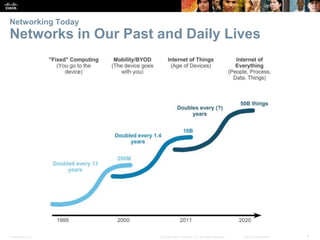
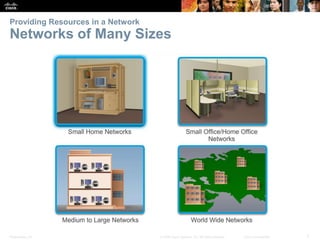
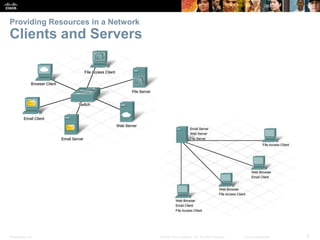
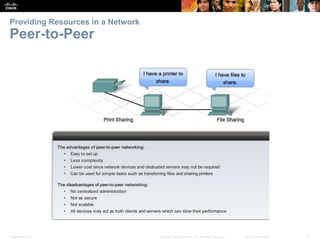
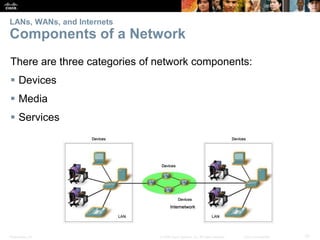
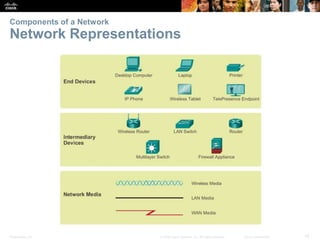
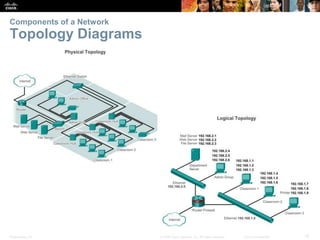
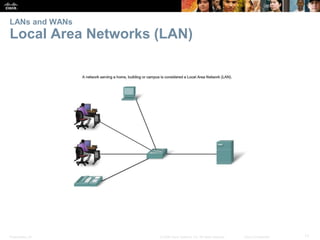
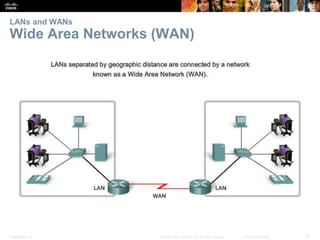
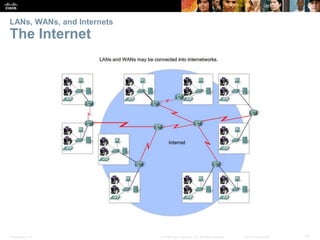
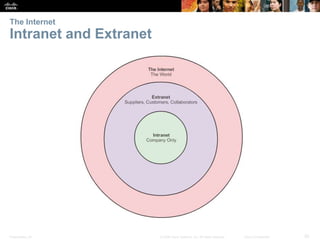
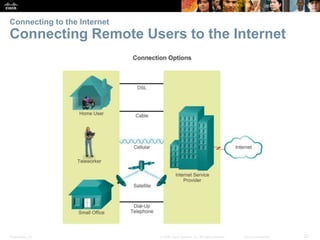
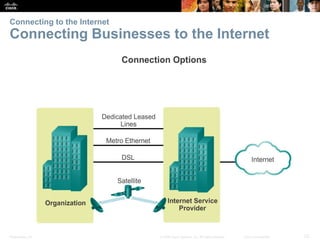
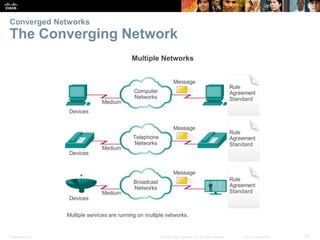
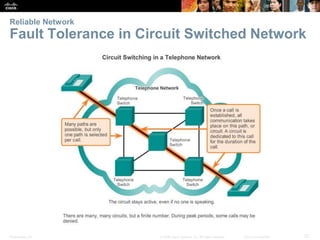
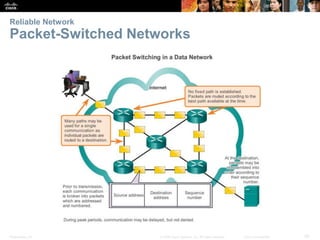
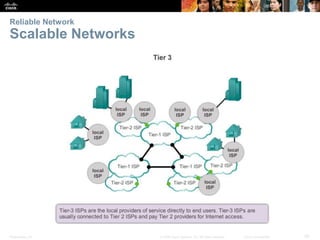
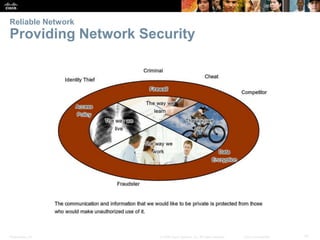
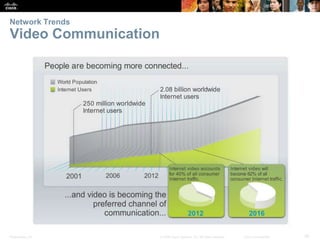
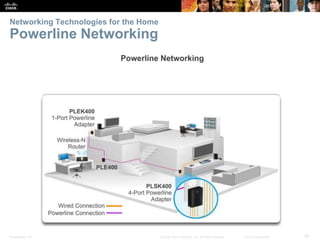
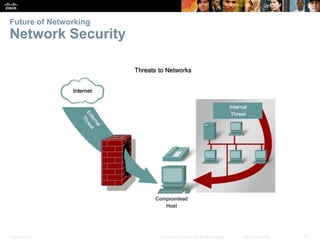
This document provides an overview of networking concepts. It discusses how networks are used in daily life for communication, learning, work and entertainment. It describes the components of networks including devices, media and services. Local area networks (LANs) connect devices within an organization, while wide area networks (WANs) connect multiple LANs and devices over long distances. The largest network is the Internet, which connects millions of networks globally. Emerging trends include bring your own device (BYOD), online collaboration, video communication and cloud computing. The chapter also covers network security threats and solutions.