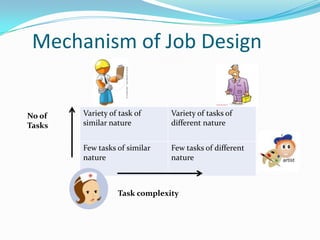
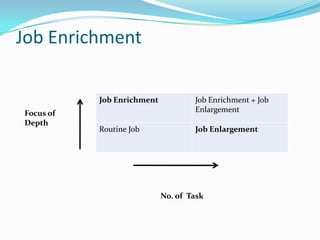
Job design integrates work content, rewards, and qualifications to meet employee and organizational needs. It includes traditional scientific management approaches as well as motivational design using core job characteristics like skill variety and autonomy. Mechanisms of job design include job simplification, rotation, enlargement, and enrichment. Job enrichment focuses on depth while enlargement adds tasks. Employee empowerment gives means, ability and authority through approaches like allowing more control. Quality of work life programs aim to satisfy personal needs through flexibility, autonomous work groups, and participation to increase job involvement, competence, and satisfaction.