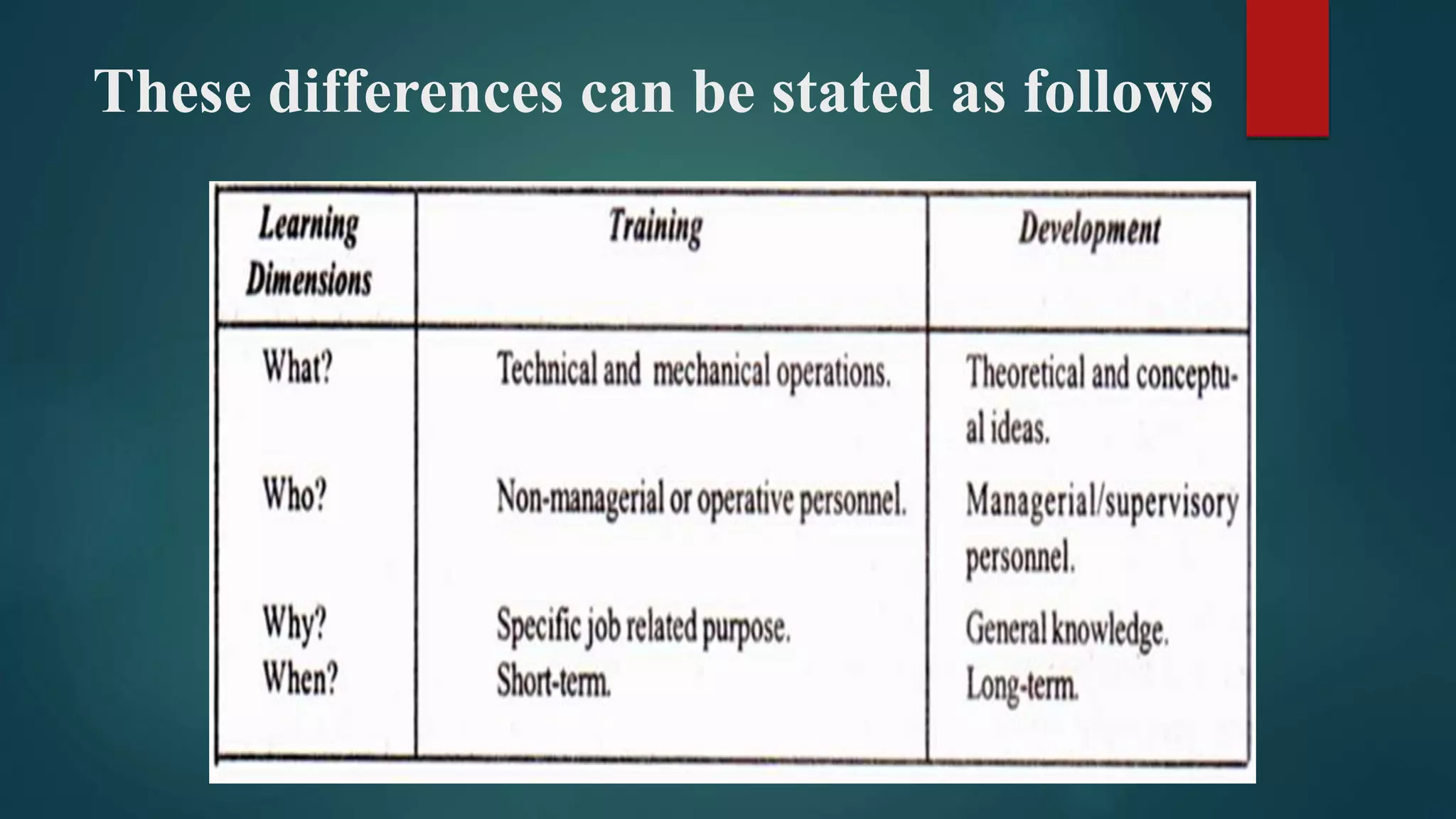
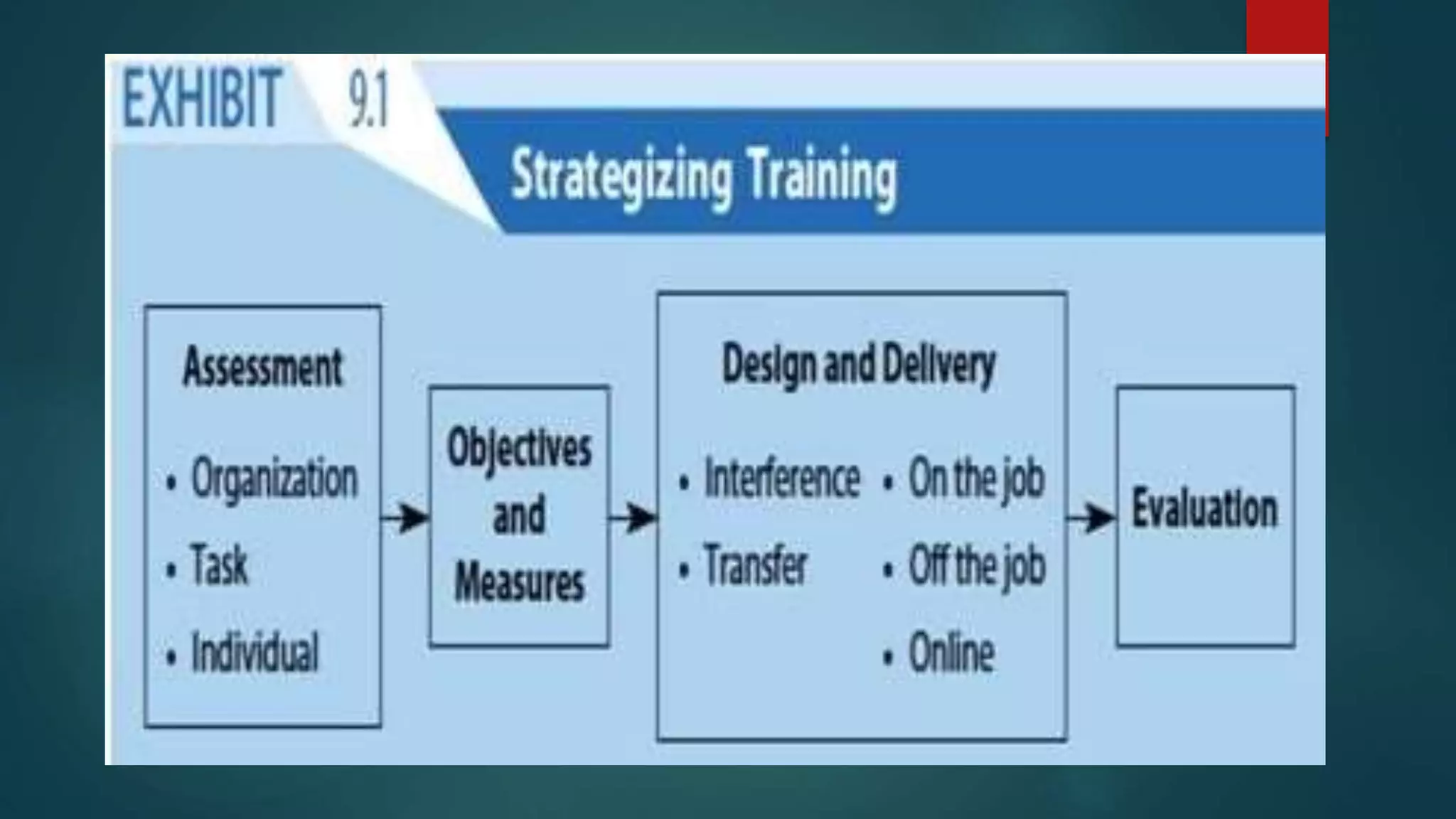
The document discusses the concepts of training and development, defining training as the process of enhancing employees' skills for their specific jobs, while development encompasses broader personal growth. It highlights the importance of training and development in improving organizational performance, employee morale, and adaptability to change, while also addressing various methods and challenges associated with these processes. Additionally, it contrasts on-the-job and off-the-job training methods, emphasizing the significance of effective training strategies for both individuals and organizations.