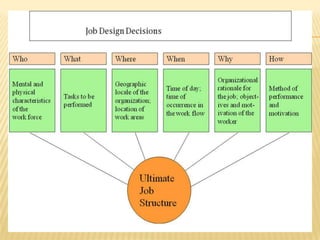
Job design involves organizing job tasks, duties, and responsibilities to achieve objectives like productivity and job satisfaction. It addresses what motivates people, significant job characteristics, identifying alternatives, and implementing changes. The goals of job design are high job satisfaction and performance. Elements include task, worker, and environmental analysis. Techniques include job simplification, specialization, enlargement, enrichment, and rotation. Outcomes include performance, safety, learning, and work-life balance.