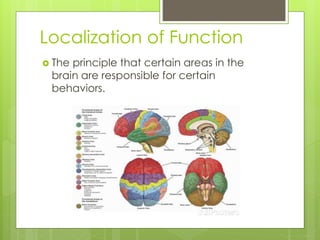
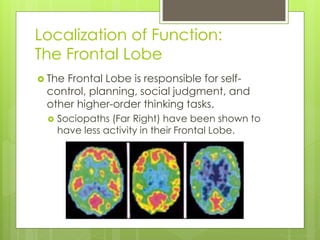
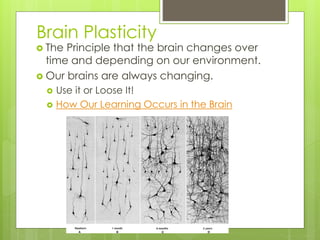
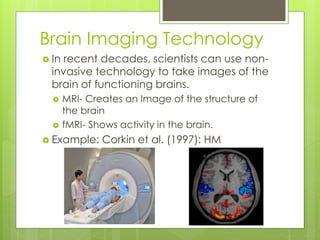
This document provides an introduction to the human brain, including objectives, key terms, and examples of research studies. It discusses the principles of localization of function and brain plasticity. Examples are given of different methods neurologists use to study the brain, including post-mortem examination, analysis of brain damage cases, and modern brain imaging technologies like MRI and fMRI. Specific studies summarized include Rosenzweig on brain plasticity in rats, Dimasio on Phineas Gage's frontal lobe damage, and Corkin on patient H.M.'s hippocampal removal.