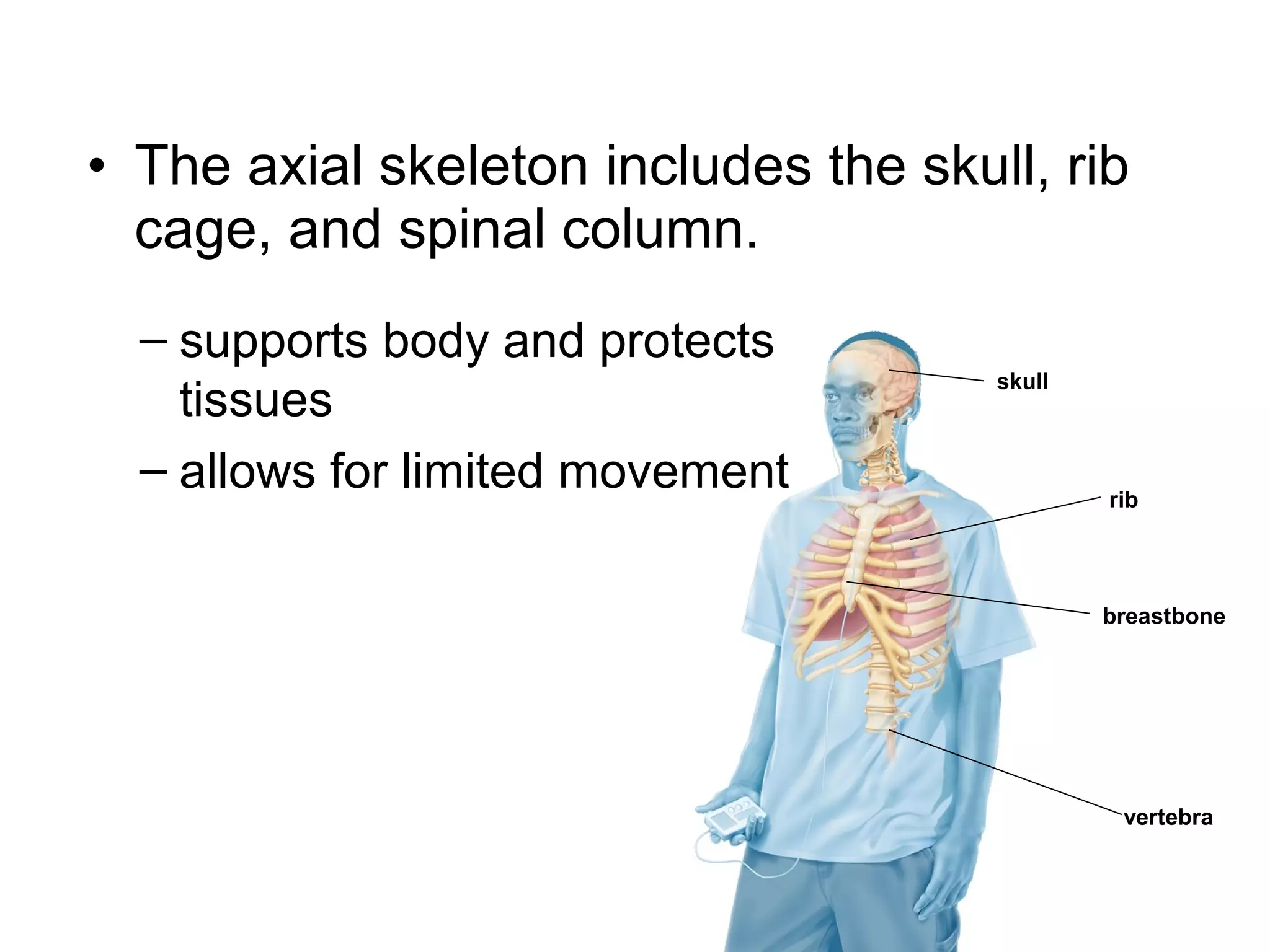
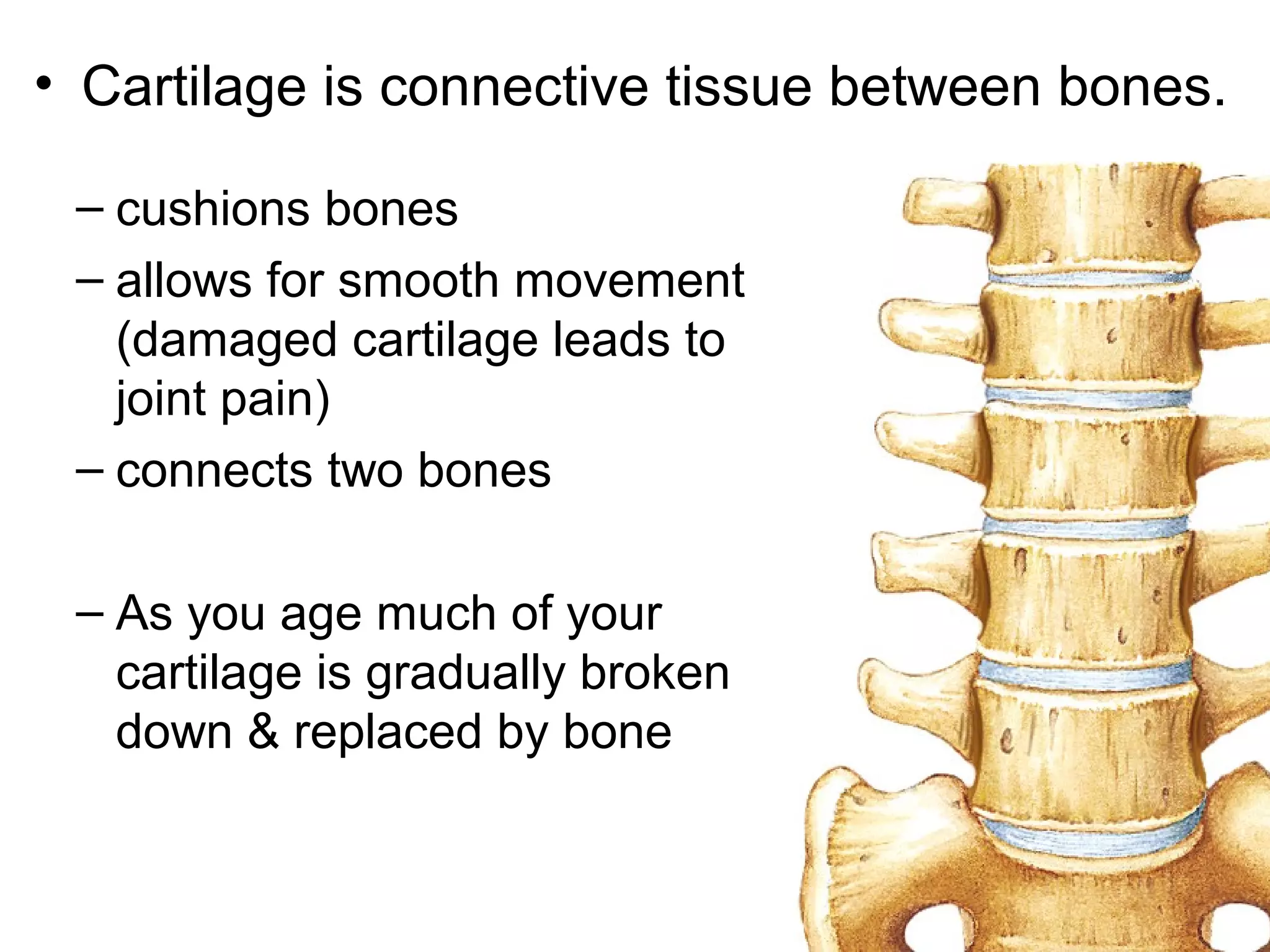
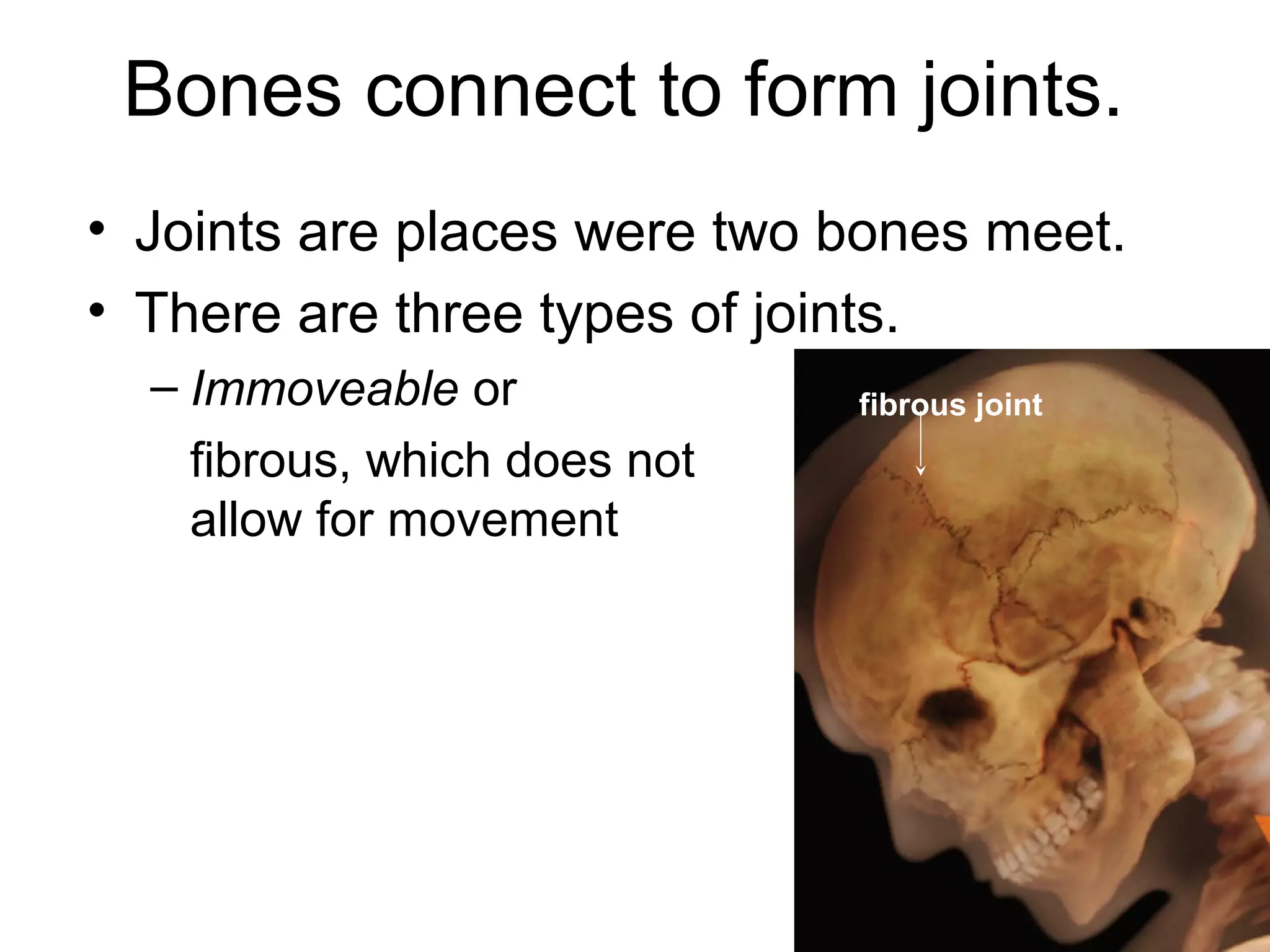
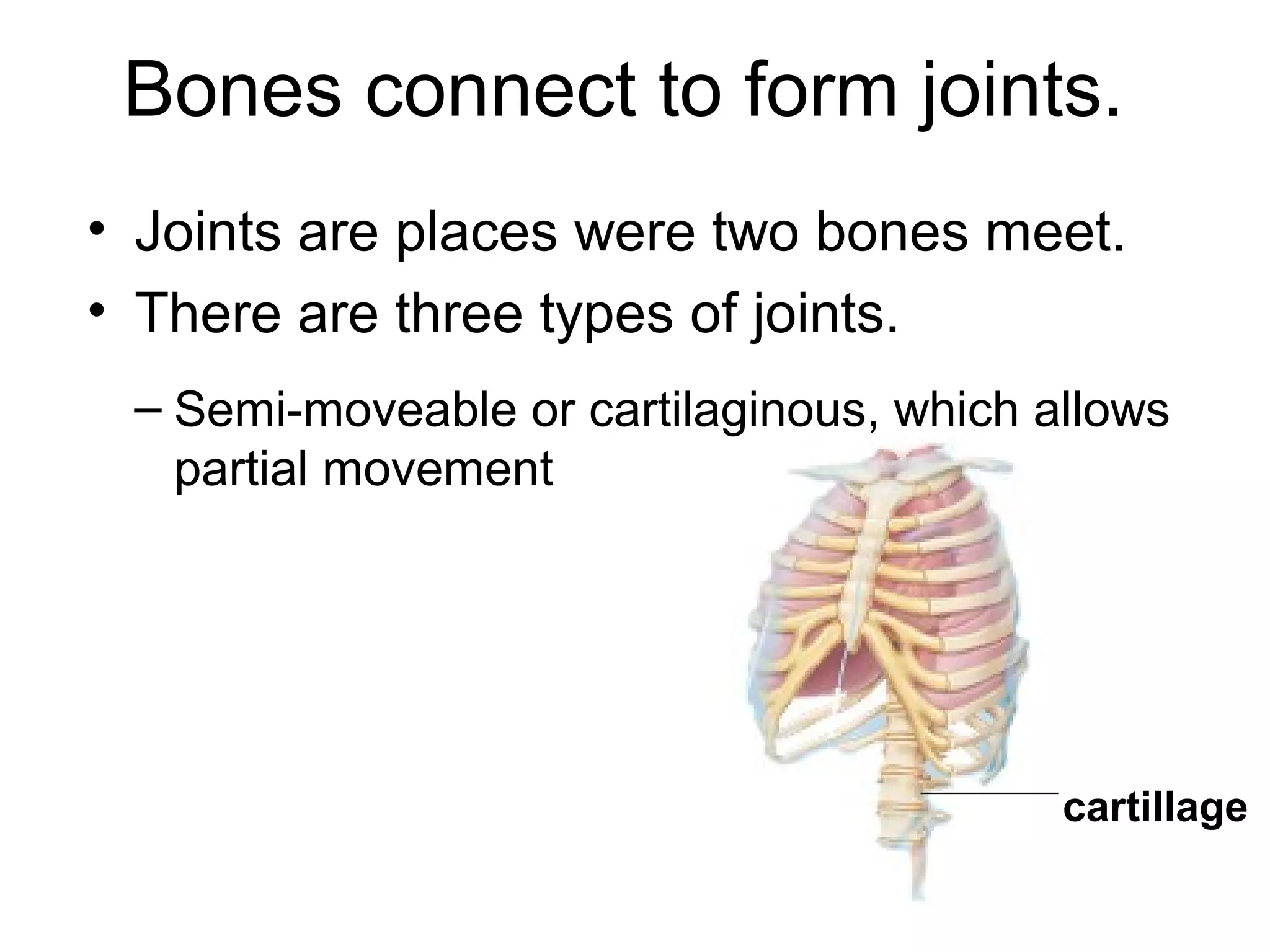
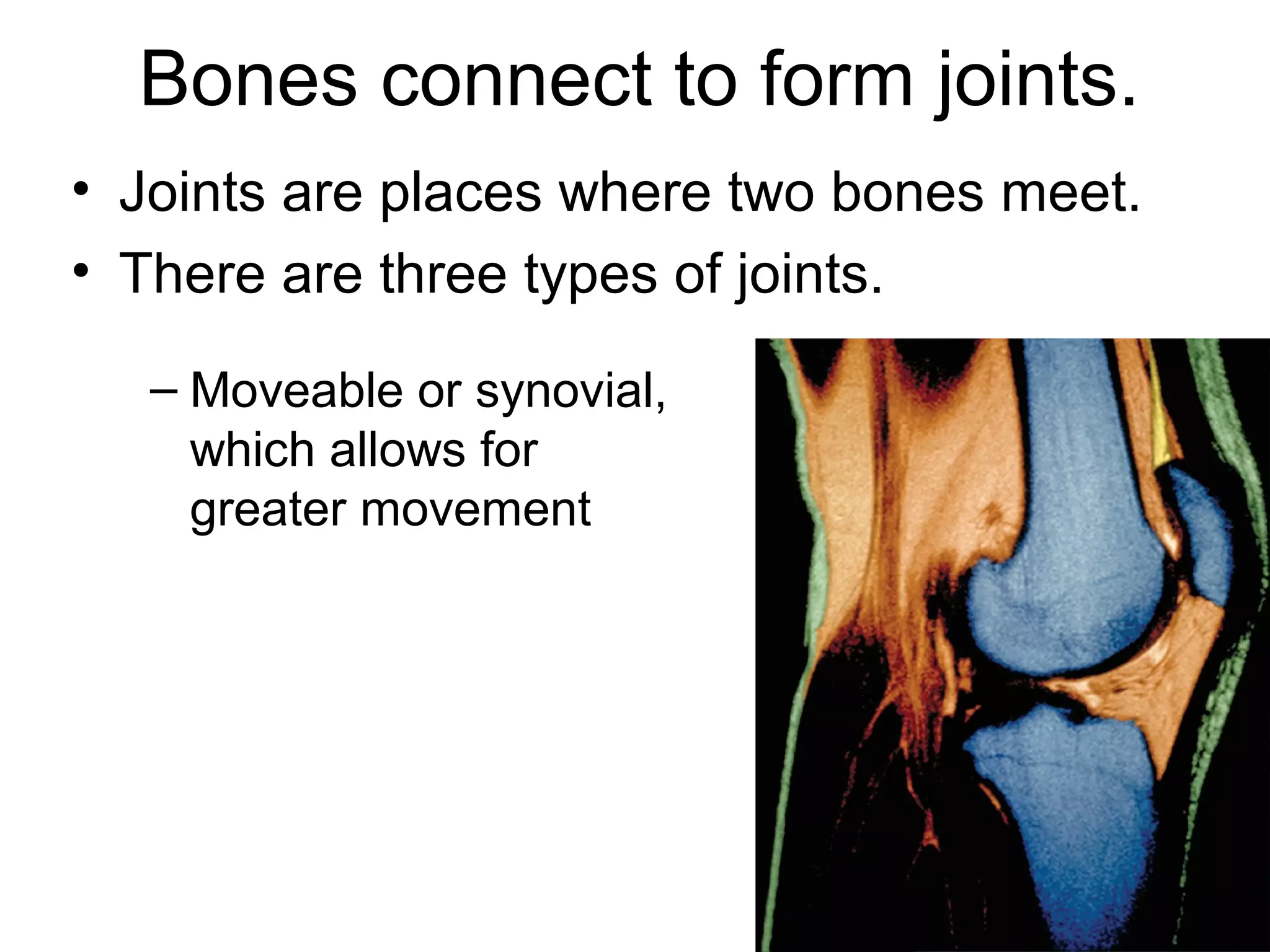
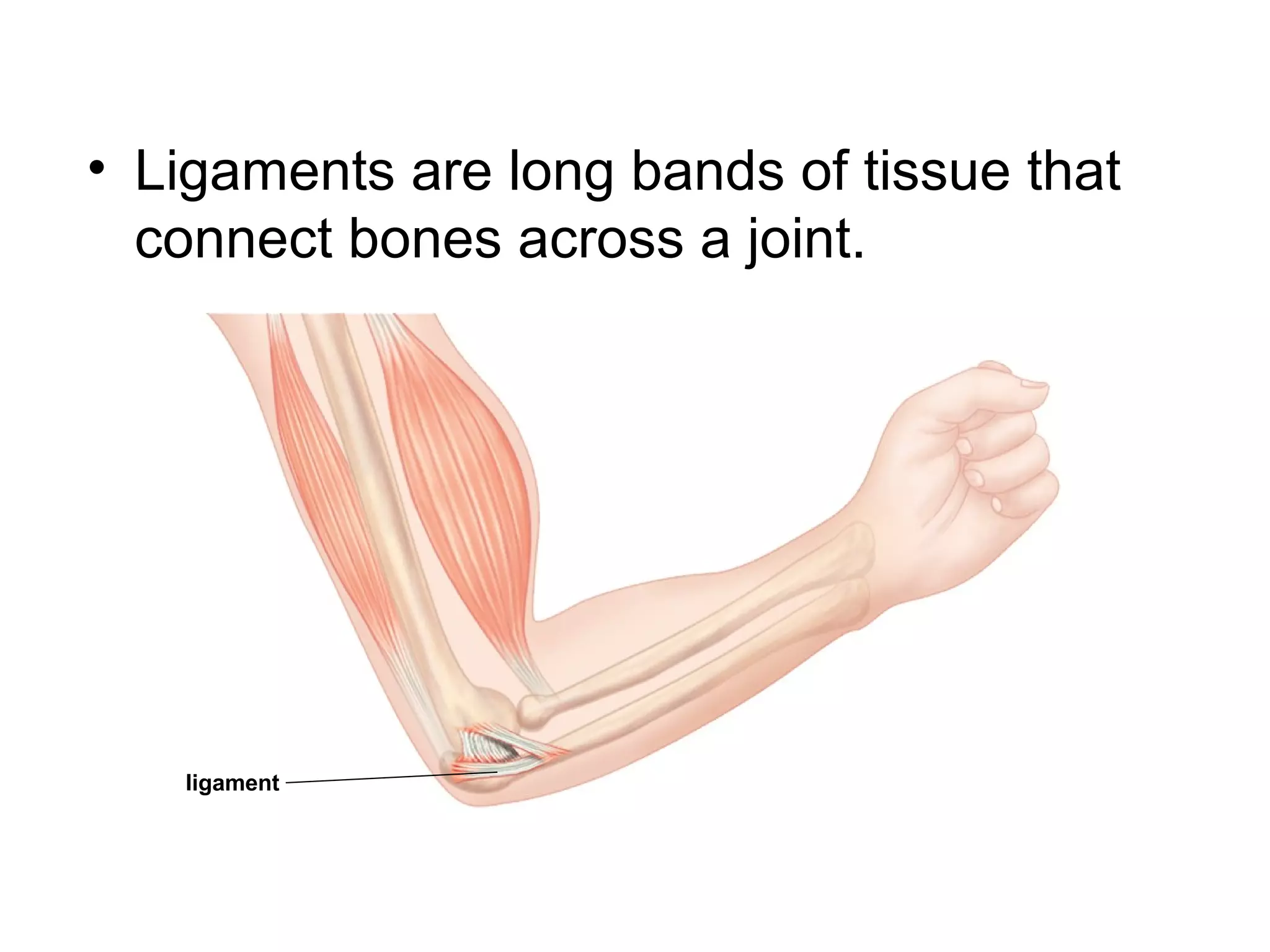
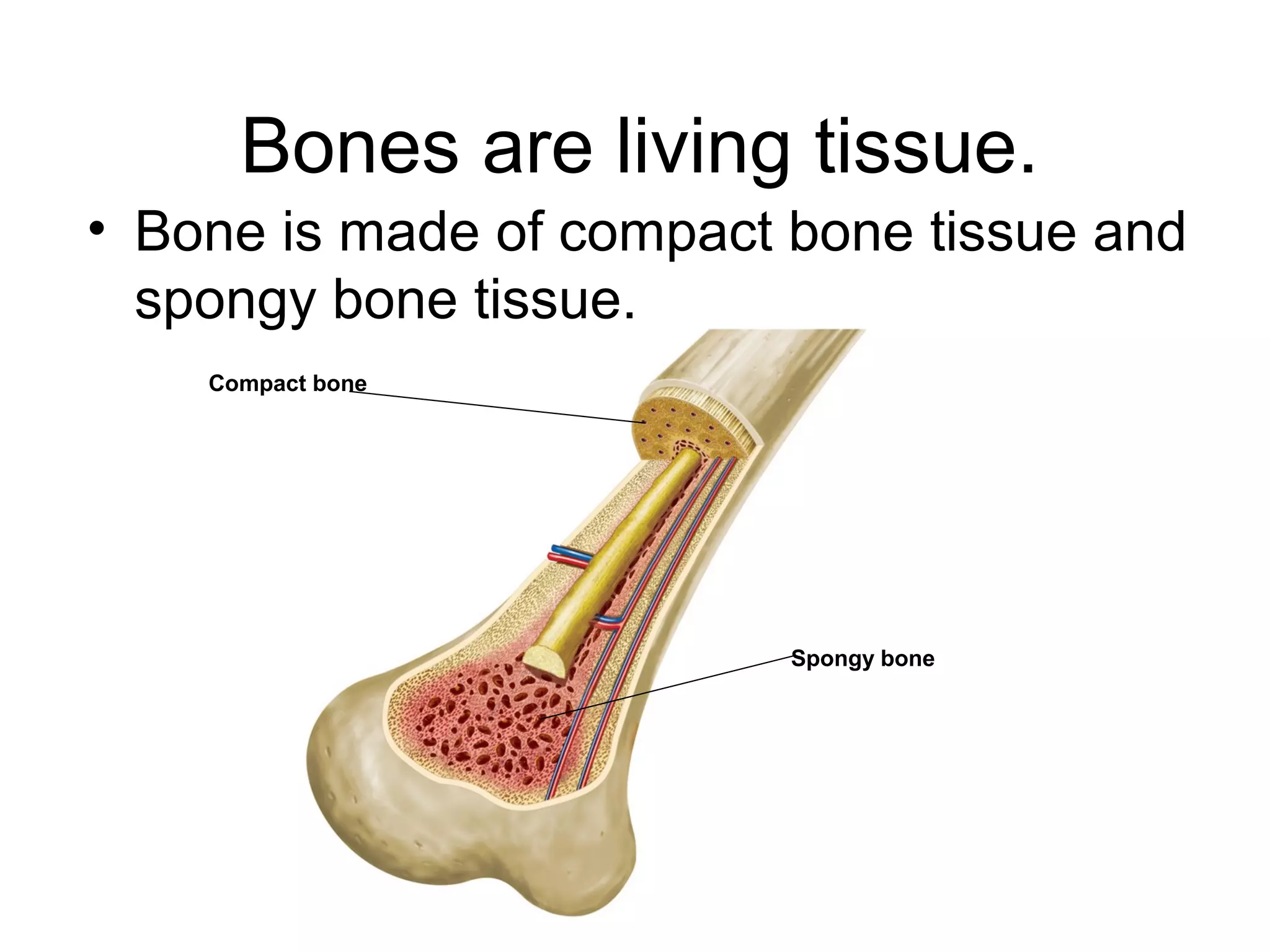
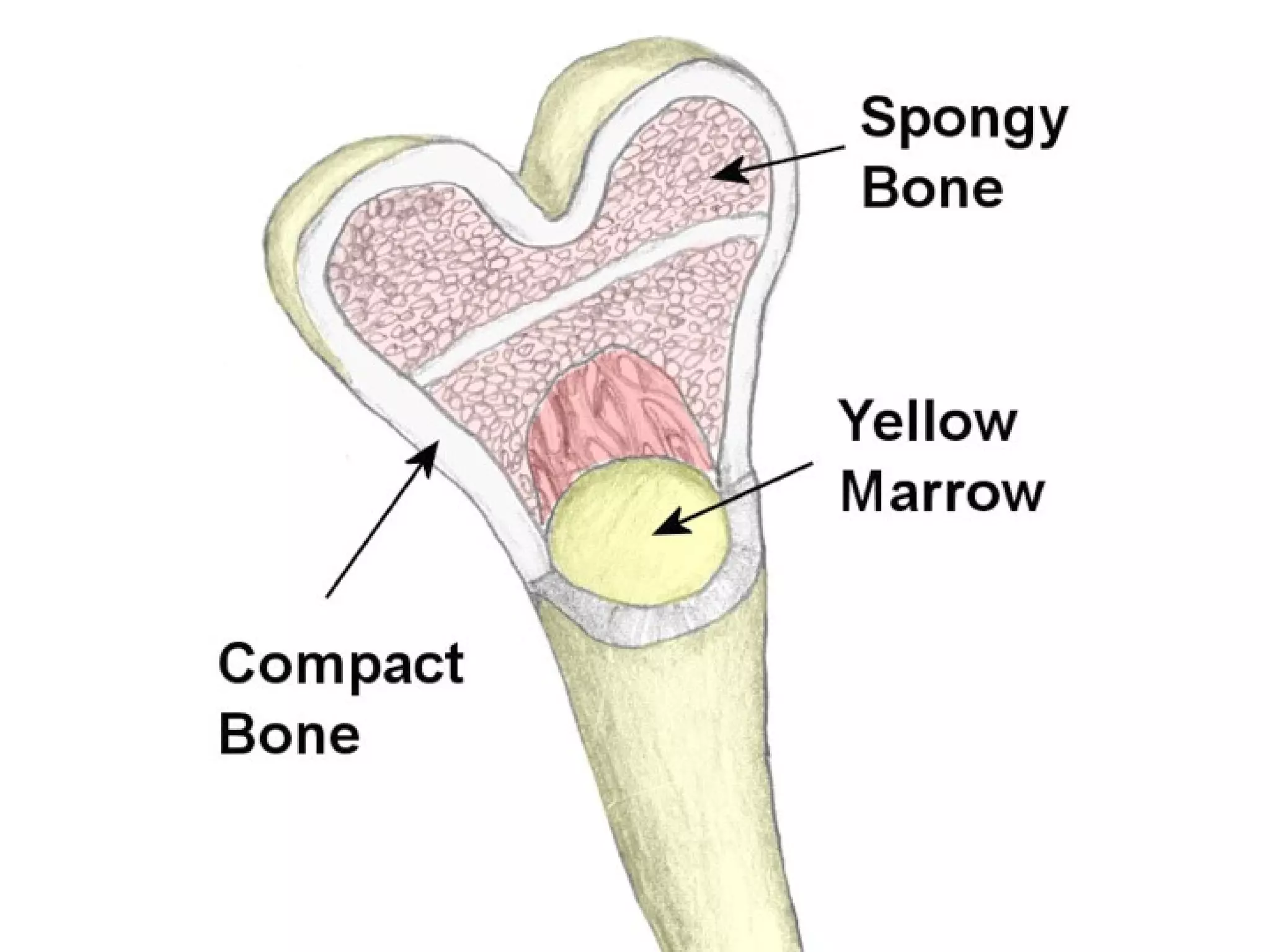
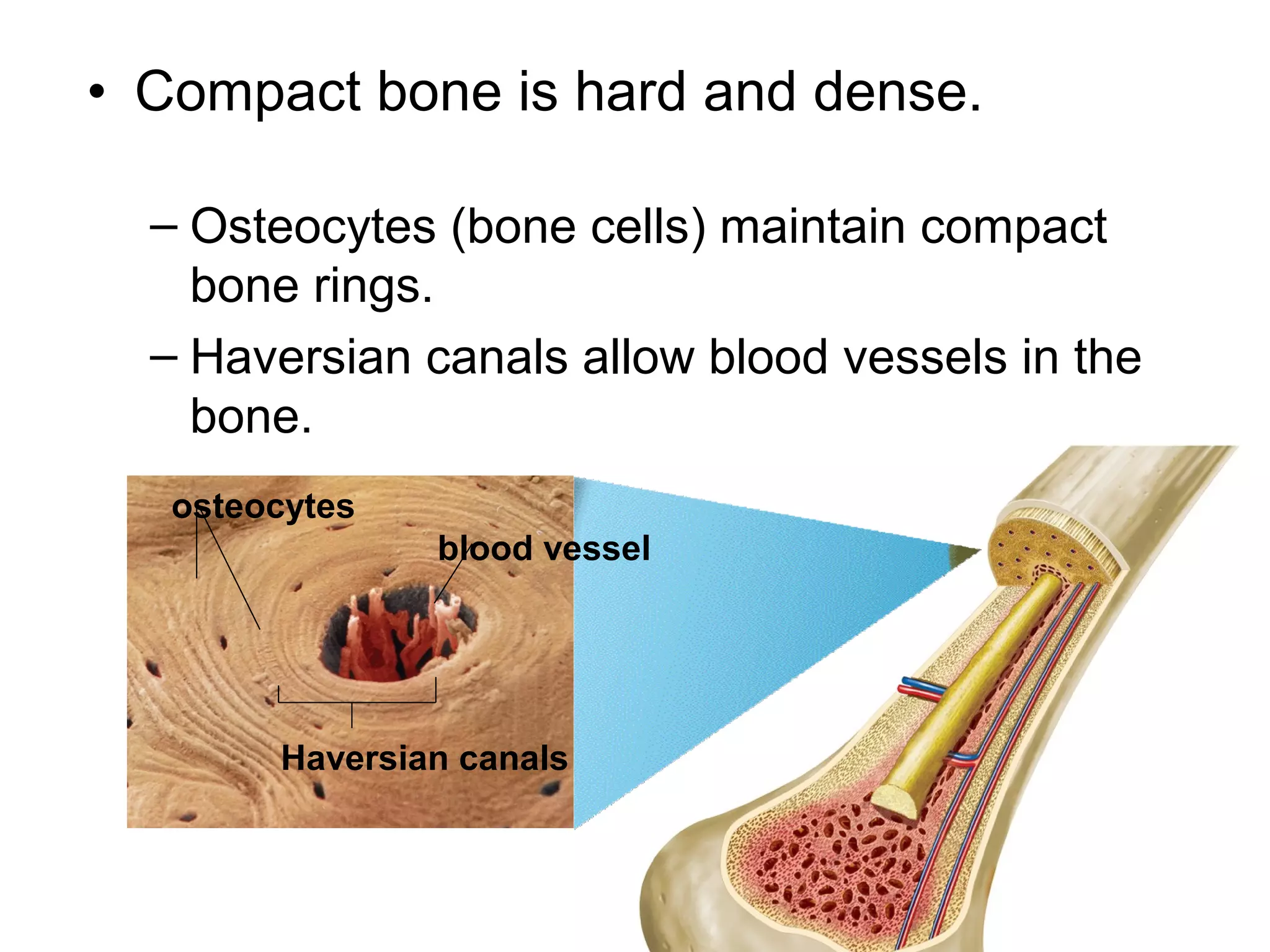
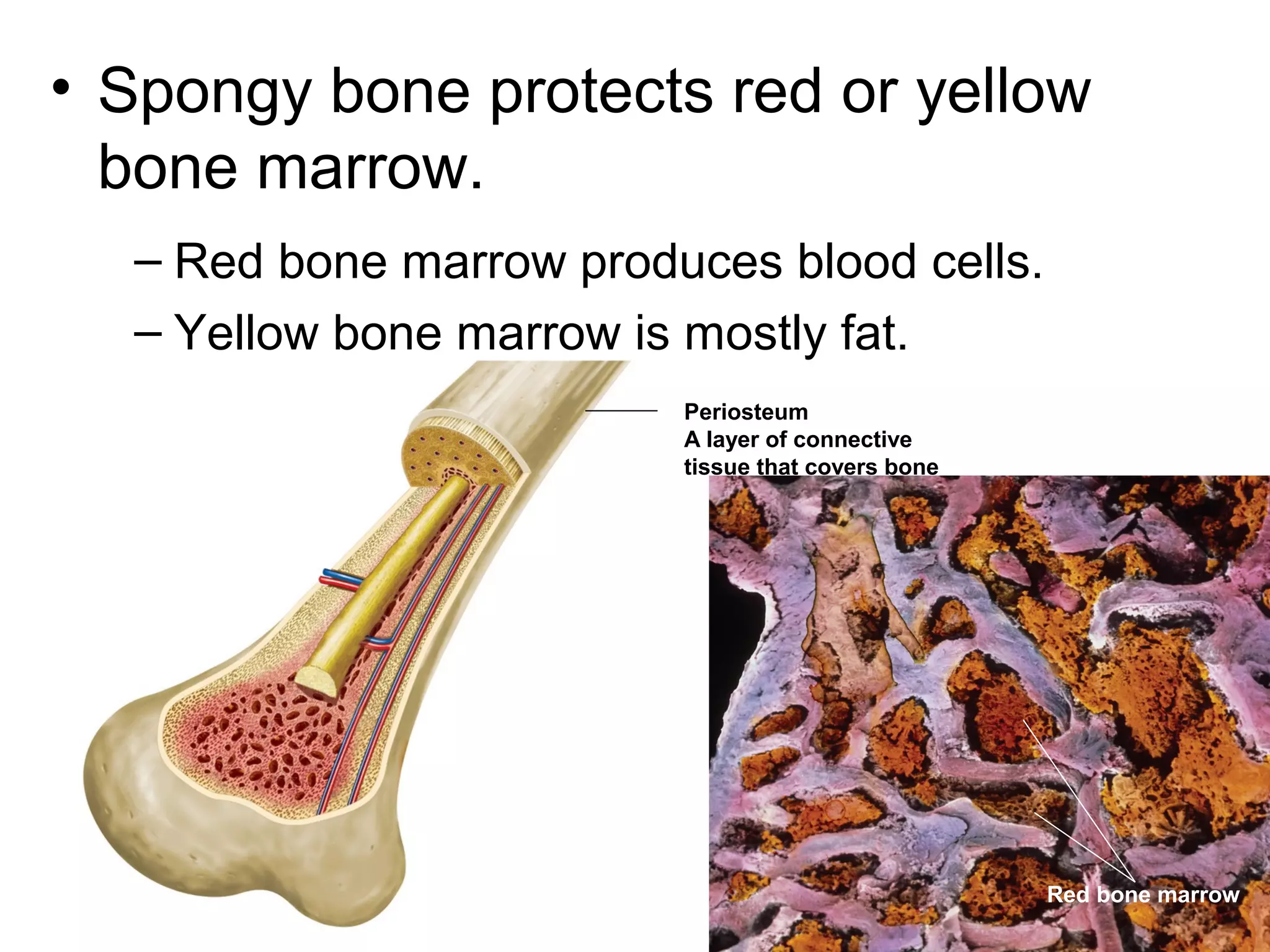
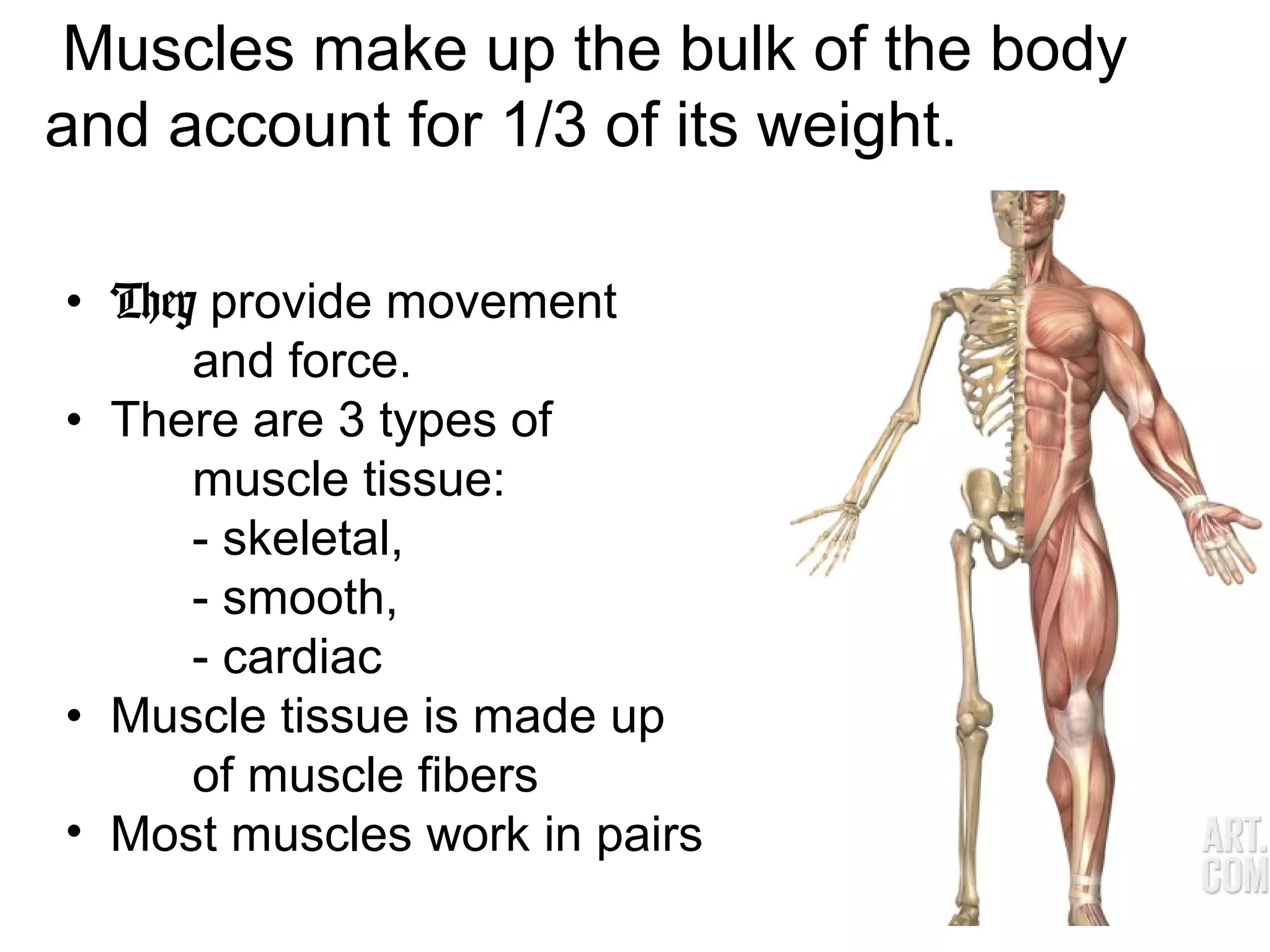
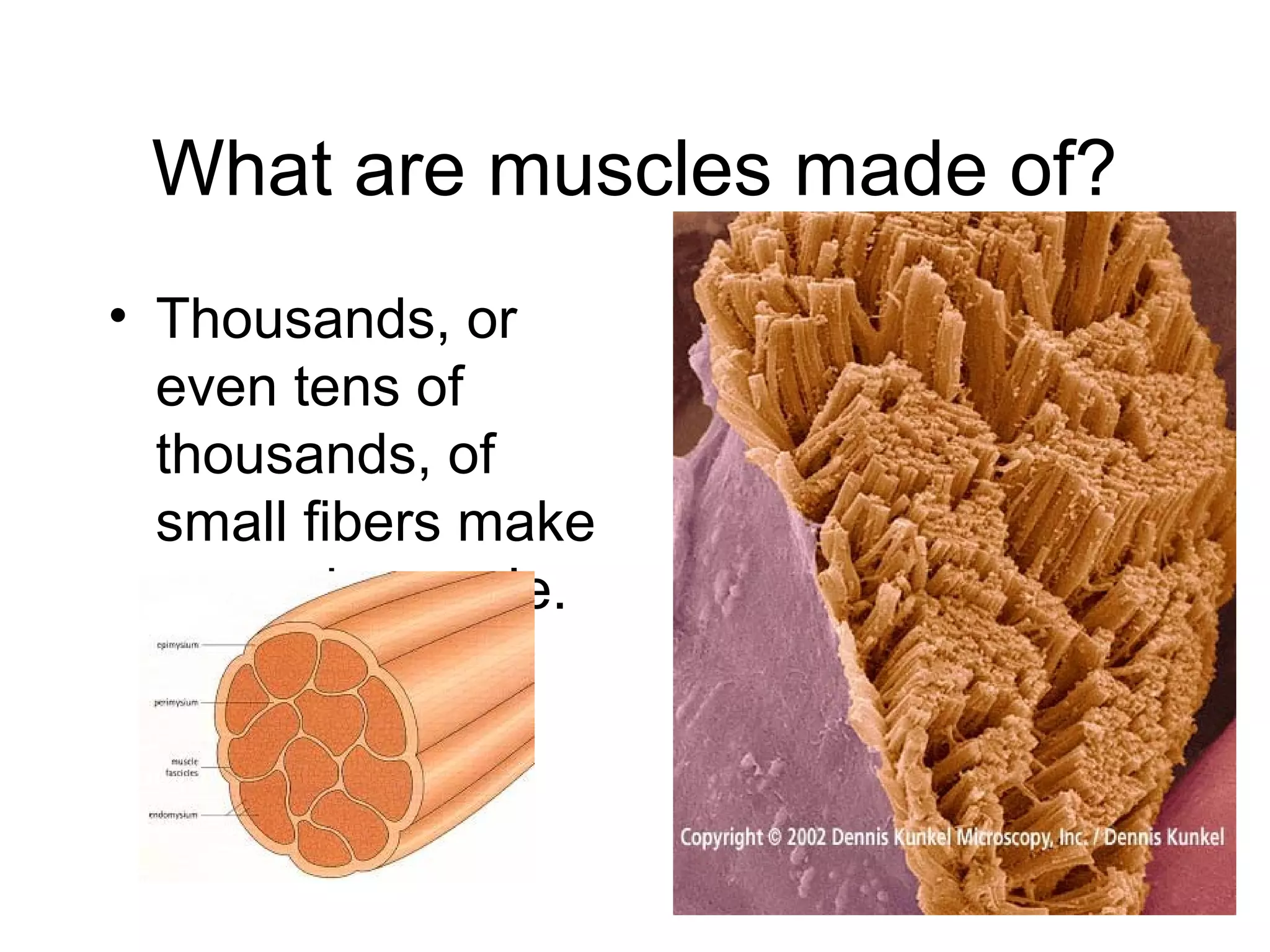
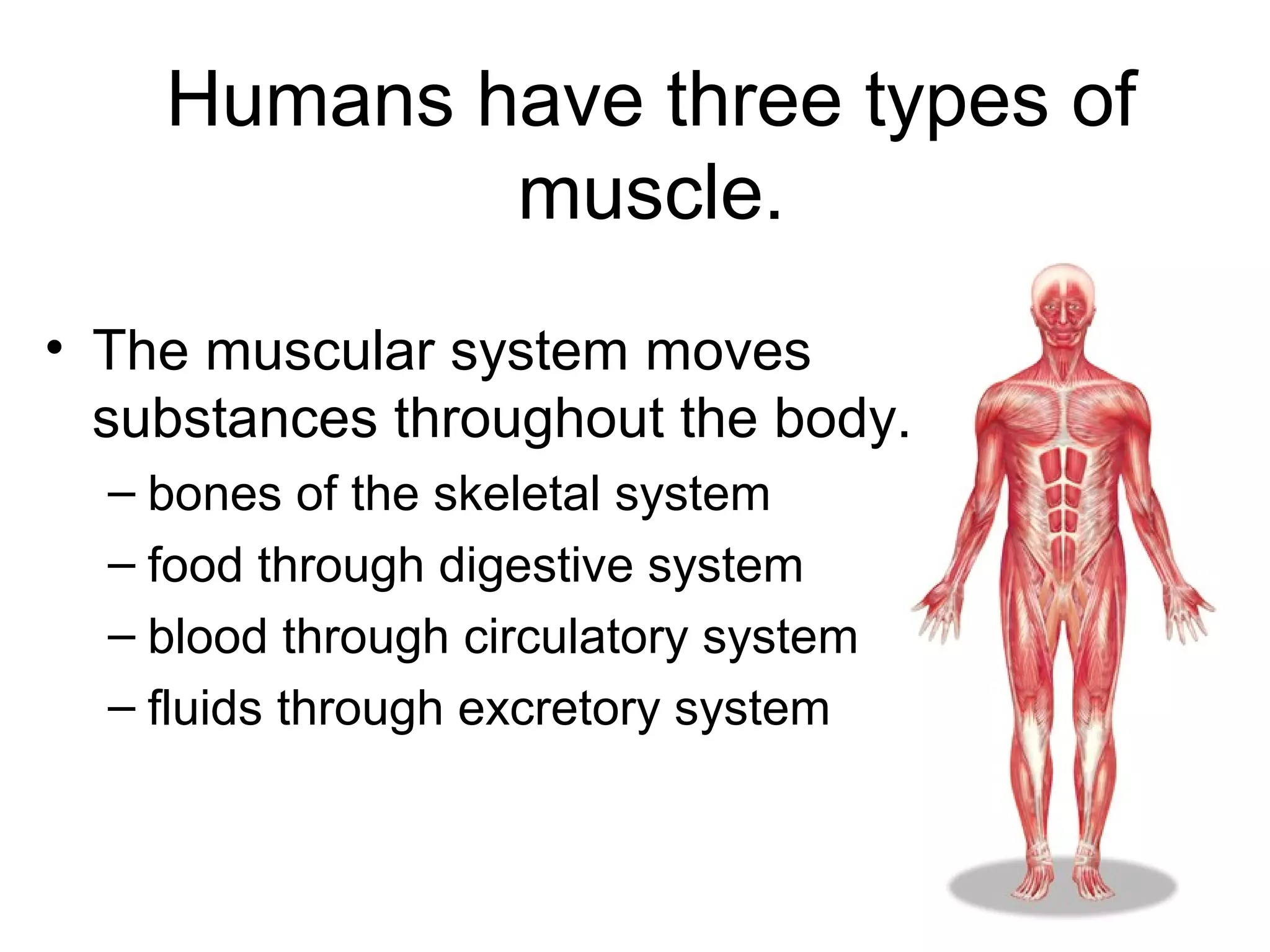
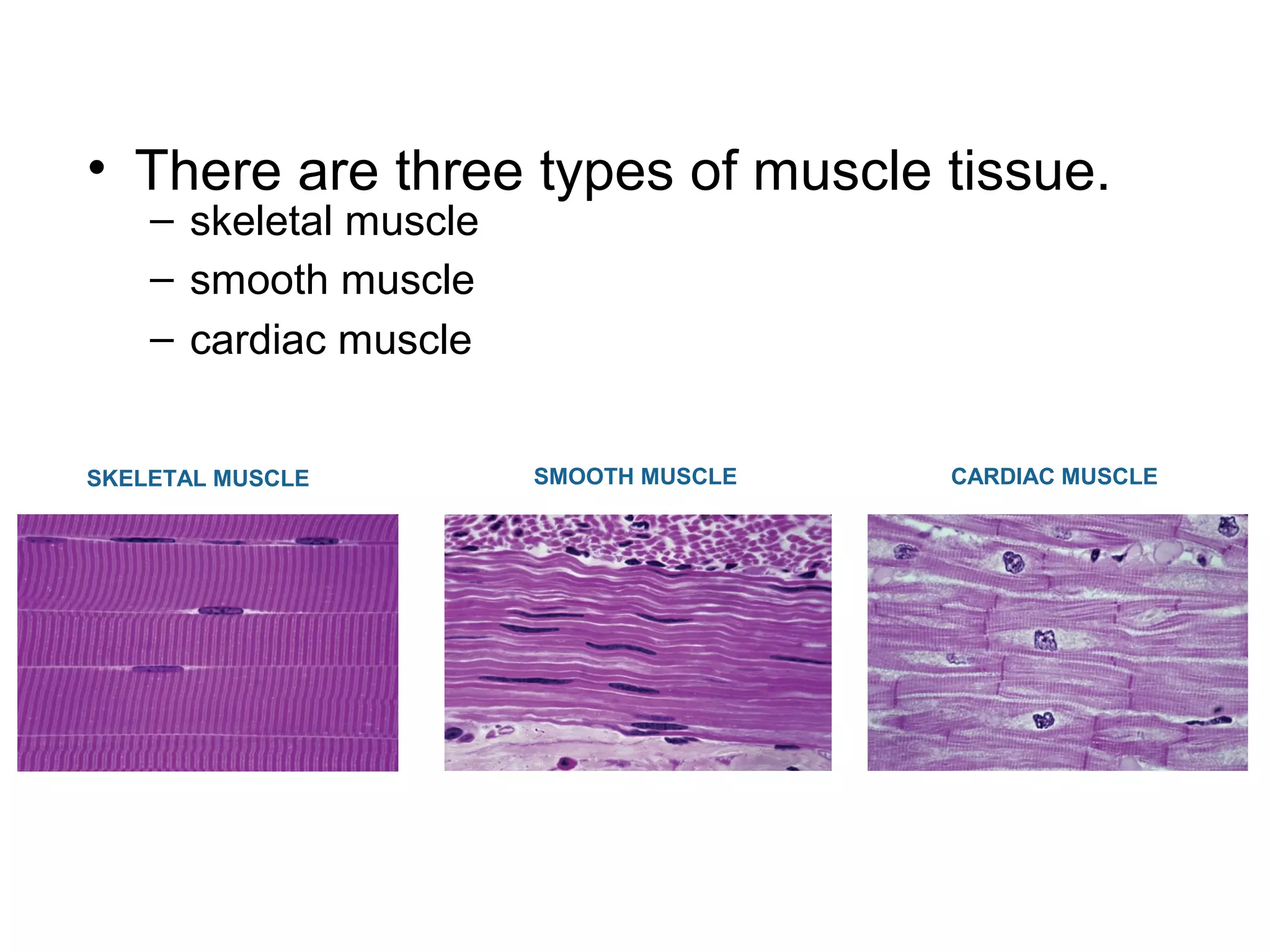
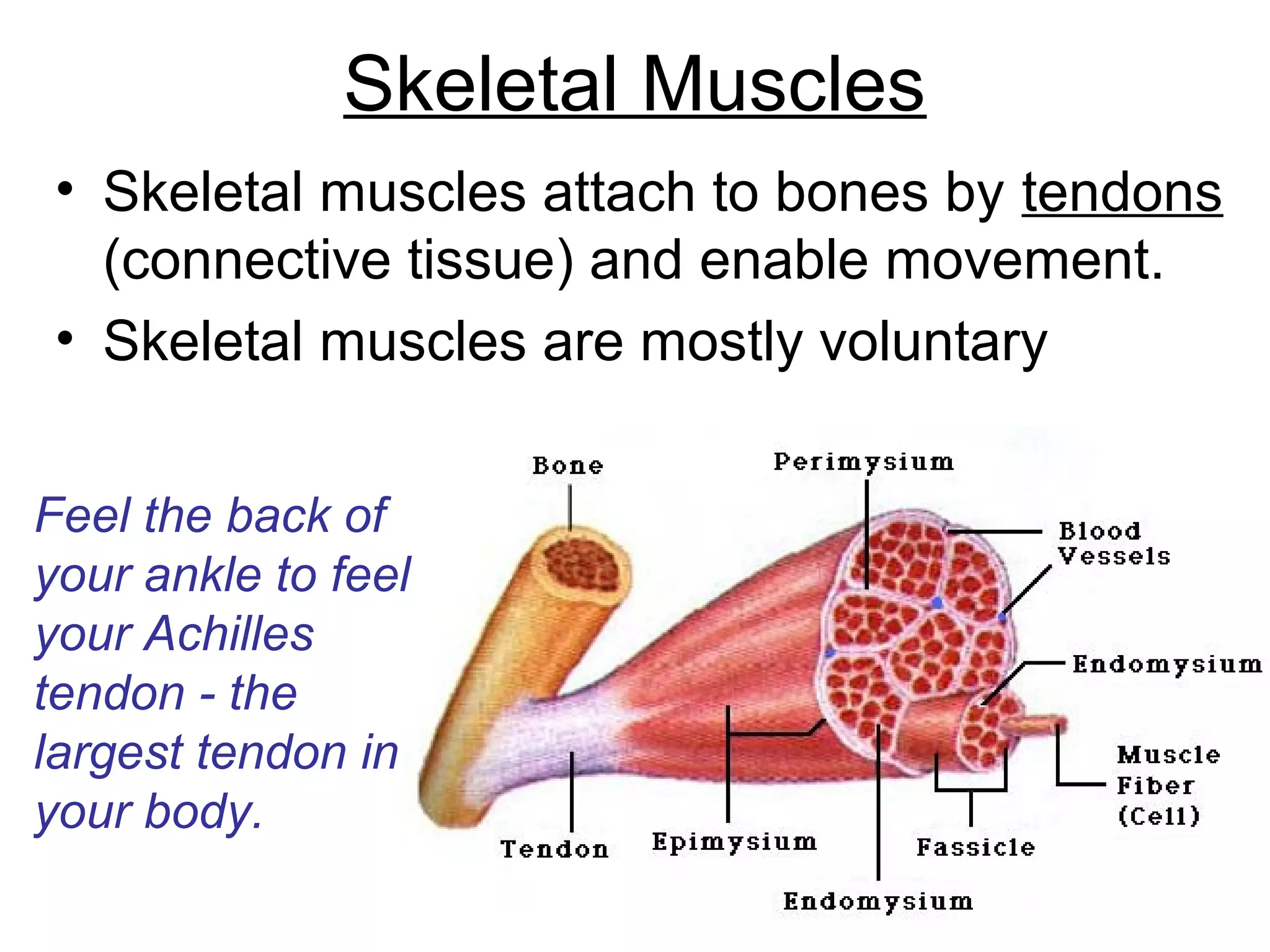
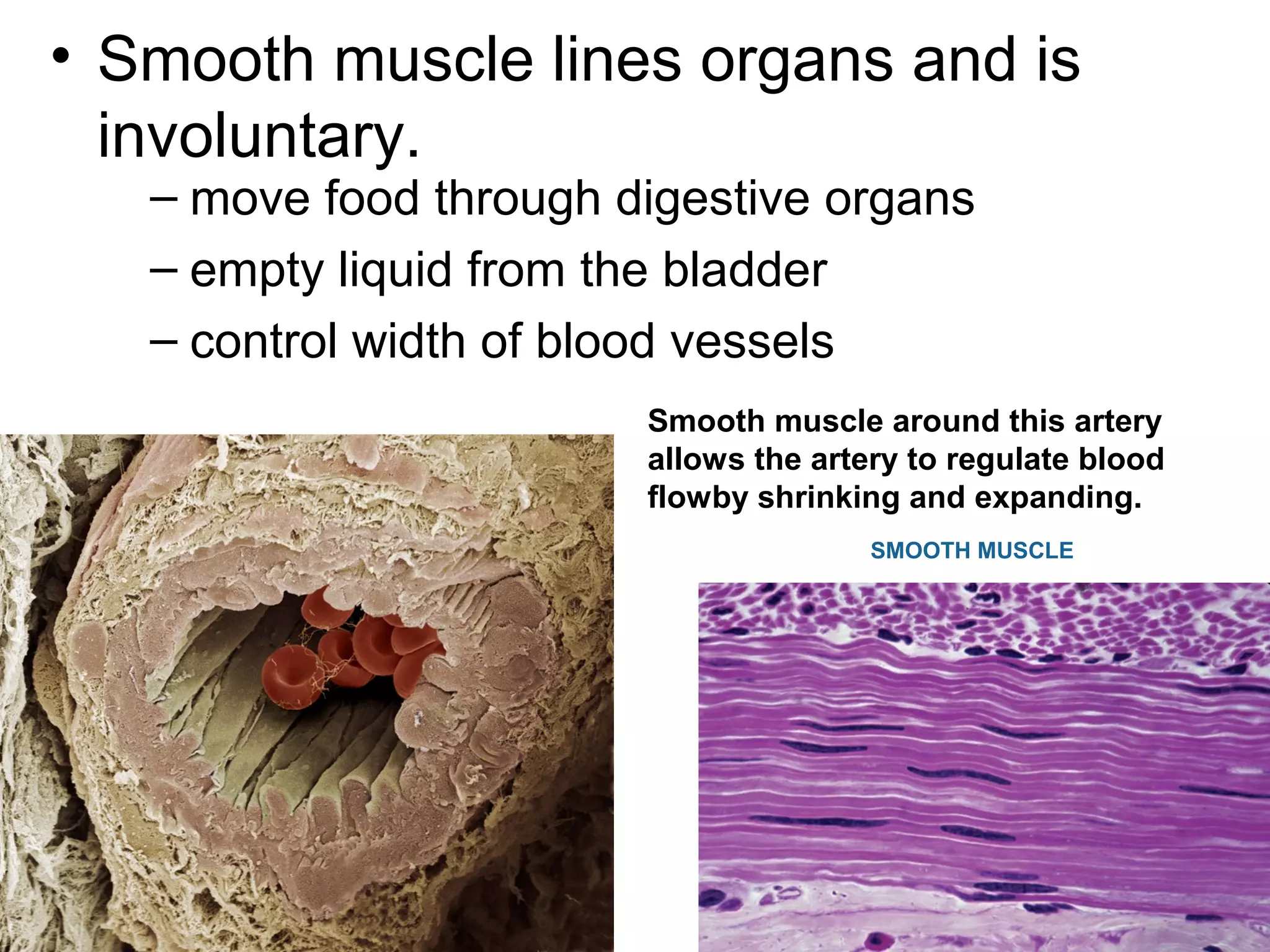
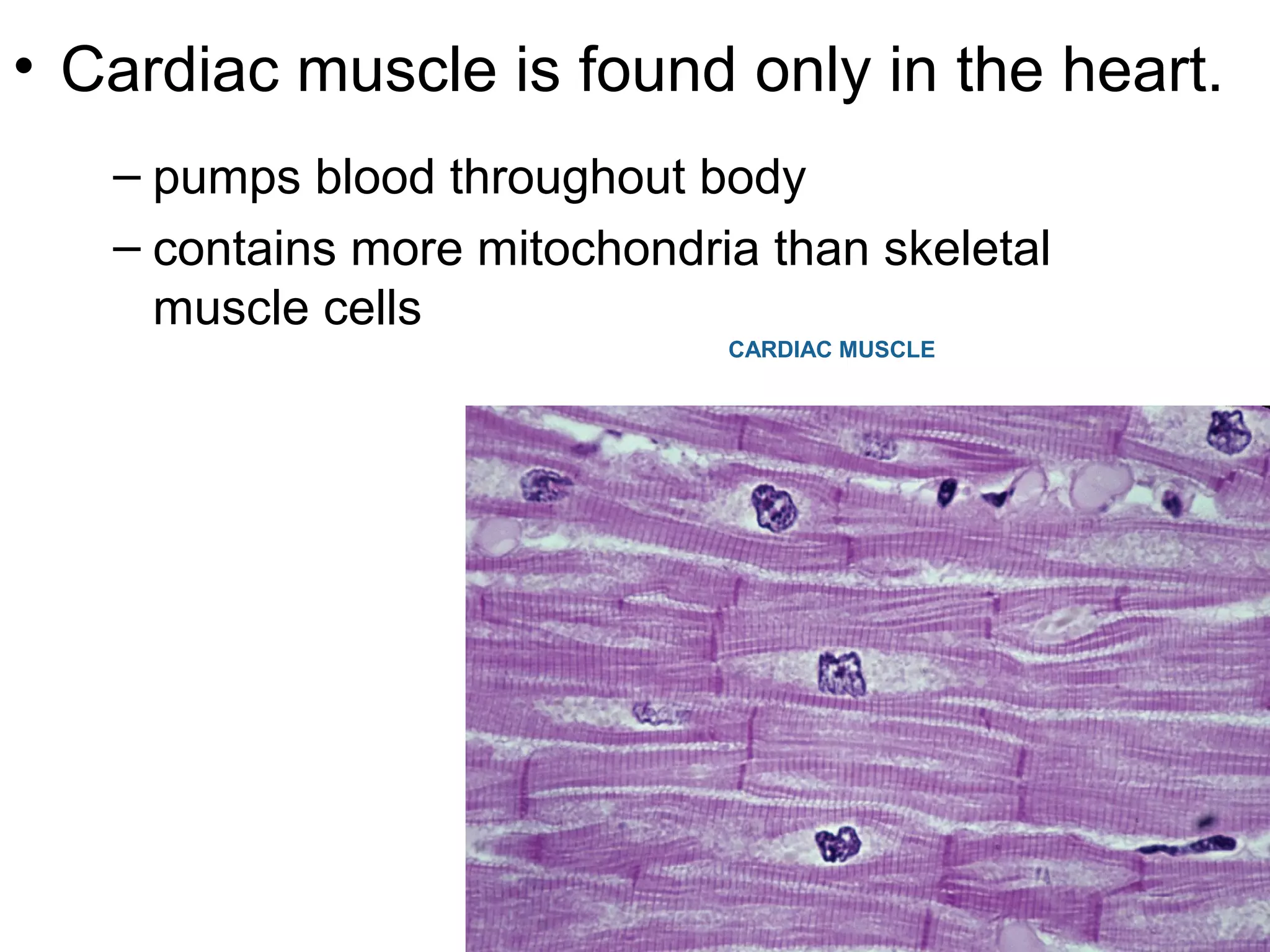
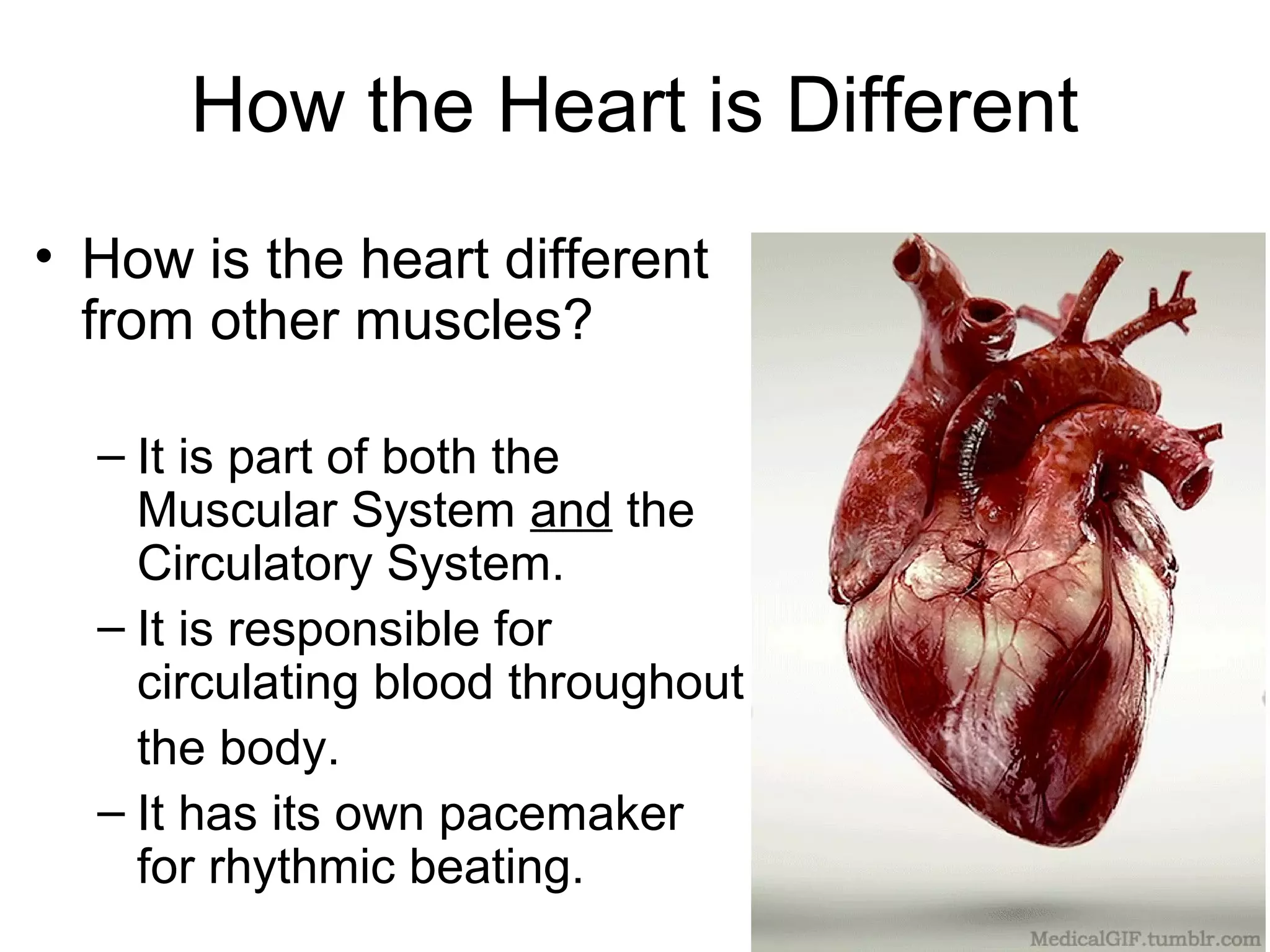
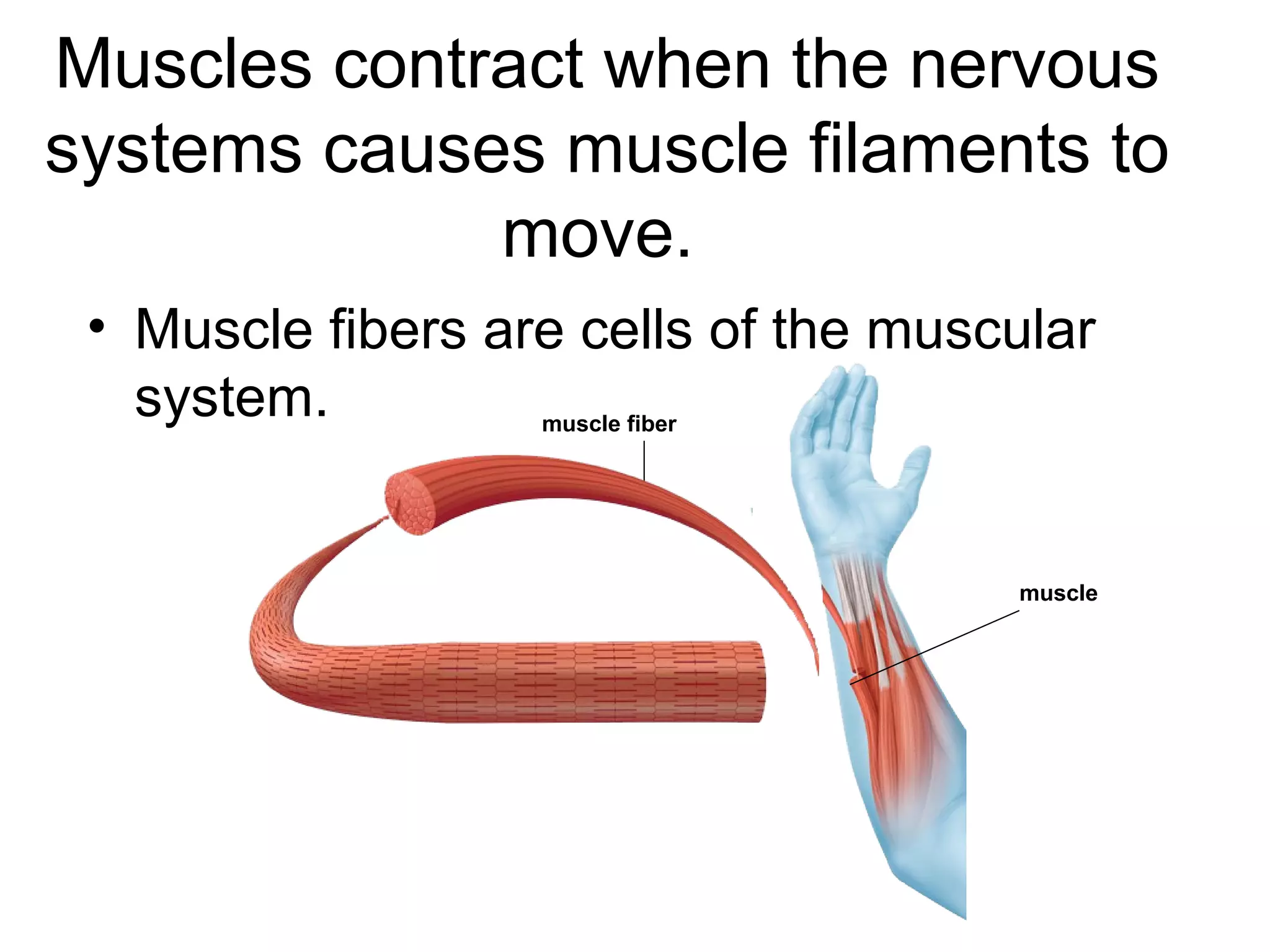
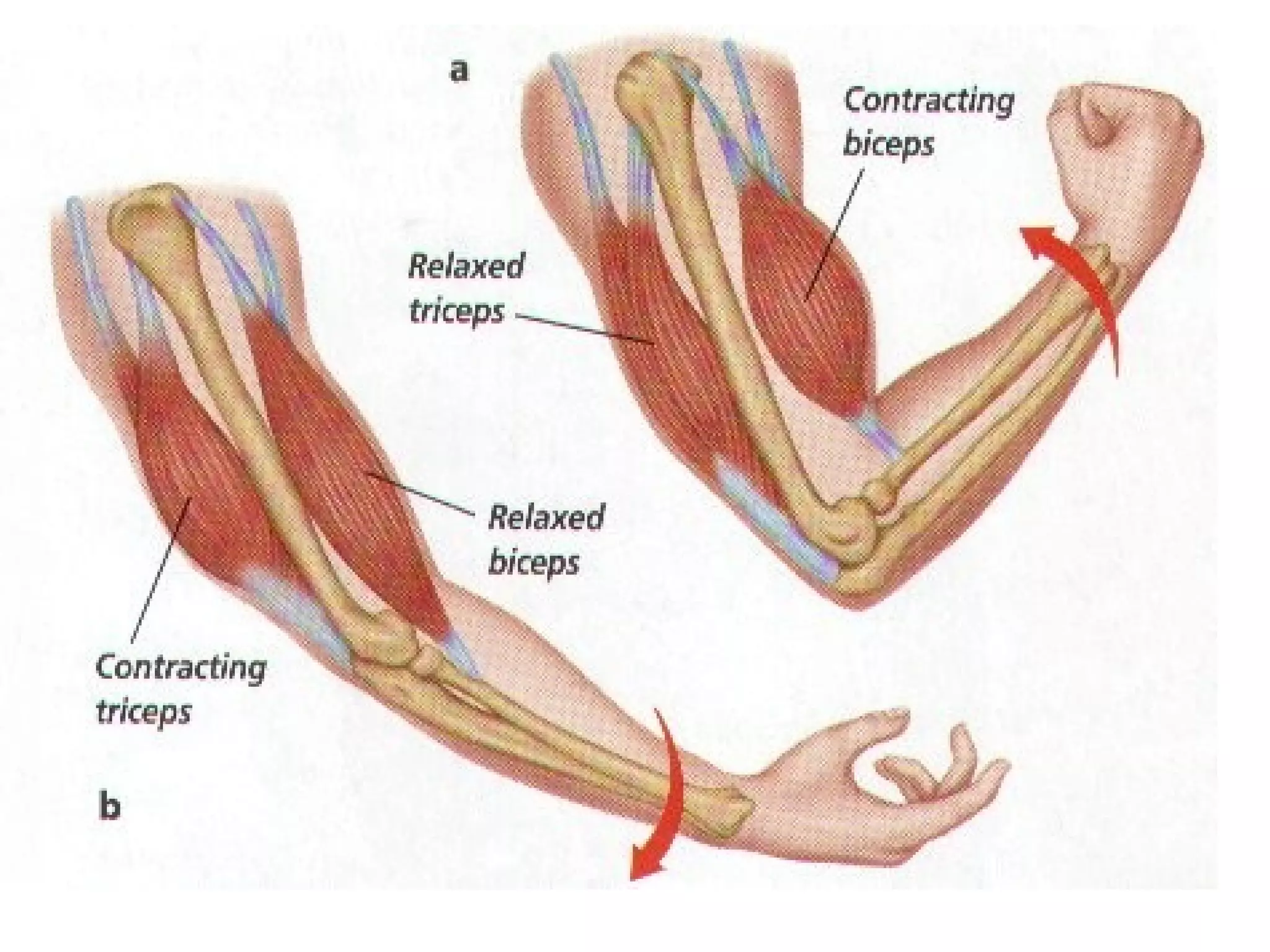
The document provides an overview of the skeletal and muscular systems. It discusses that the skeletal system includes bones, cartilage, joints, ligaments, and tendons that support, protect, and allow movement of the body. It also notes there are over 200 bones in the adult body. The document also outlines the three types of muscle tissue - skeletal, smooth, and cardiac - and their different functions. In summary, the document provides a high-level introduction to the key components and functions of the skeletal and muscular systems.