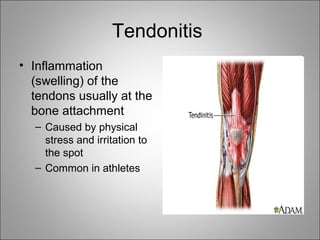
Human locomotion involves the coordinated movement of bones, cartilage, muscles, tendons, and ligaments to allow movement from place to place. The skeletal system contains variously shaped bones that support the body structure, anchor muscle action, enable movement, and produce blood cells. Cartilage provides flexibility and cushioning between joints. The muscular system contains three muscle types - smooth and involuntary visceral muscles, striped and involuntary cardiac muscles of the heart, and skeletal muscles which are striped, voluntary, and control movement by pulling on bones. Tendons connect muscles to bones while ligaments connect bones at joints. Common problems affecting the system include arthritis which causes joint inflammation and pain, and tendonitis which is inflammation of tendons at