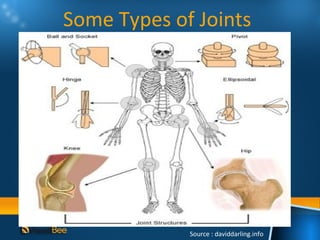
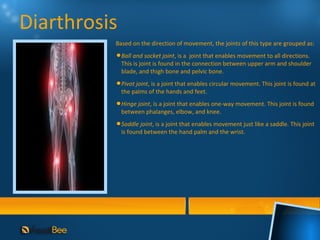
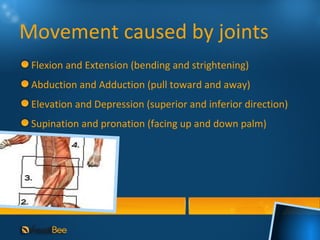
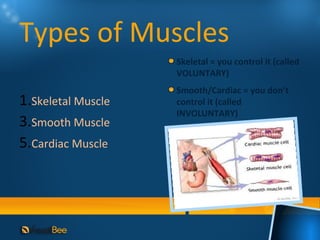
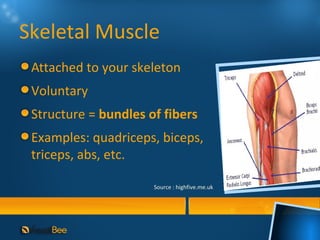
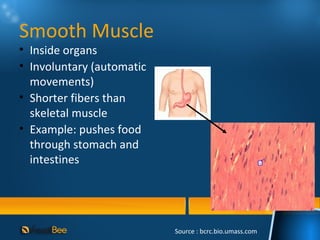
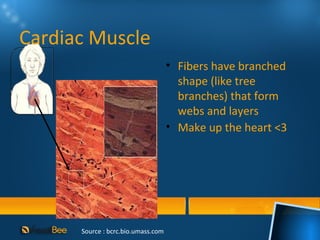
This document discusses joints and muscles in the human body. It describes the main types of joints, including ball-and-socket, hinge, and synovial joints, and their roles in enabling different movements. It also outlines the three main types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles, and their distinguishing characteristics such as whether they are voluntary or involuntary. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and controlled voluntarily, while smooth and cardiac muscles function involuntarily within internal organs and the heart.

![Do you ever think how our
body can move?
[Divider Picture]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jointsandmuscles-130220000525-phpapp01/85/Joints-and-muscles-2-320.jpg)



![To be continue at abnormalities
of movement system…
[Divider Picture]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jointsandmuscles-130220000525-phpapp01/85/Joints-and-muscles-13-320.jpg)