1. The document is a student project report on job analysis, design, and evaluation submitted to their professor.
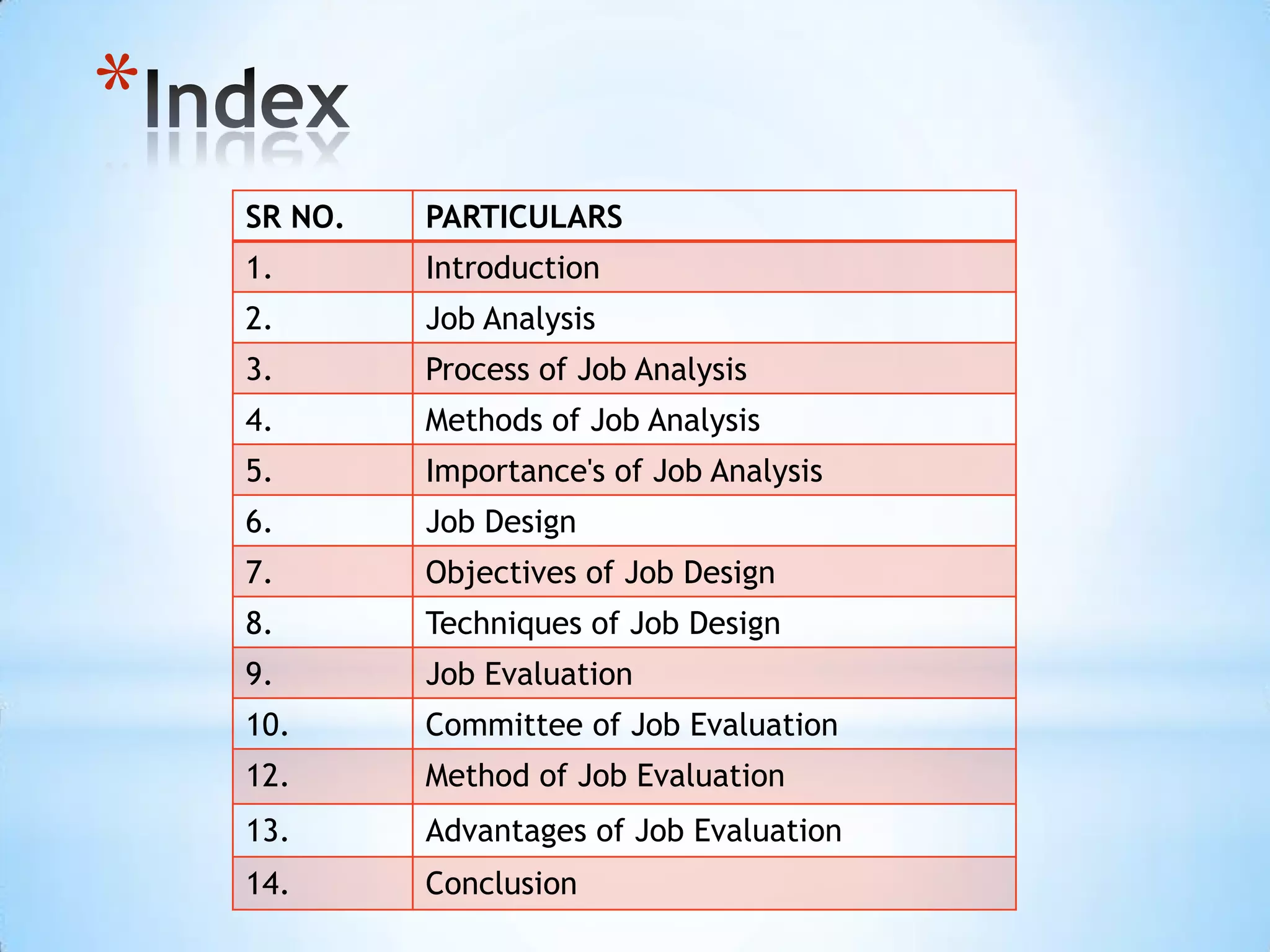
2. It includes an introduction, sections on job analysis, job design, job evaluation, and a conclusion.
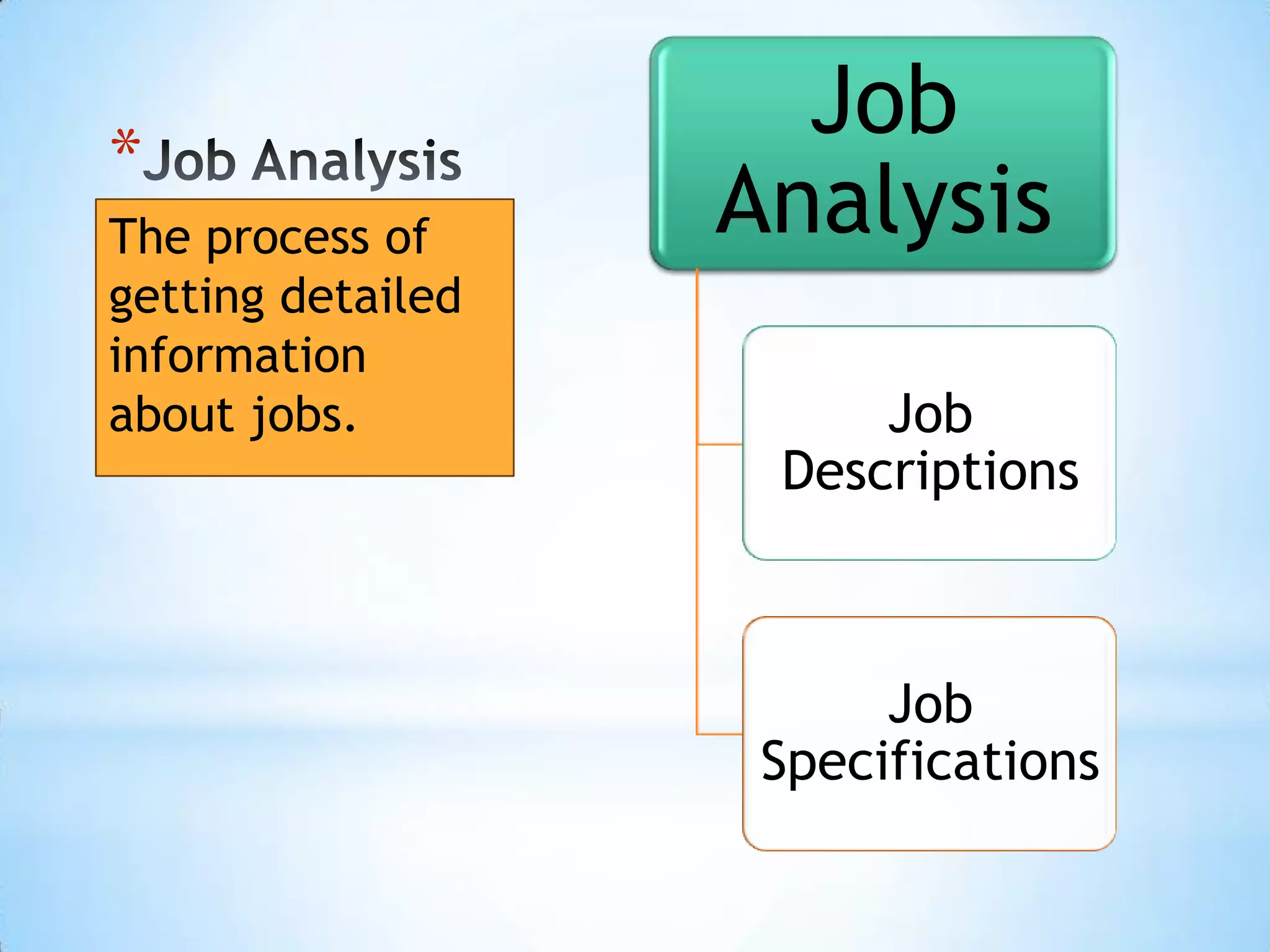
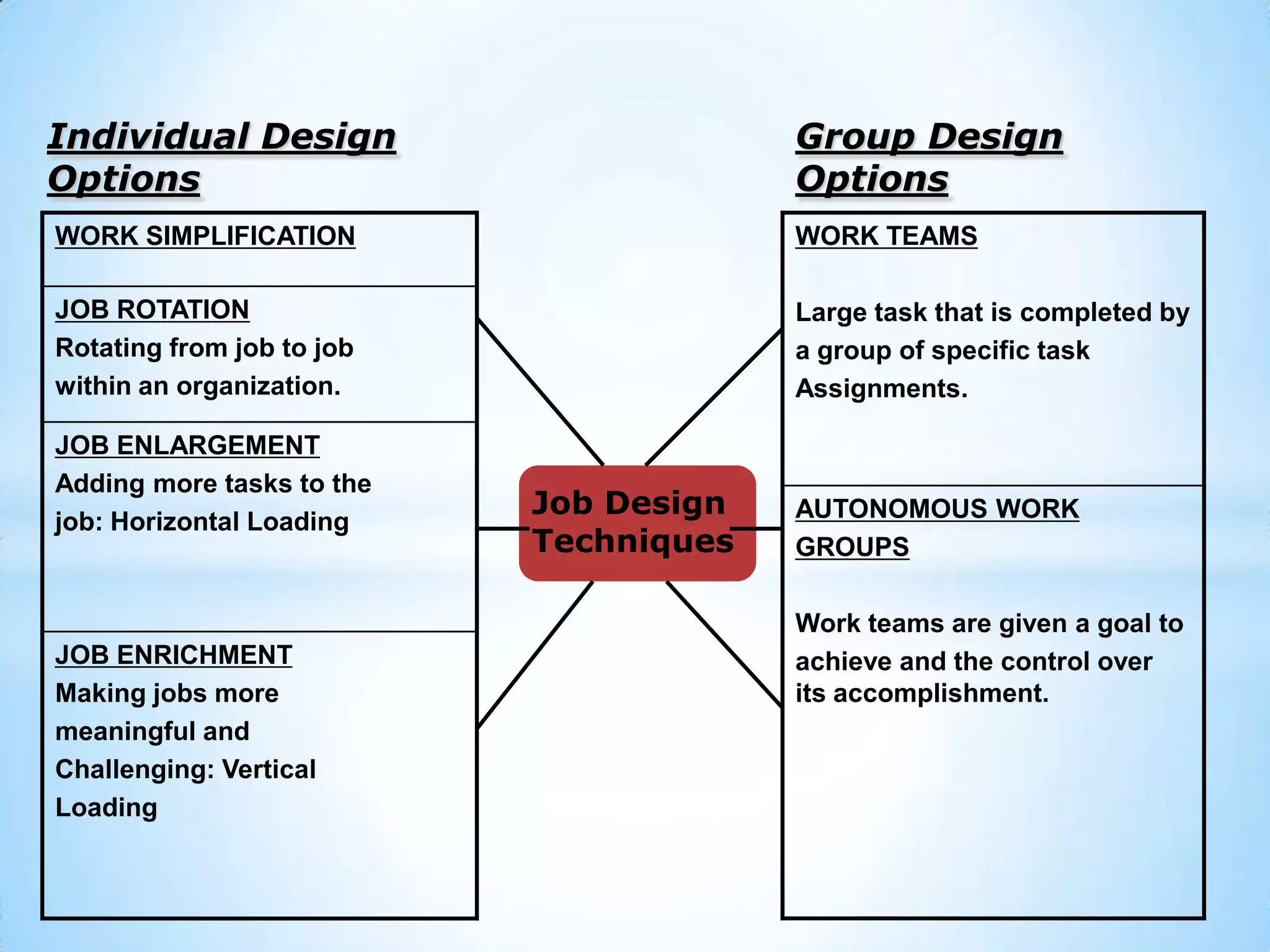
3. Job analysis involves studying job duties and responsibilities, job design organizes tasks to achieve objectives, and job evaluation determines the relative worth of jobs.