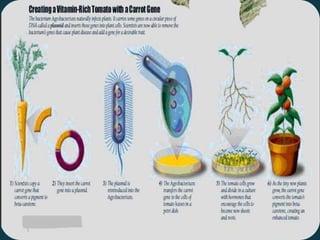
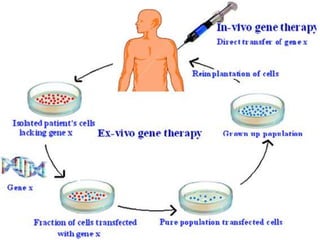
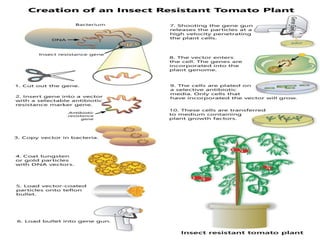
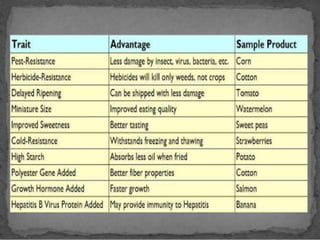
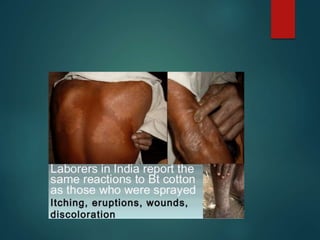
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are organisms whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering. GMOs have a wide range of applications including human gene therapy, producing transgenic plants and crops with desirable traits like pest or disease resistance, researching uses of microbes and mammals, and more. However, GMOs also raise social concerns about potential health risks to animals and humans from consumption, environmental risks of cross-contamination with wild species, and issues around labeling, patents, and ethical use of biological resources.