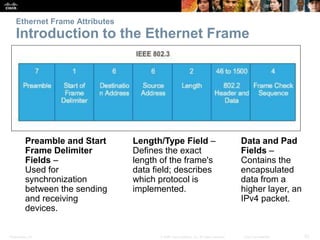
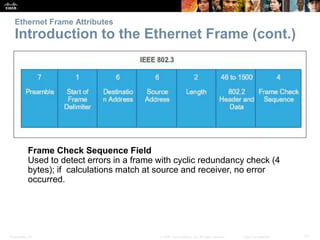
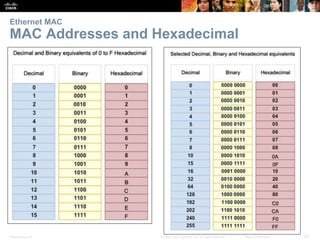
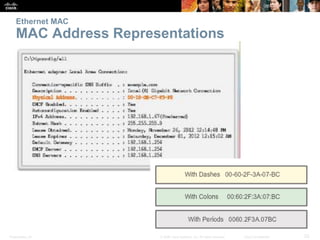
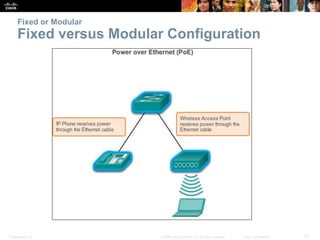
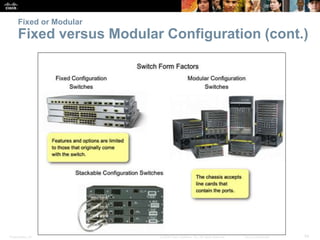
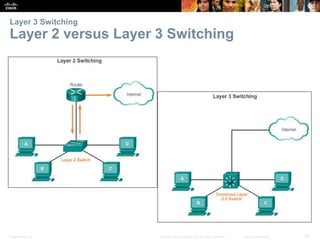
This document provides an overview of Ethernet networking concepts including:
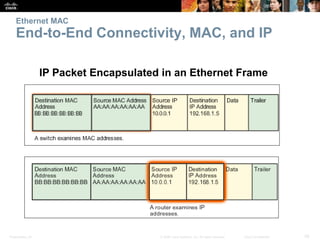
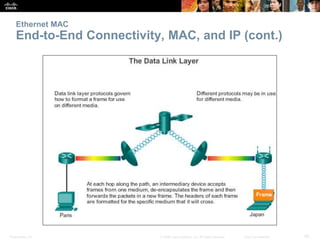
- How Ethernet frames are encapsulated and the purpose of the MAC sublayers.
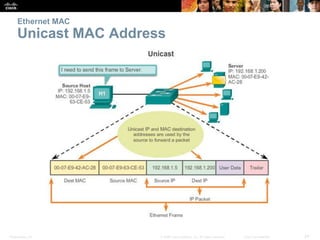
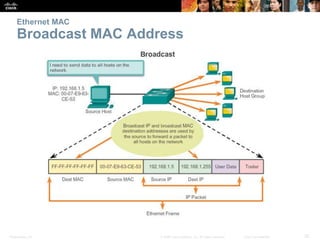
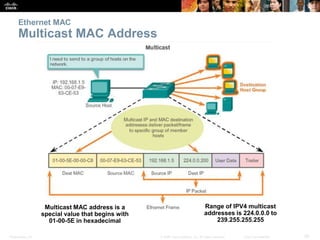
- How MAC addresses are assigned and their role in end-to-end communication.
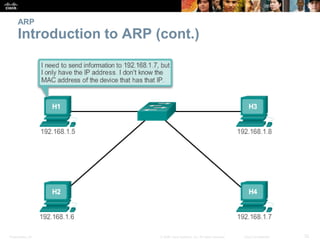
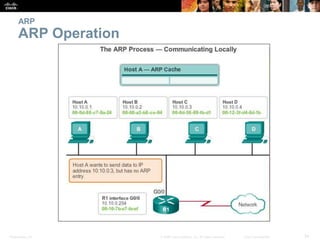
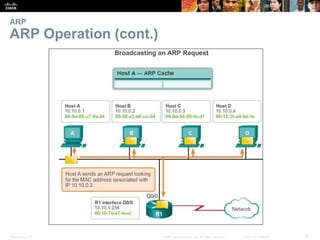
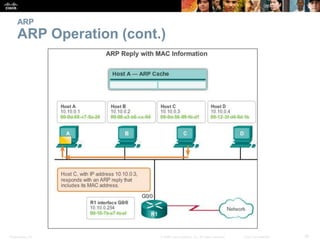
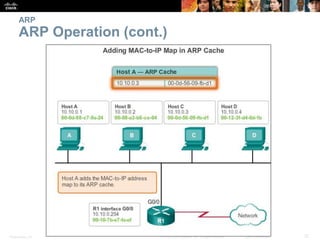
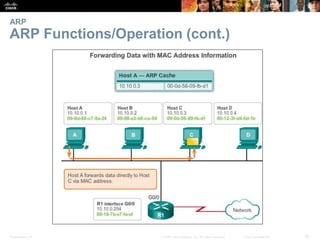
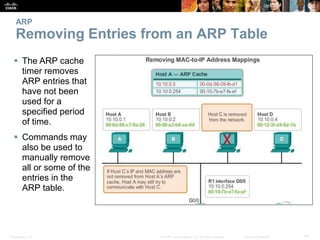
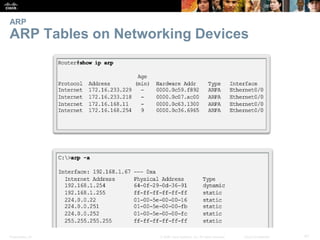
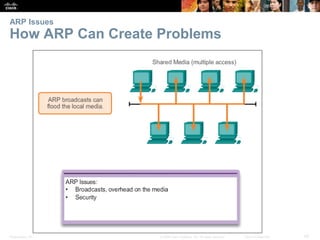
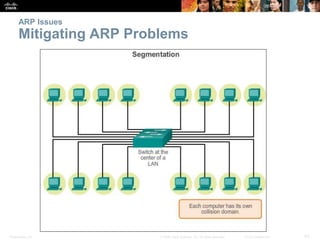
- The purpose and process of ARP for resolving IP addresses to MAC addresses.
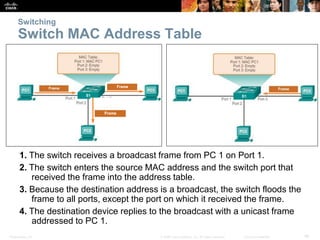
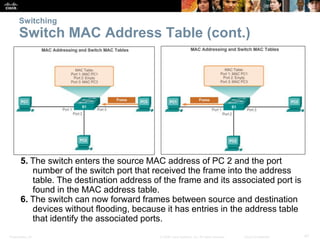
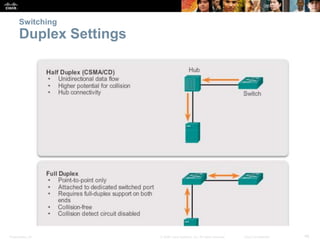
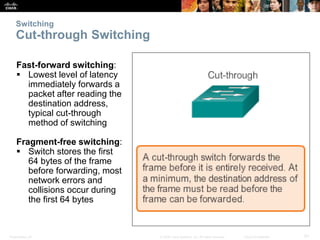
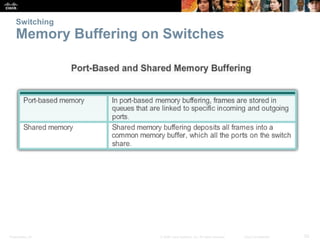
- Basic functions of network switches including building the MAC address table and frame forwarding methods like cut-through switching.