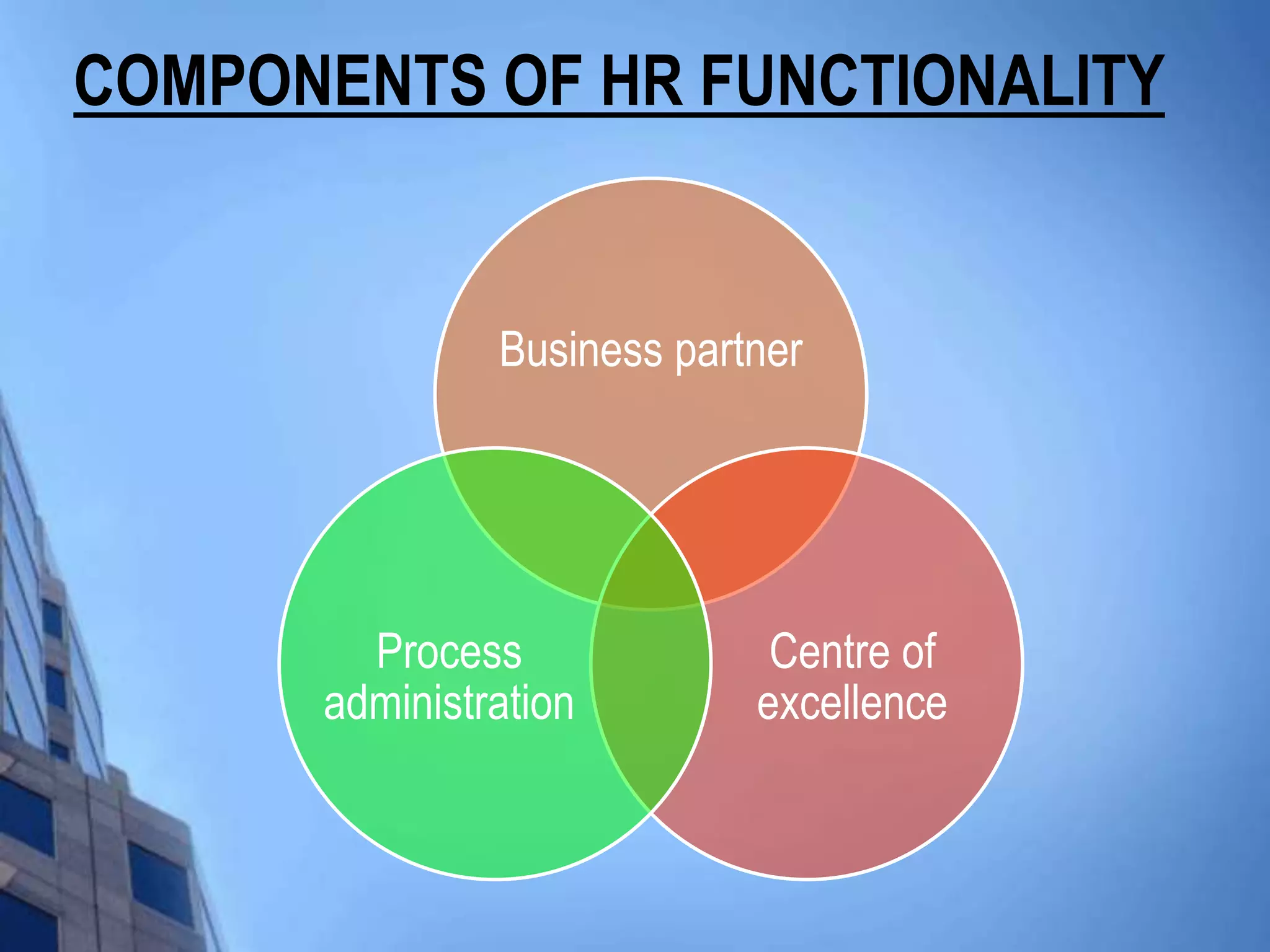
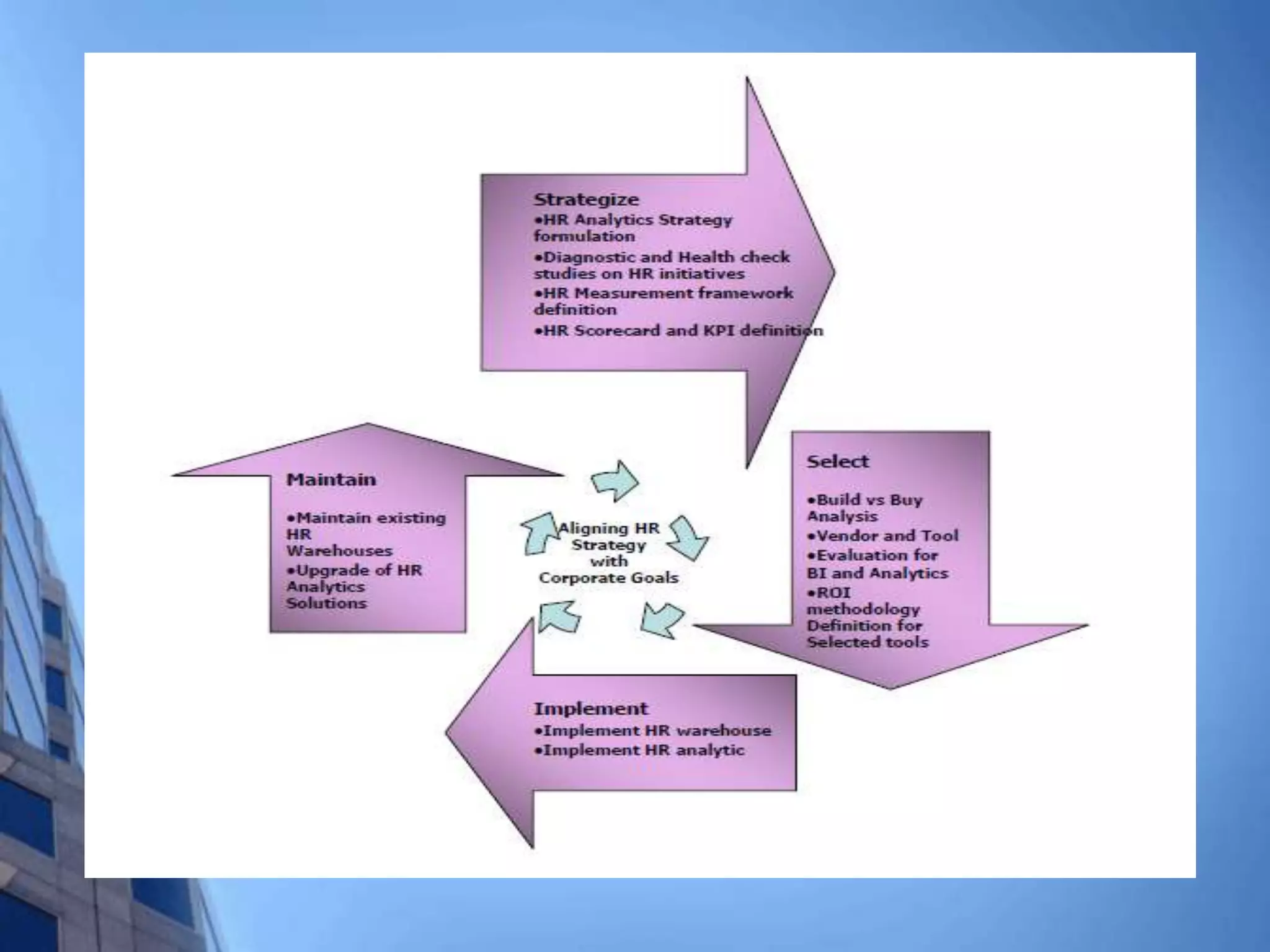
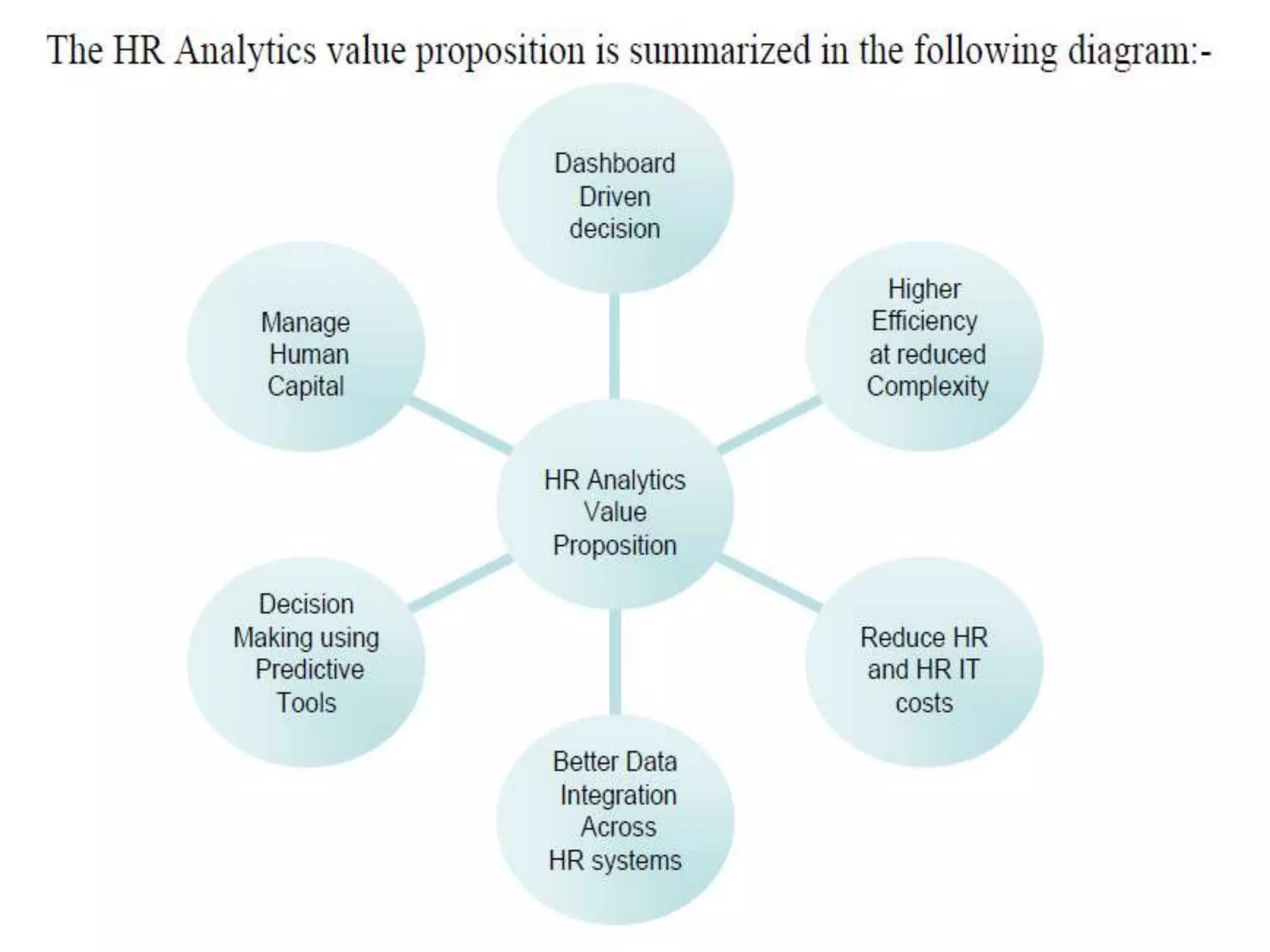
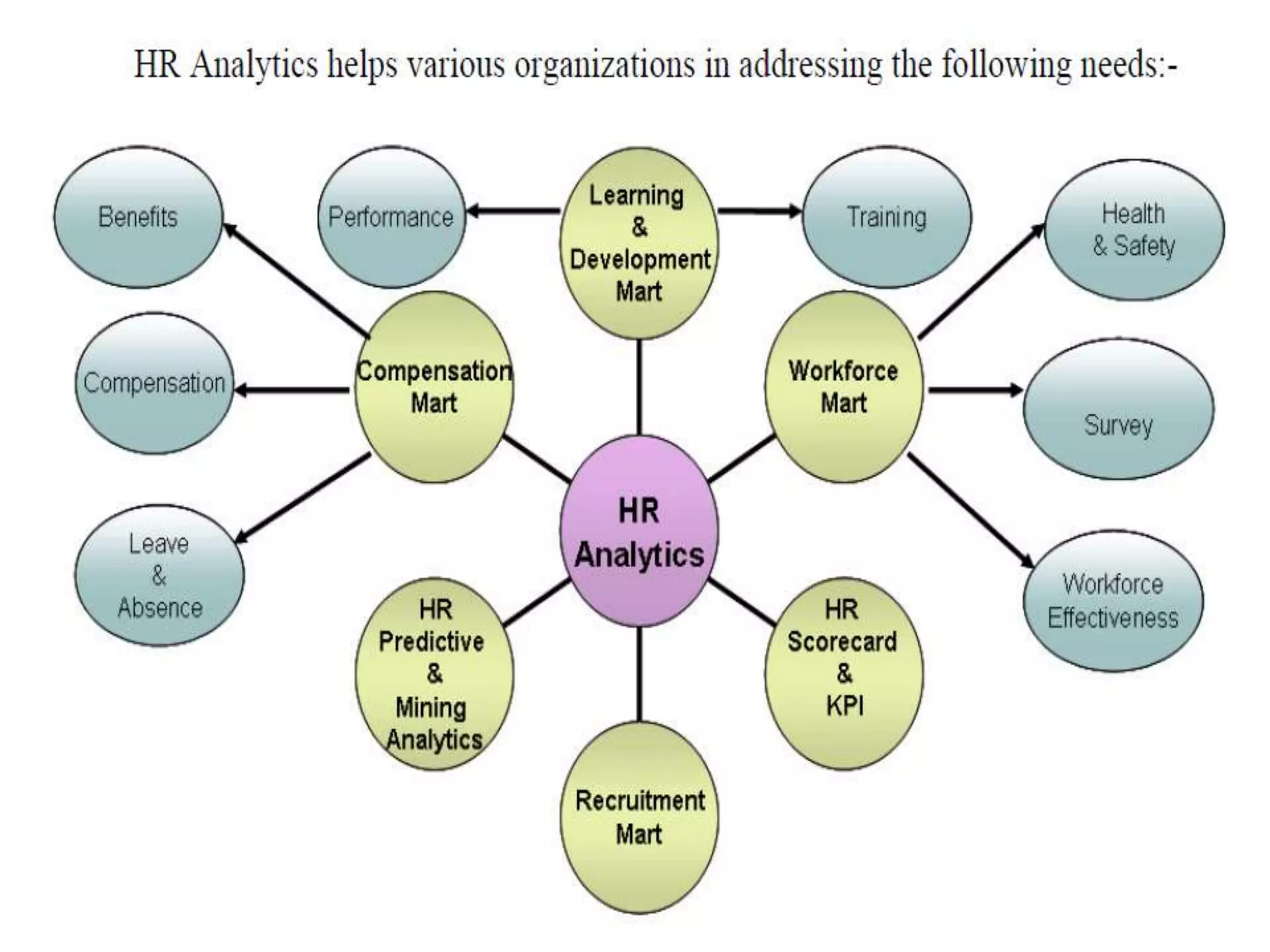
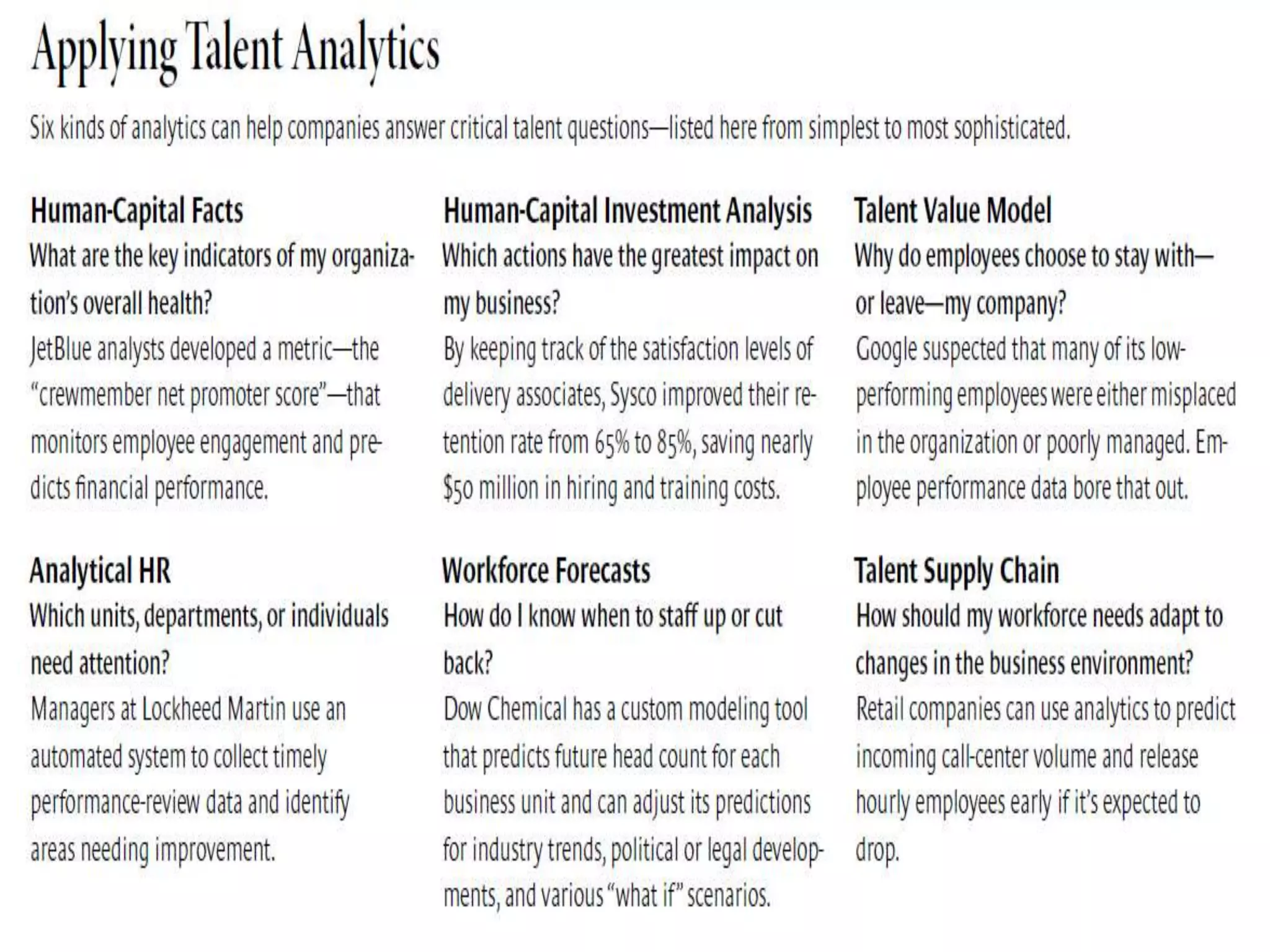
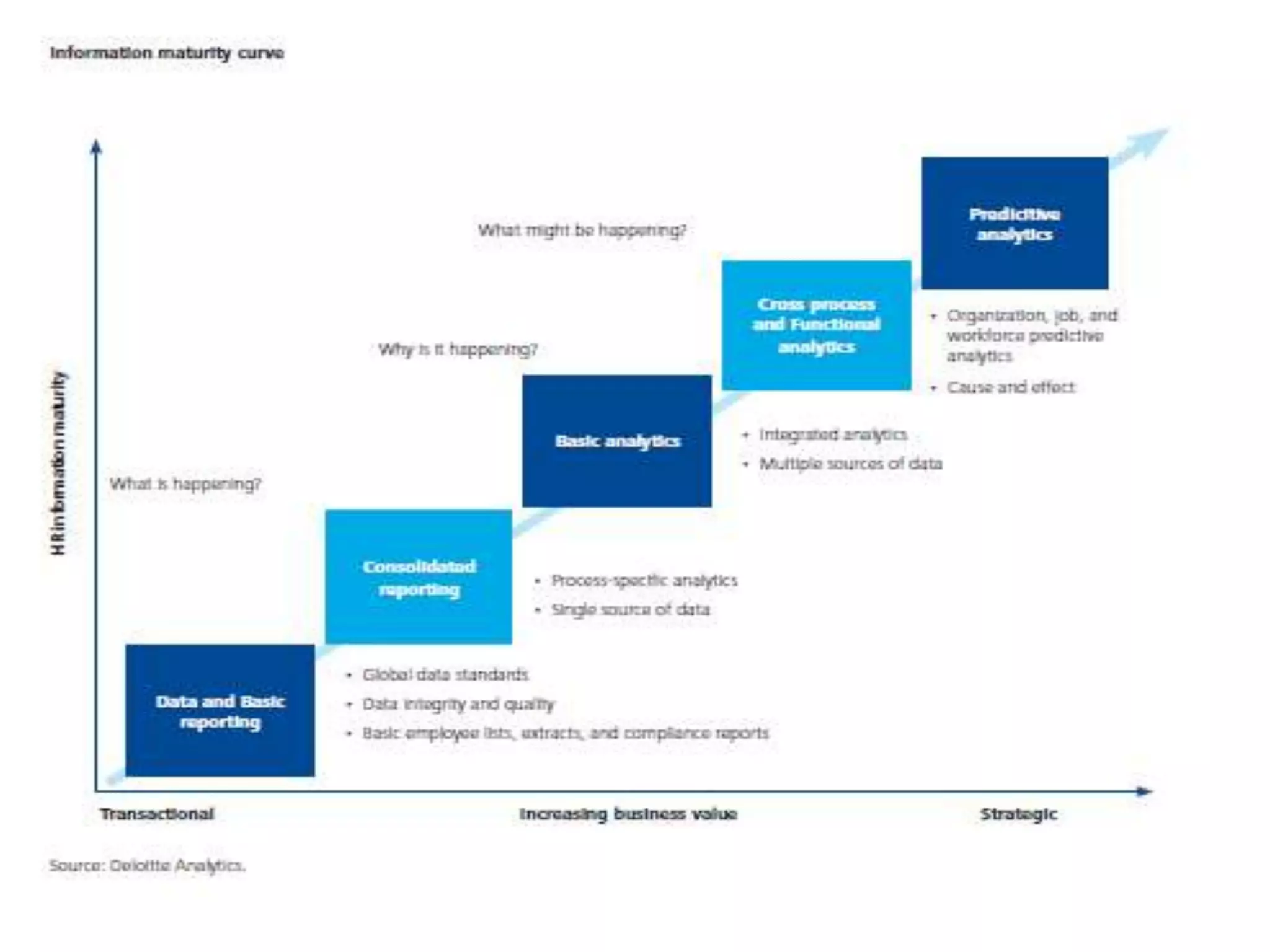
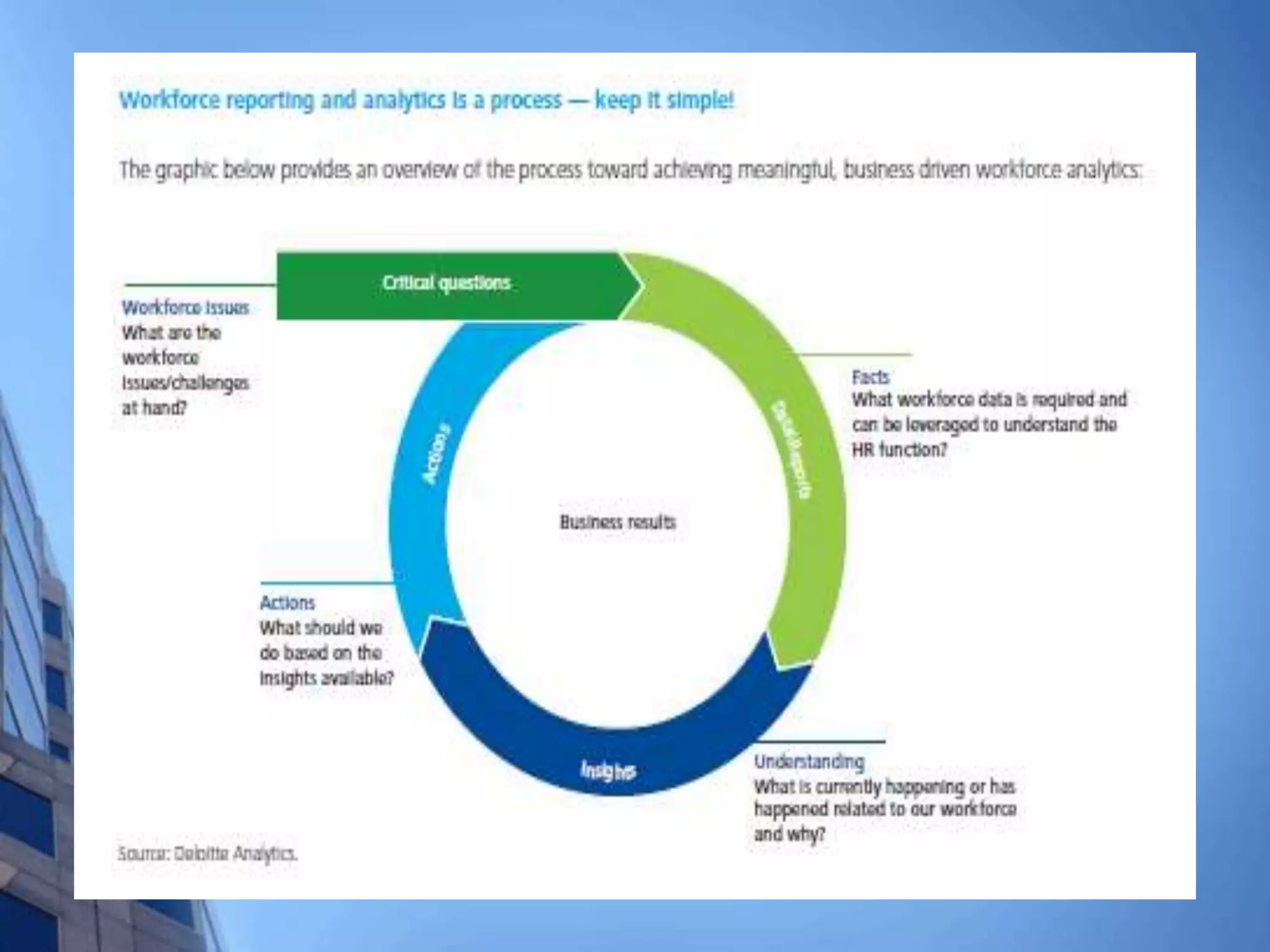
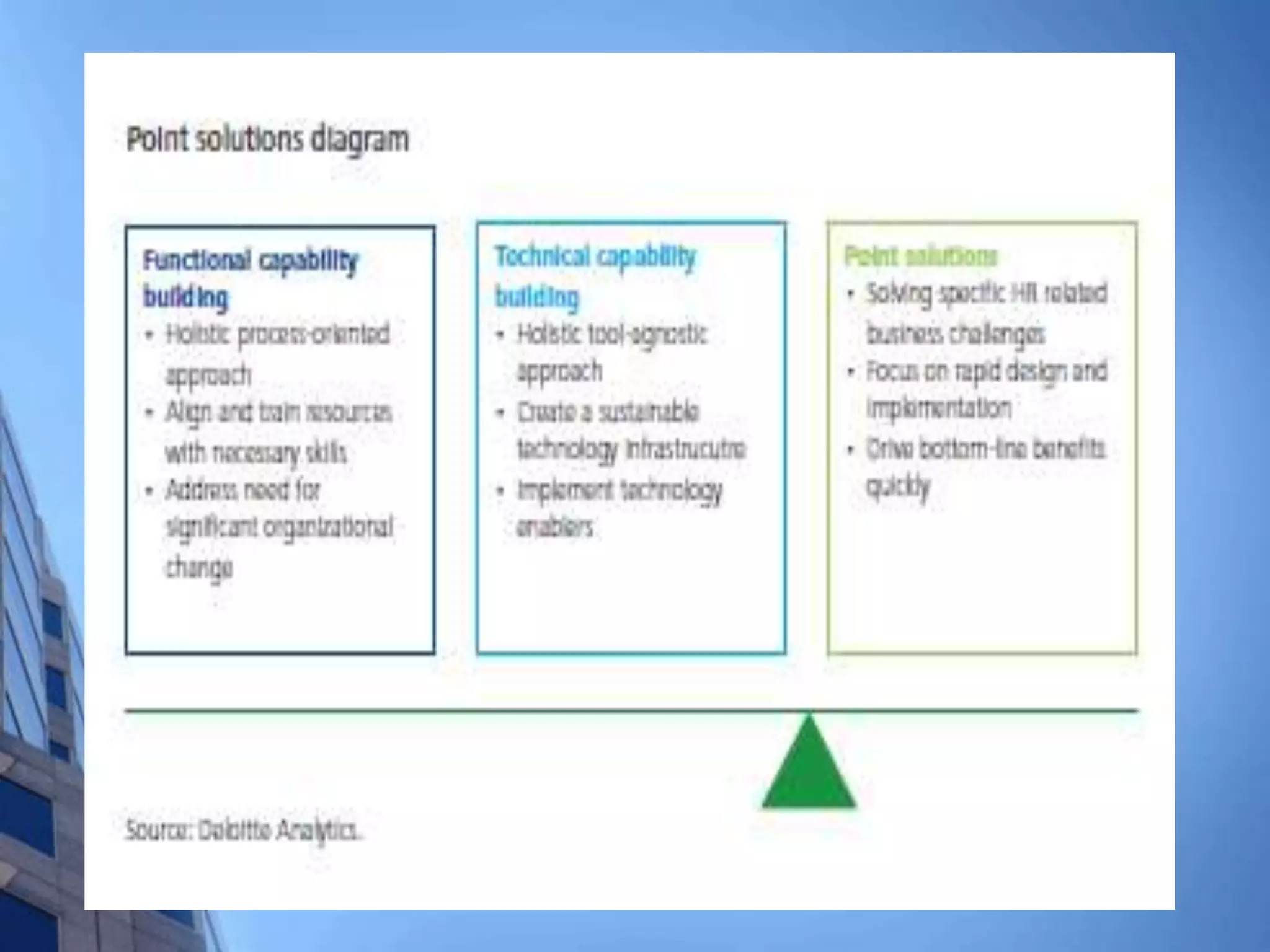
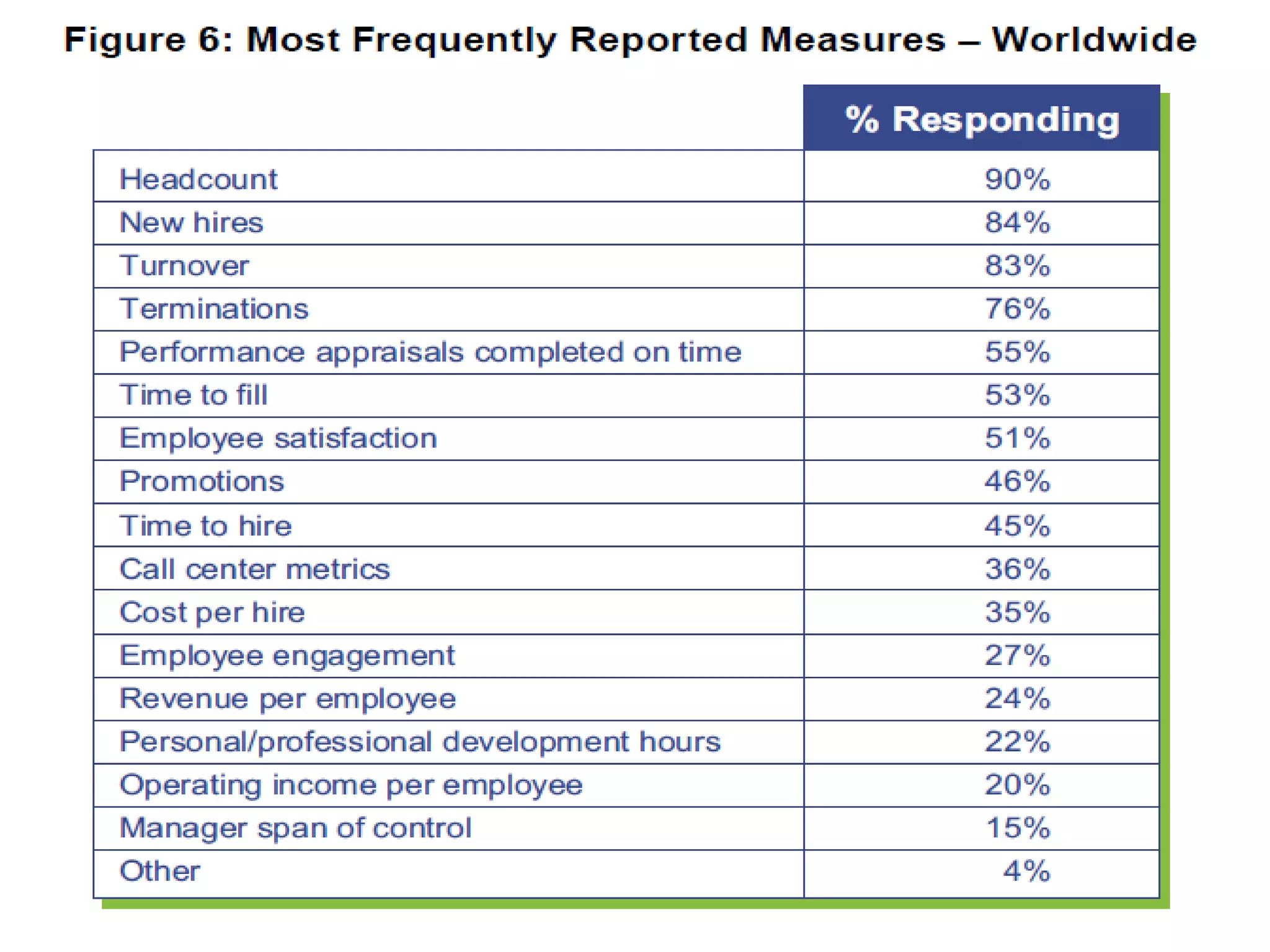
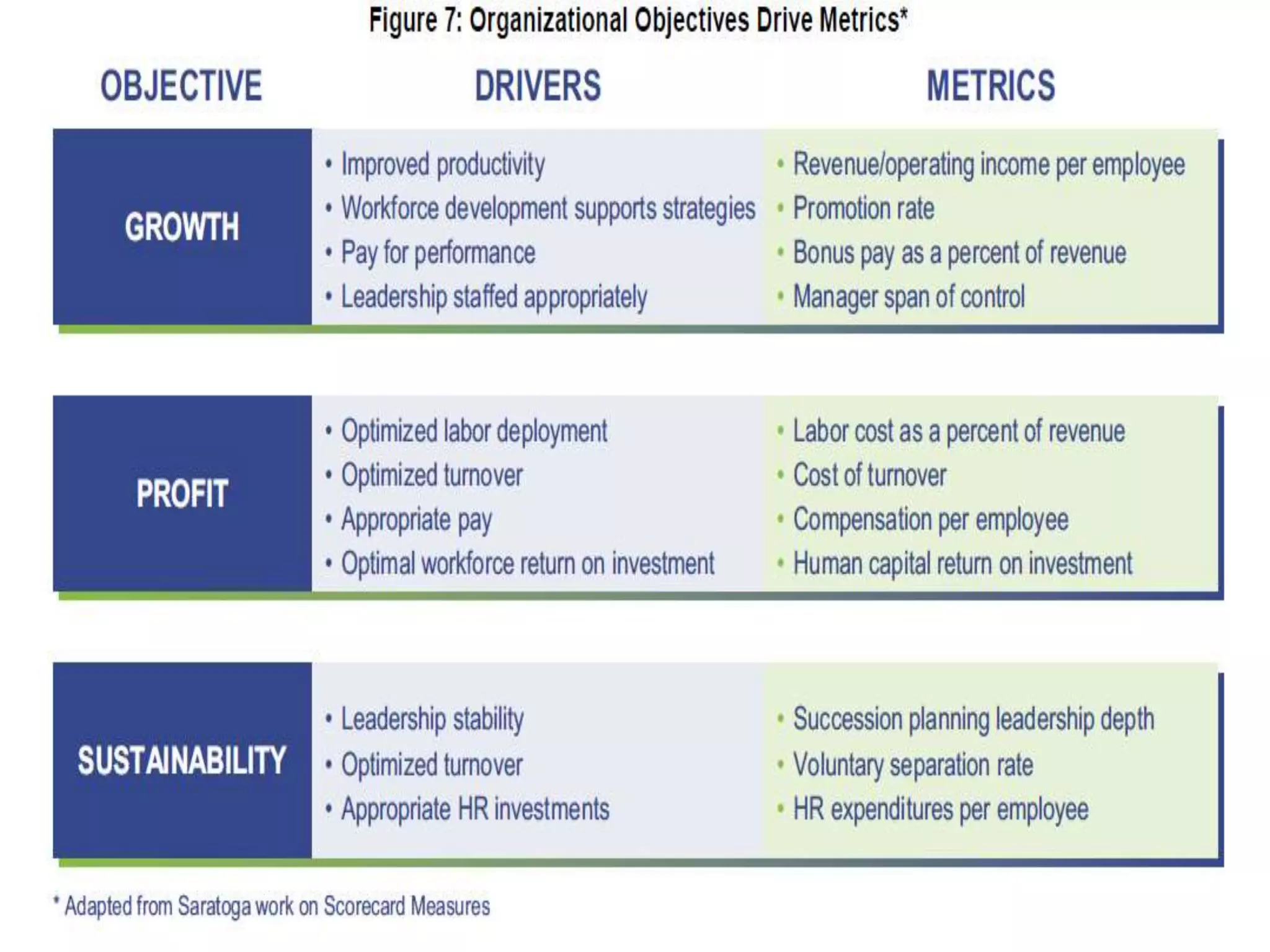
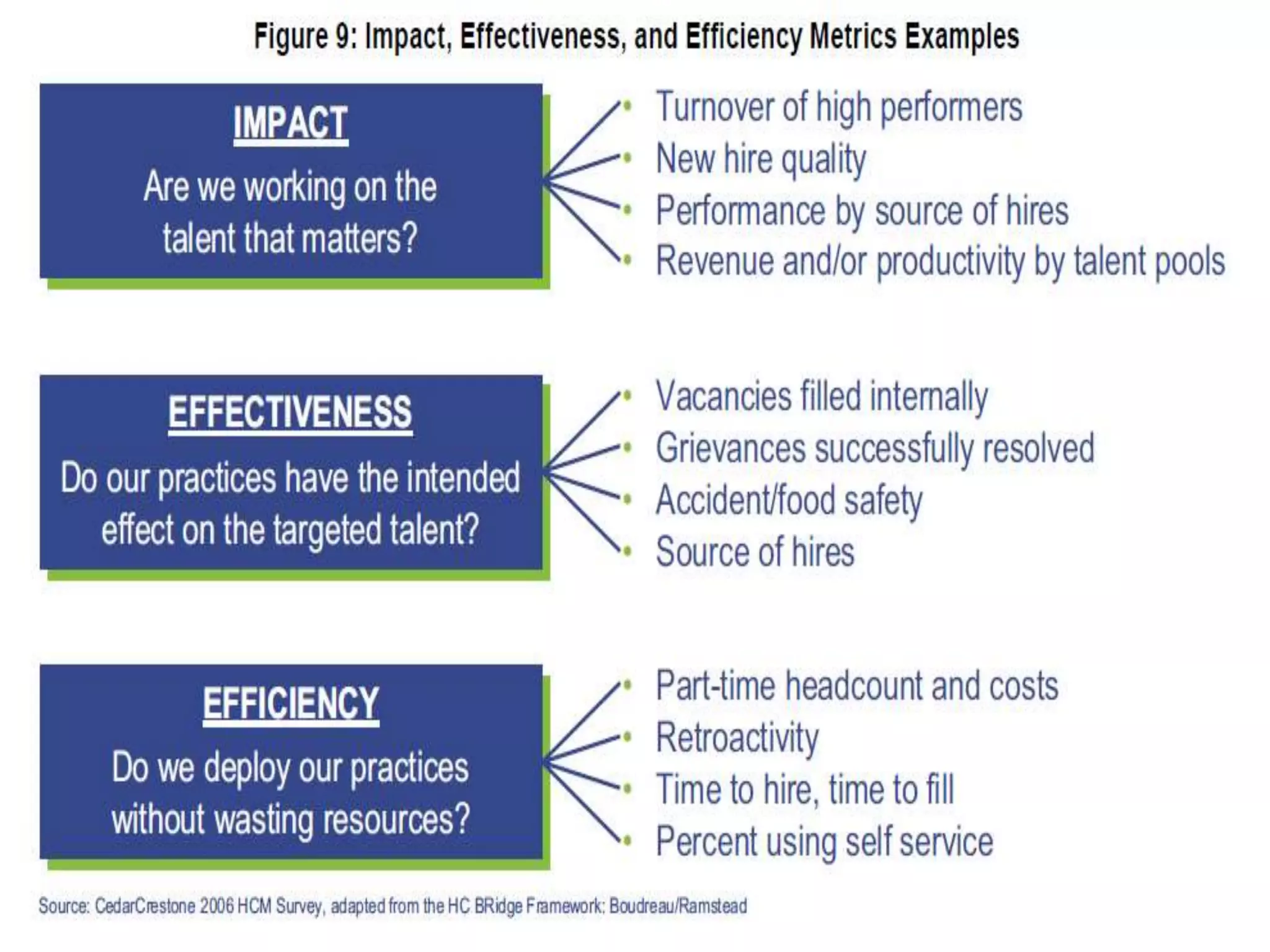
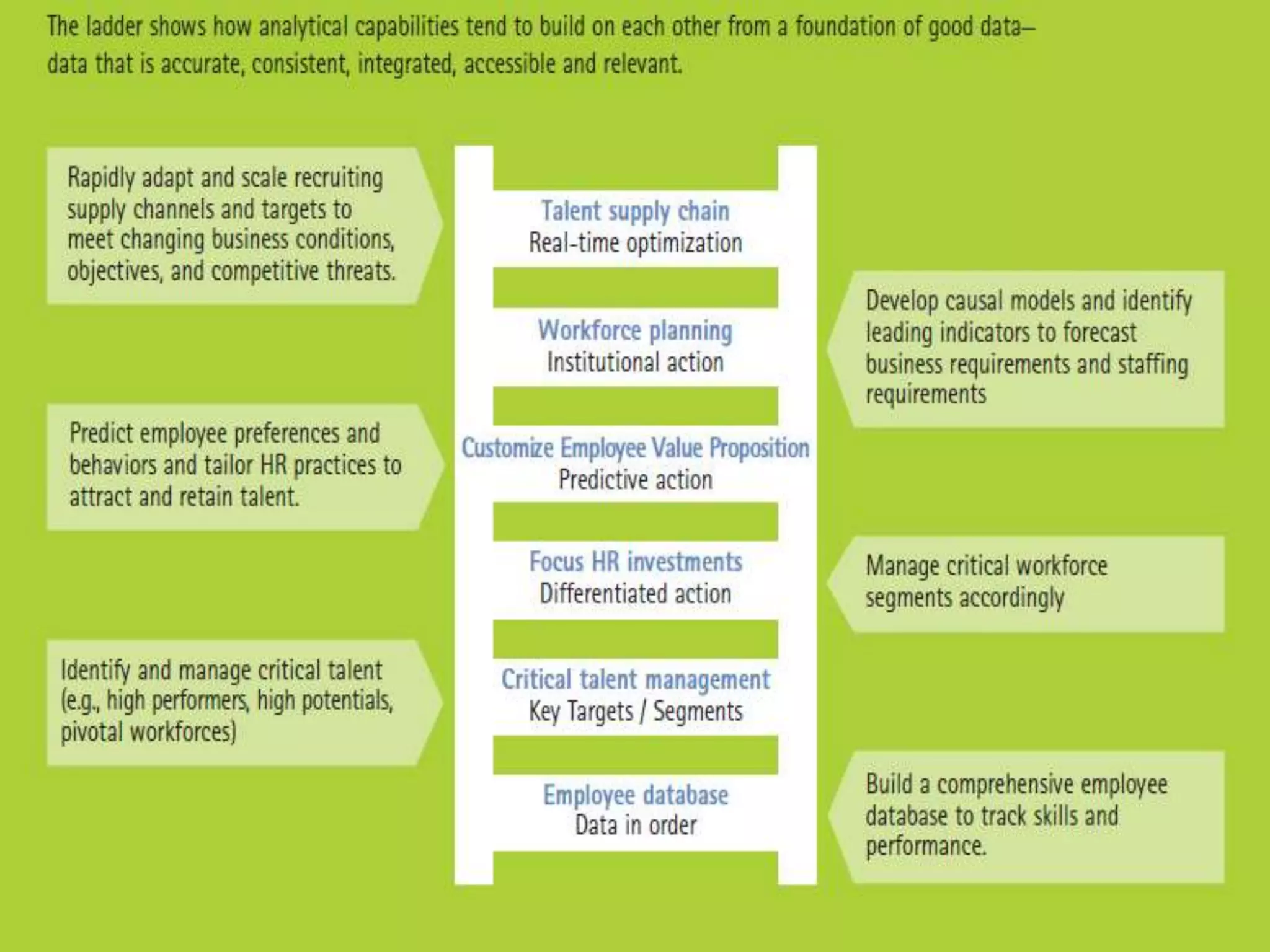
This document discusses HR analytics and workforce analytics. It provides an overview of the history and current state of HR analytics. Some key uses of HR analytics include problem solving, decision making, and improving HR process efficiency. The document outlines various HR activities that can be analyzed, such as reporting, benchmarking, and predictive analysis. It emphasizes that HR analytics should focus on relevant metrics and provide context to be most useful. Overall, the document promotes the use of workforce analytics to gain insights that can provide competitive advantages and more effective organizational functioning.