Embed presentation
Downloaded 75 times

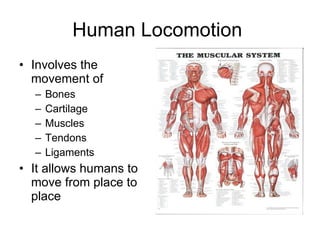
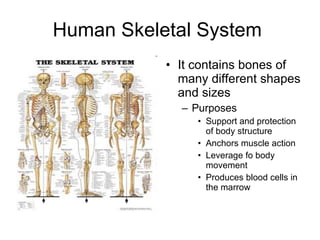
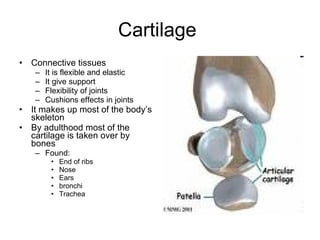
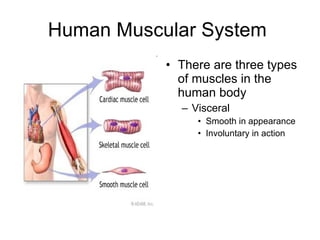
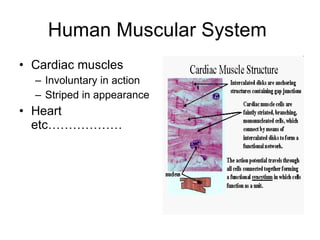
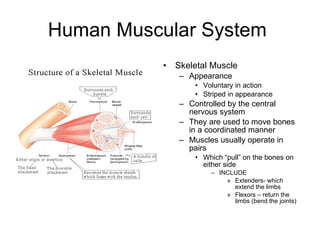
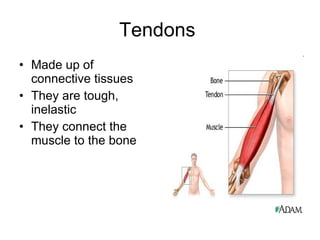
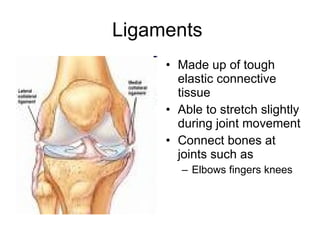

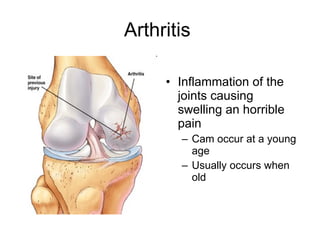
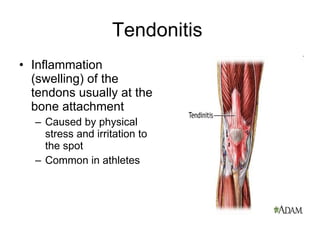
Human locomotion involves the movement of bones, cartilage, muscles, tendons, and ligaments to allow humans to move from place to place. The skeletal system contains bones of different shapes and sizes that provide support, protection, and leverage for movement. Cartilage gives joints flexibility and cushioning, and is found at the ends of ribs, nose, ears, and other areas. The muscular system contains three types of muscles - visceral, cardiac, and skeletal - which work with tendons and ligaments to control bone movement and provide structural support at joints. Common problems affecting the locomotive system include arthritis and tendonitis.











