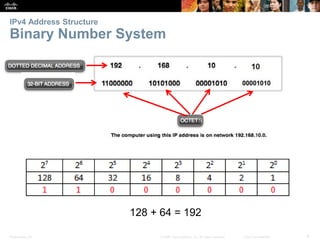
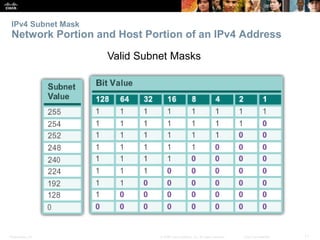
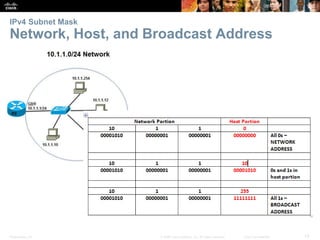
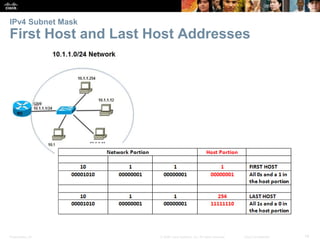
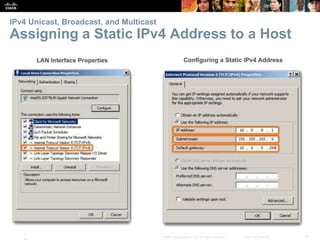
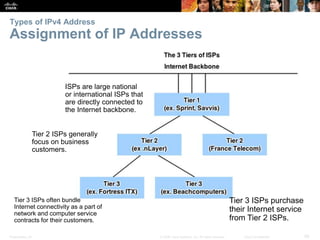
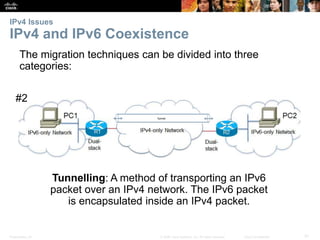
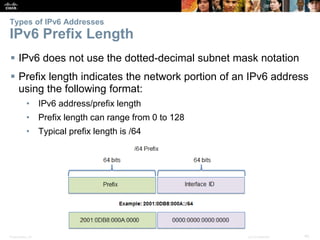
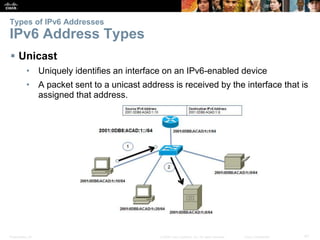
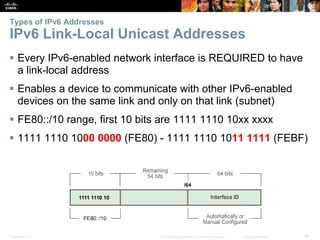
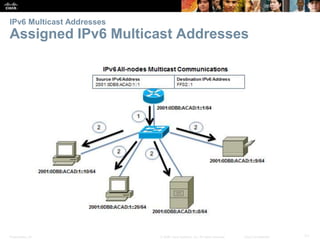
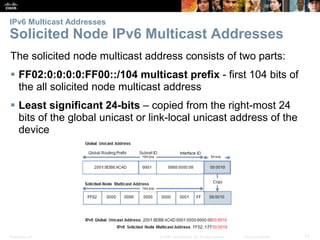
This document provides an overview of IP addressing concepts. It begins with an introduction to binary and hexadecimal numbering systems used in IP addressing. The document then covers the basics of IPv4 addressing, including address structure, subnet masks, network vs host portions of addresses, and address types. It also discusses IPv6 addressing and the need to transition to IPv6 to address limitations in IPv4. Key topics include IPv6 address formats and types of IPv6 unicast addresses.