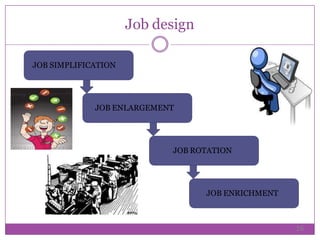
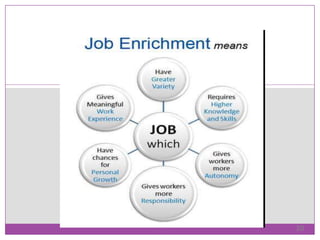
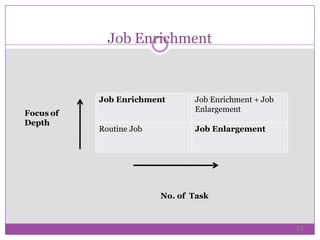
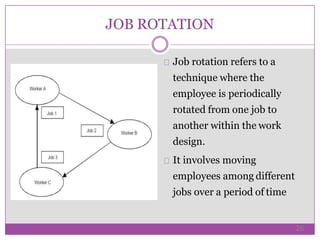
Job design, essential in human resource management, involves structuring jobs to meet technological, organizational, and employee needs. Key objectives include providing work/rest breaks, task variety, training, adjustment periods, and mental activity variation. The process of job design requires assessing current practices, analyzing tasks, designing jobs, gradual implementation, and continuous re-evaluation to enhance worker satisfaction and productivity.