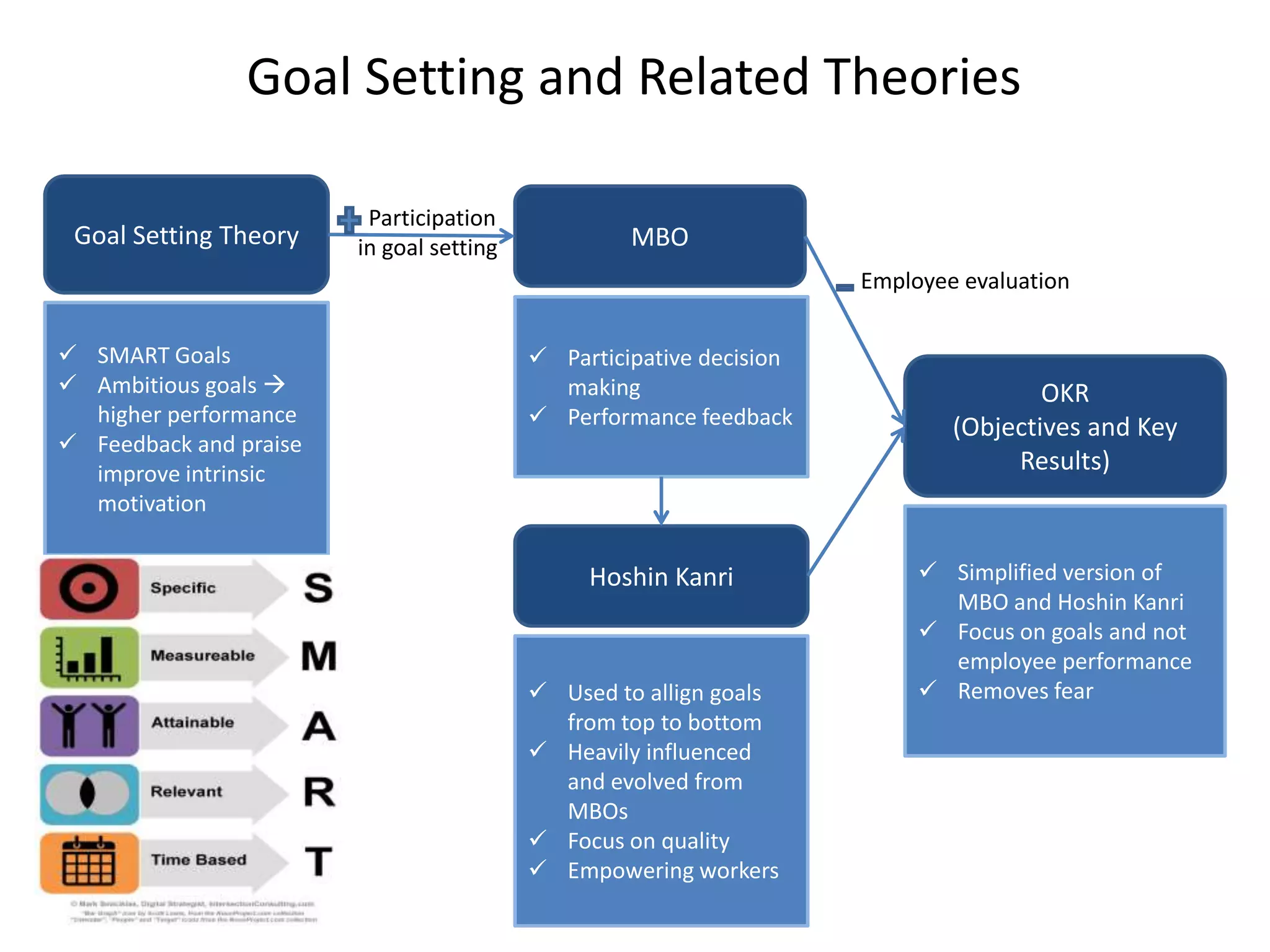
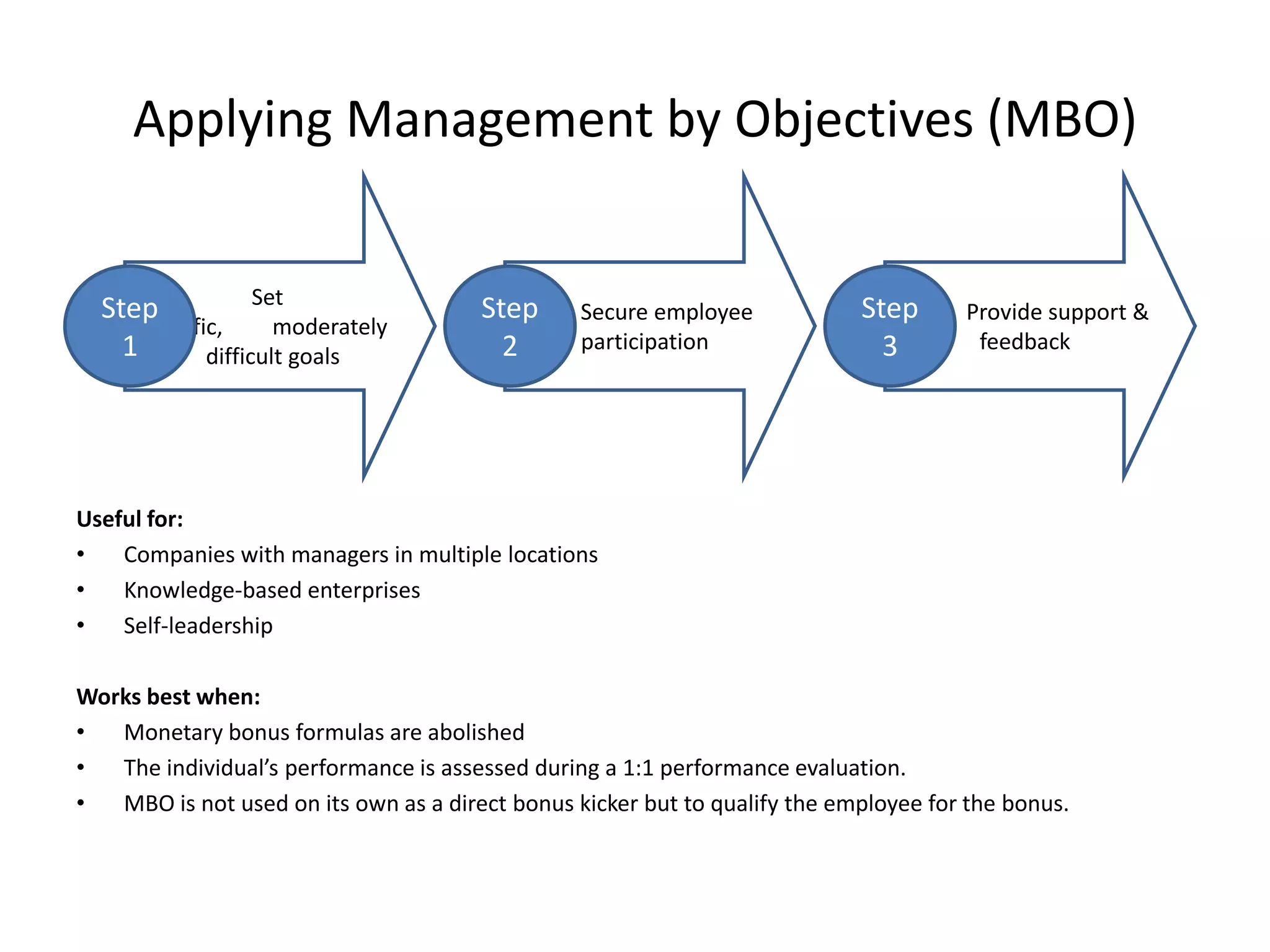
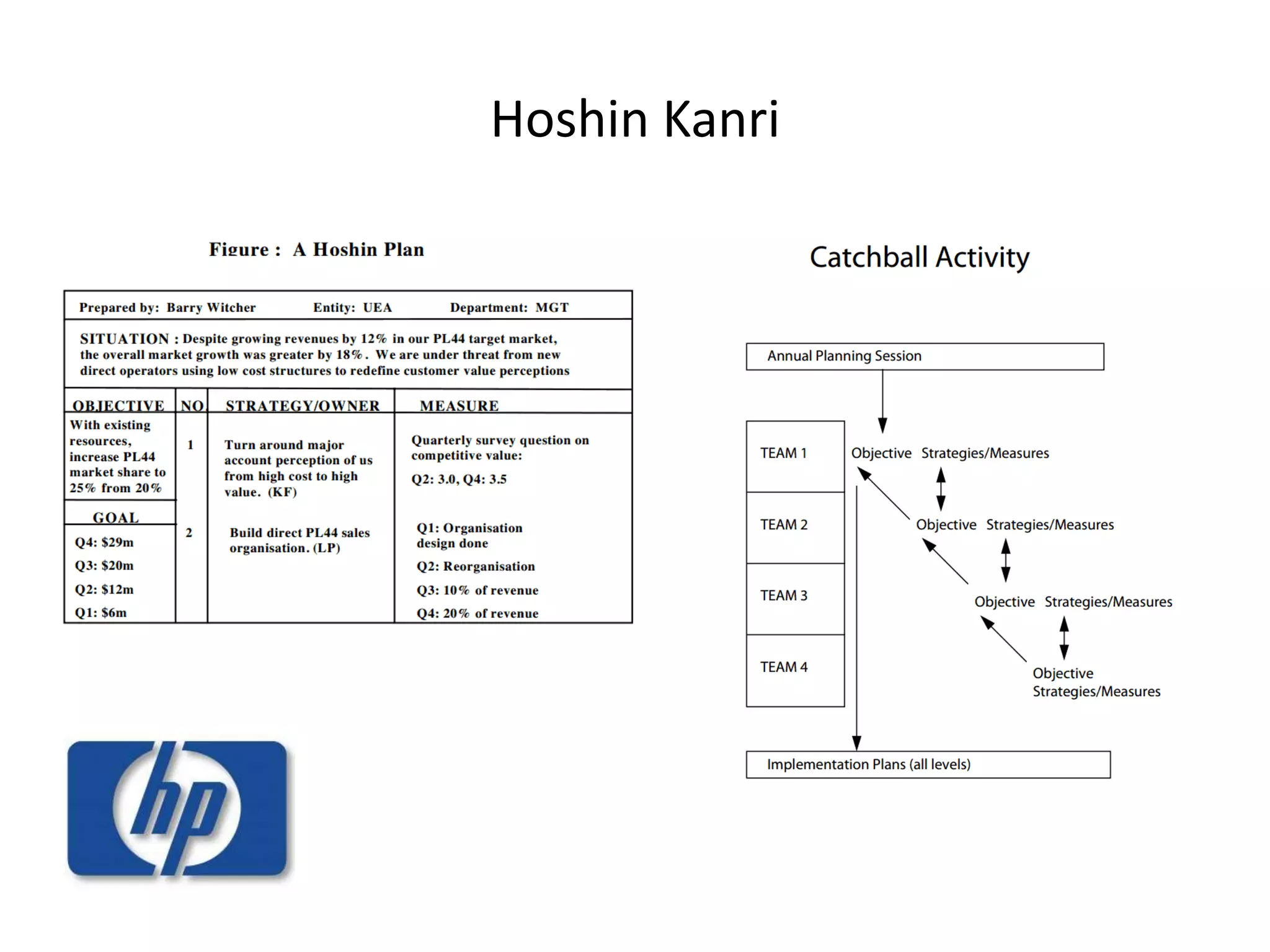
This document discusses different goal setting and management theories including Management by Objectives (MBO), Hoshin Kanri, and Objectives and Key Results (OKRs). MBO involves setting specific, measurable goals and evaluating employee performance against those goals. Hoshin Kanri is a more detailed version that breaks down hierarchies. OKRs focus on goals and contributions rather than performance evaluations. These theories can improve team communication, motivation, and planning when implemented properly with participation, feedback, and alignment of goals across levels of an organization. However, they also face challenges like being time-consuming and potentially creating conflicts if not applied carefully.