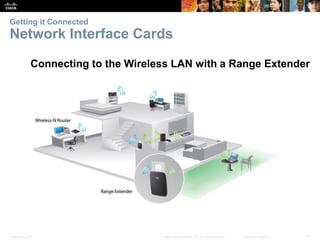
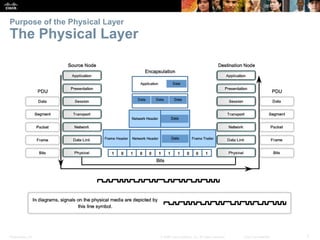
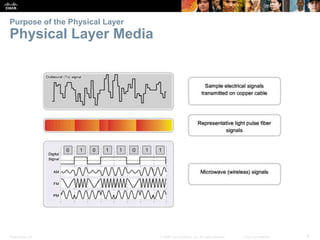
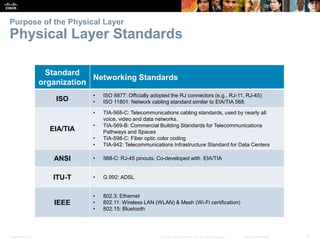
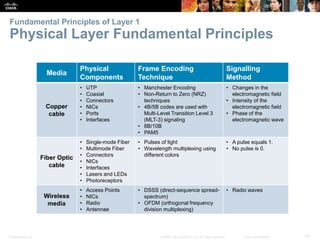
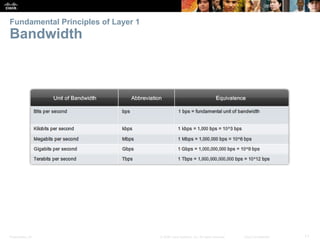
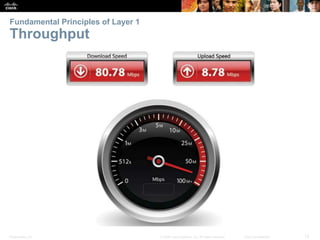
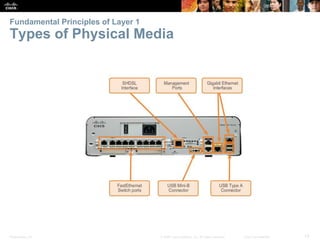
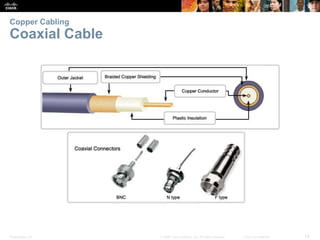
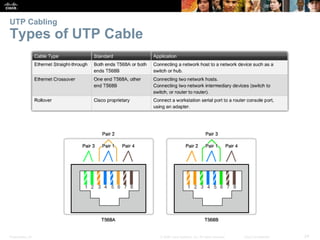
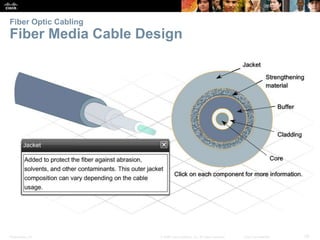
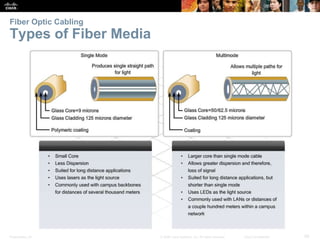
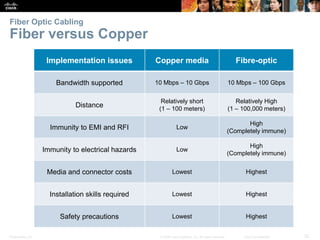
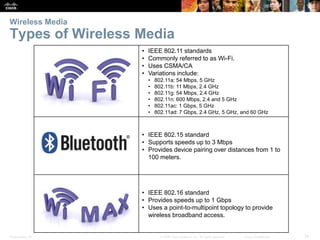
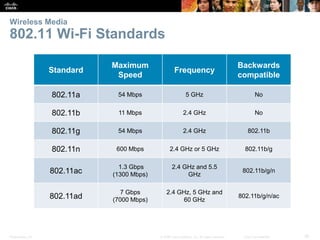
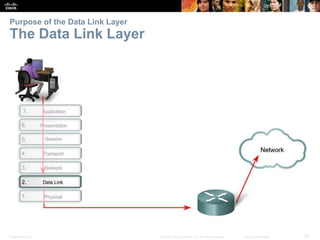
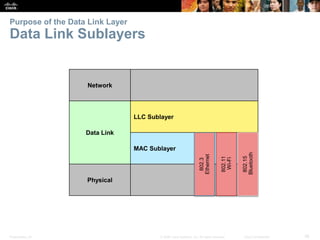
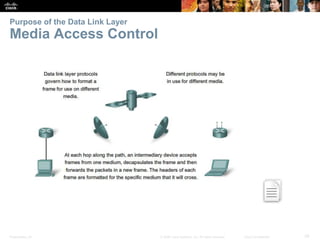
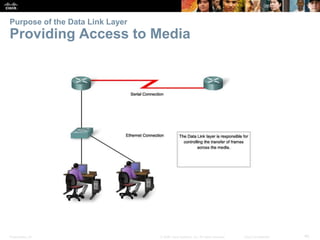
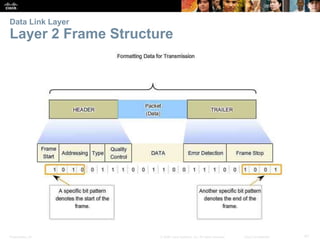
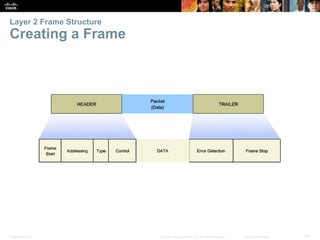
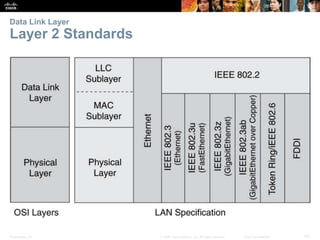
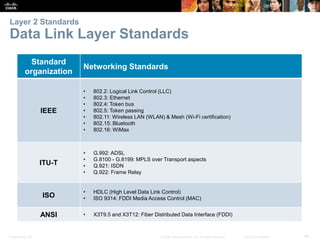
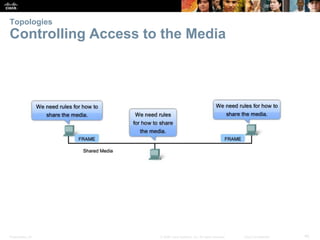
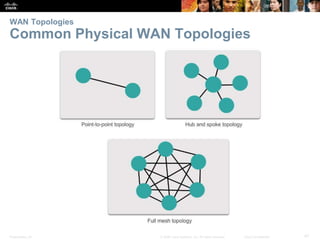
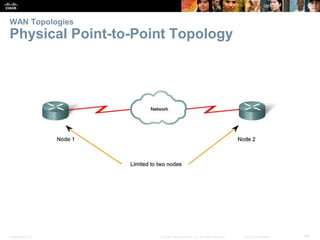
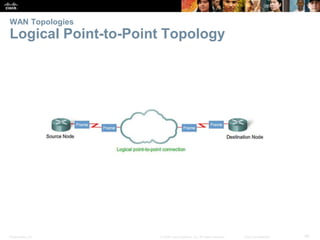
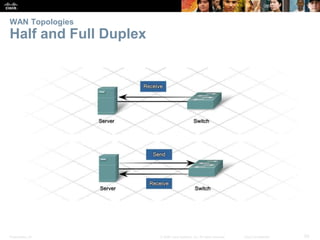
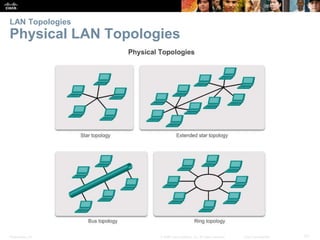
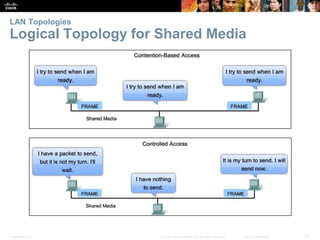
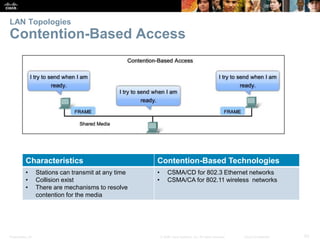
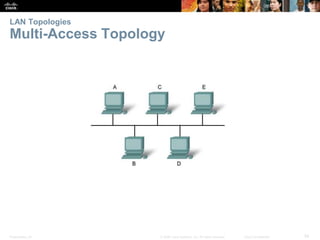
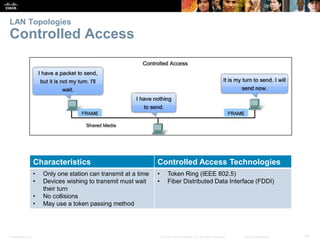
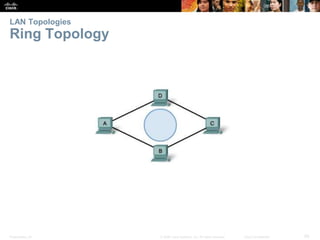
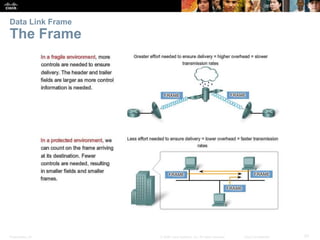
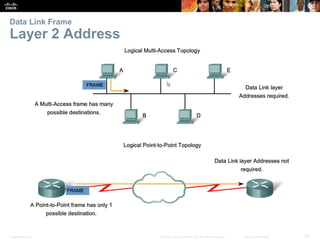
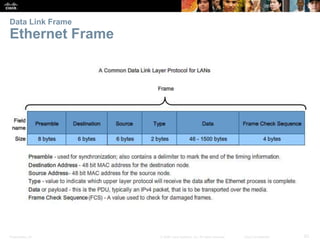
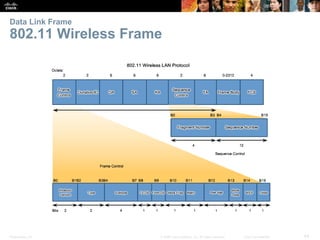
The document is a chapter from a Cisco networking textbook that covers network access and the physical and data link layers. It includes sections on physical layer protocols and network media like copper, fiber optic and wireless; data link layer protocols; and media access control techniques. The chapter aims to explain how these protocols and services support communication across networks and compares different media access control and logical topologies.