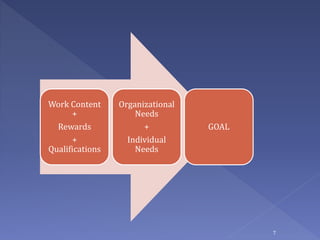
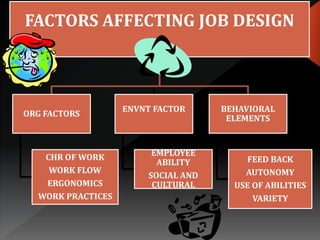
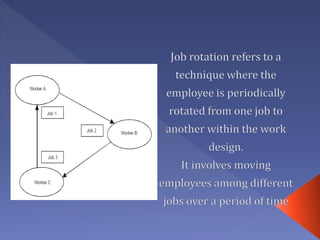
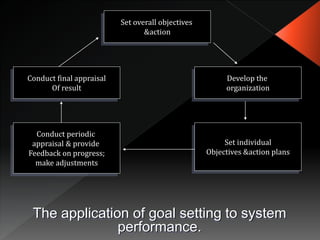
Job design is the process of outlining specific tasks, methods, and relationships within an organization to improve efficiency and employee motivation. It involves various strategies such as job rotation, job enrichment, goal setting, job sharing, telecommuting, and flextime to enhance job satisfaction and performance. Factors affecting job design include organizational needs, employee abilities, and environmental considerations.