Embed presentation
Downloaded 144 times







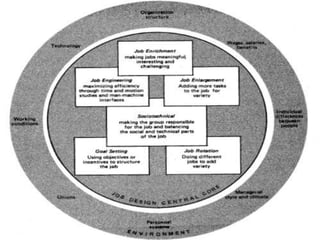


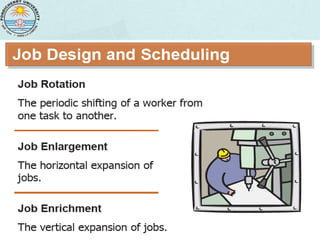














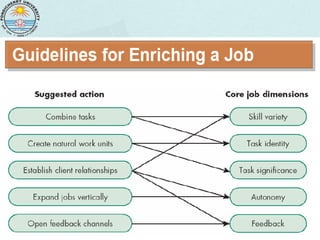









Job redesign refers to changes made to jobs to improve quality or productivity and can include job rotation, enlargement, or enrichment. Effective job redesign focuses on increasing skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback for workers by forming work units, establishing relationships, combining tasks, loading work vertically, and opening feedback channels.


































