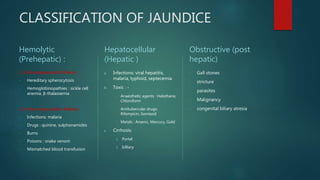
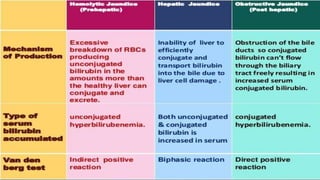
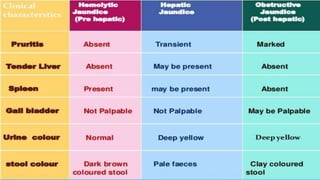
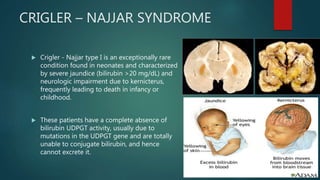
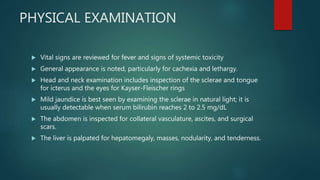
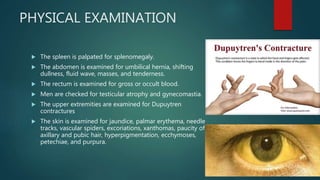
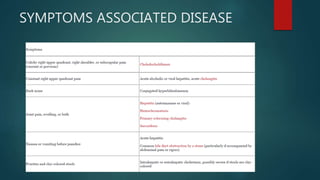
This document discusses jaundice and hyperbilirubinemia. It begins by defining jaundice as the yellowing of tissues from bilirubin deposition caused by liver disease or hemolytic disorders. It then covers bilirubin formation, metabolism, types of hyperbilirubinemia, etiologies of jaundice including prehepatic, hepatic and obstructive causes, and approaches to evaluating a patient with jaundice through history, exam, risk factors, symptoms, and investigations. Specific conditions discussed include Crigler-Najjar syndrome, Gilbert's syndrome, Dubin-Johnson syndrome, and Rotor syndrome.