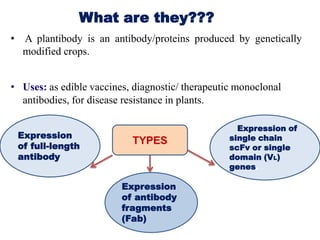
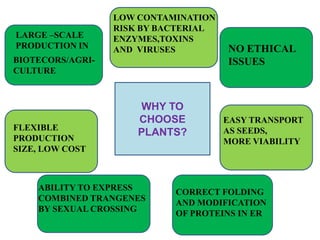
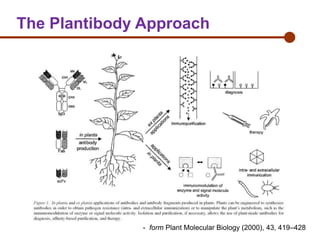
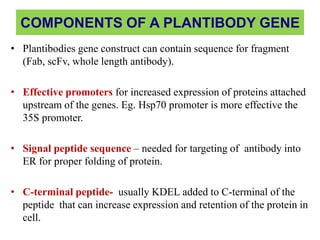
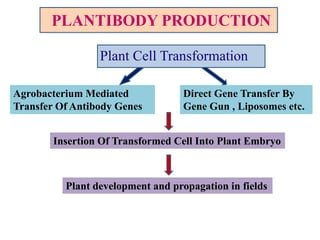
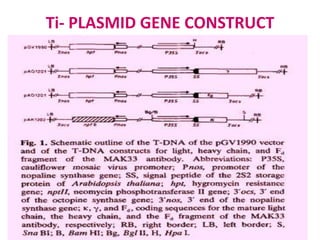
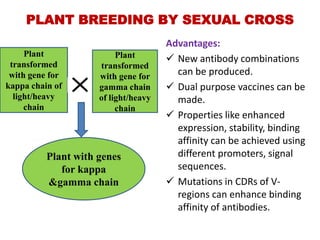
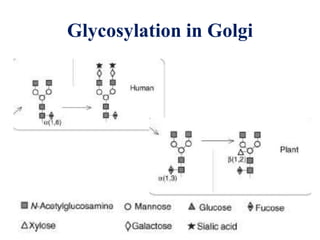
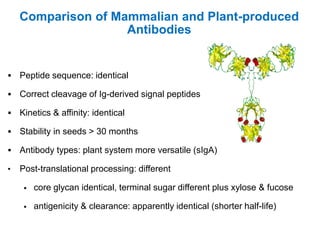
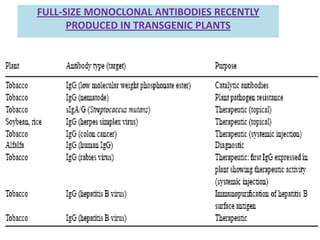
Plantibodies are antibodies or proteins produced in genetically modified crops. They can be used as edible vaccines, diagnostic or therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, or to confer disease resistance in plants. There are three main types - expression of full-length antibodies, antibody fragments, or single chain or single domain genes. Plants are an attractive production system due to low contamination risk, flexible and low-cost production, and no ethical issues. The plantibody approach involves constructing genes containing antibody sequences with effective promoters, then transforming plants and propagating through breeding or tissue culture. Applications include therapeutic antibodies for various diseases and oral vaccines delivered through edible plants. While plant-produced antibodies have identical peptide sequences and functions to mammalian ones, they have different post-