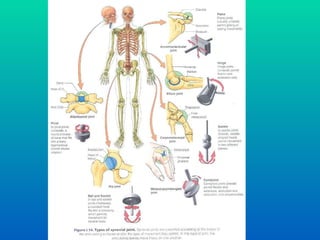
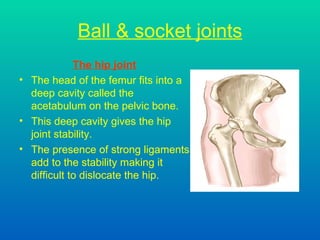
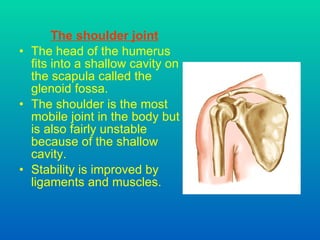
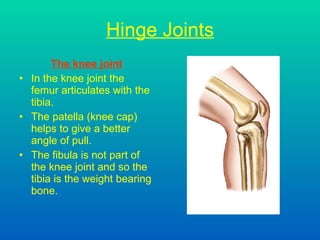
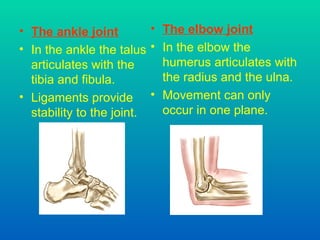
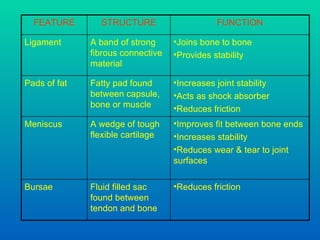
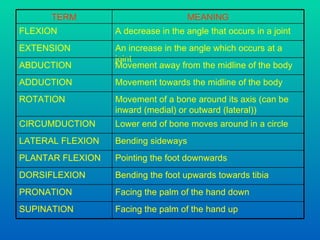
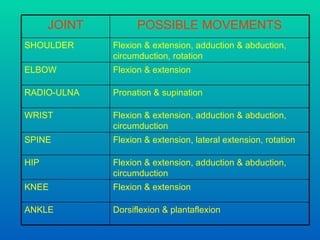
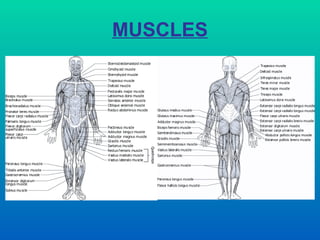
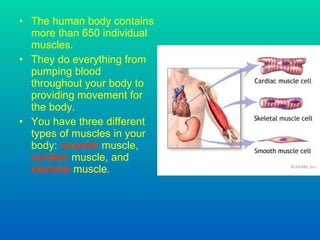
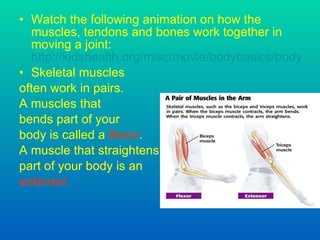
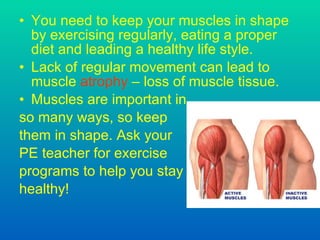
The document discusses joints and muscles in the human body. It describes the three main types of joints - fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial - and focuses on synovial joints, naming the six types: ball-and-socket, hinge, pivot, saddle, condyloid, and gliding. It provides examples of joints for each type and explains their movements. The document also outlines the three main types of muscles - smooth, cardiac, and skeletal - and describes their functions, locations, and voluntary vs involuntary control.