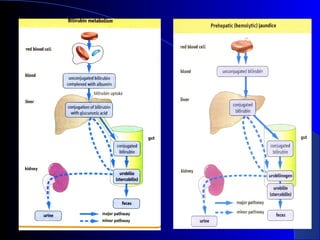
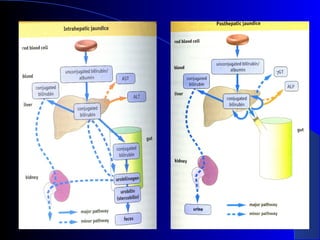
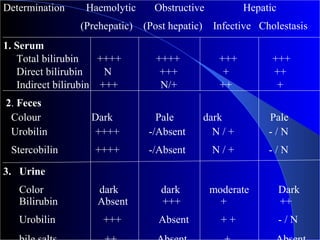
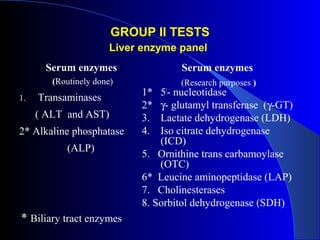
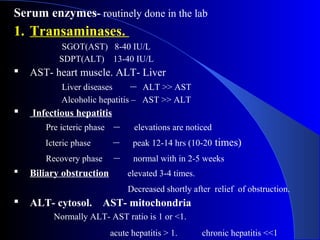
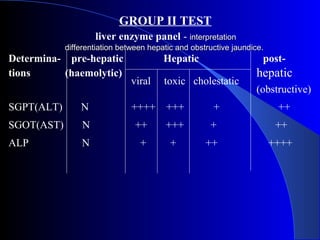
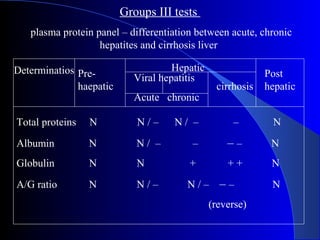
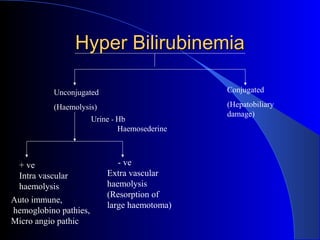
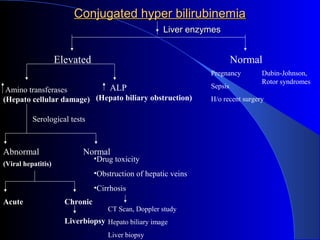
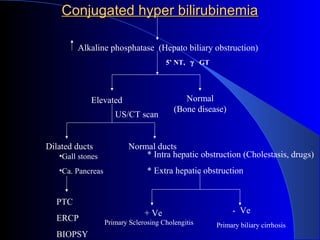
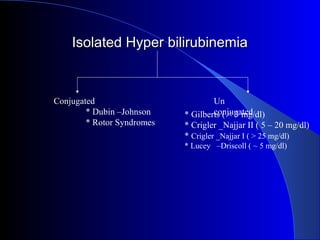
The document details laboratory investigations related to jaundice, including bilirubin production and its types, properties, and tests for bile pigments and bile salts. It outlines the classifications of jaundice, the liver enzyme panel for diagnosis, and various tests utilized to differentiate between types of jaundice. Additionally, it discusses the aspects of hyperbilirubinemia, investigation strategies, and specific conditions leading to altered bilirubin levels.