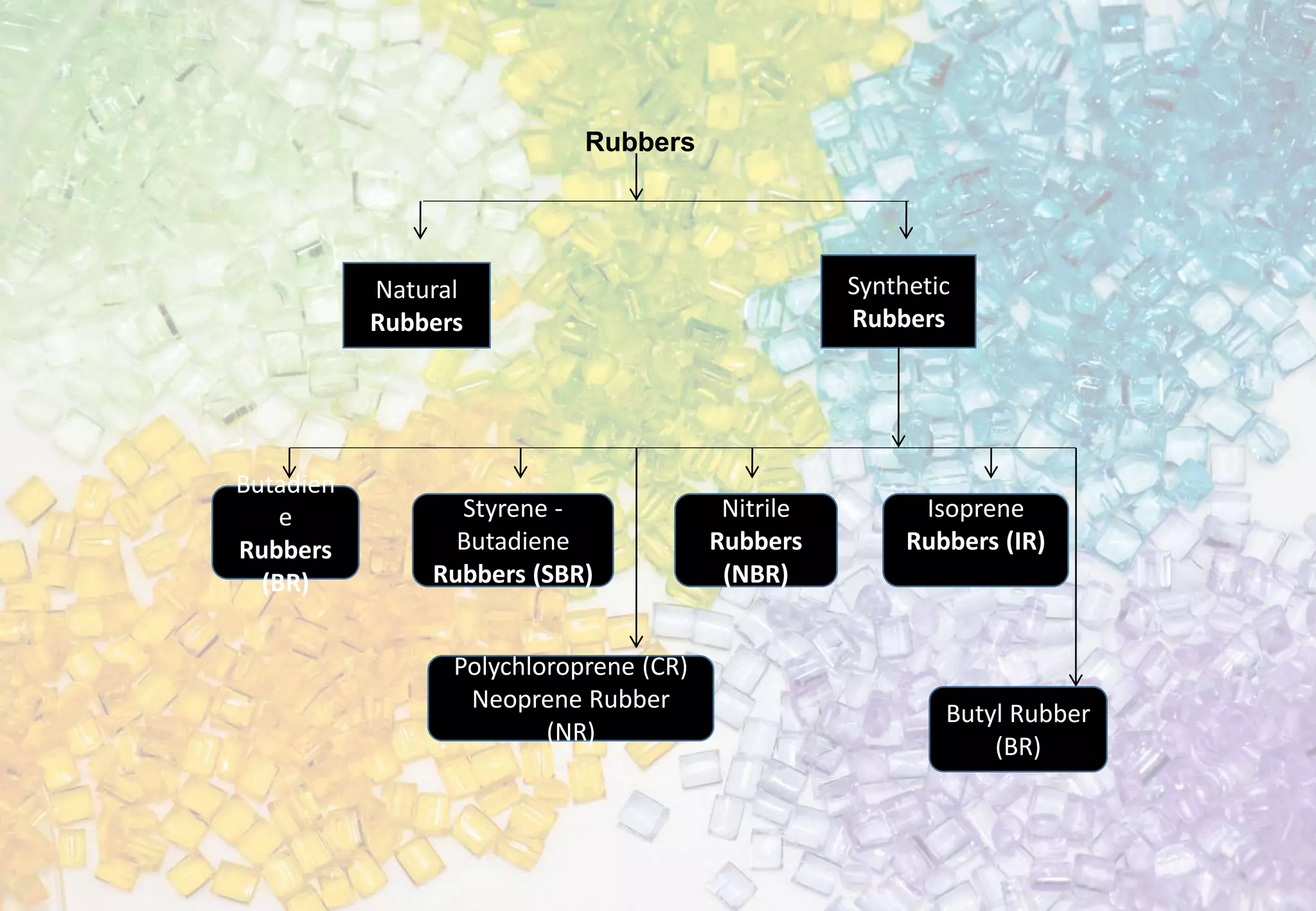
This document provides information on plastics and rubbers, including their composition, classification, and common types. It discusses thermoplastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, PVC, and ABS, as well as thermosetting plastics like phenol formaldehyde, urea formaldehyde, and polyurethane. Common rubbers like natural rubber and synthetic rubbers are also outlined. The document aims to inform the reader about the basic properties and applications of important plastic and rubber materials.