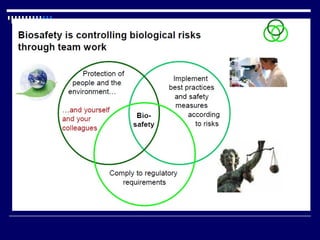
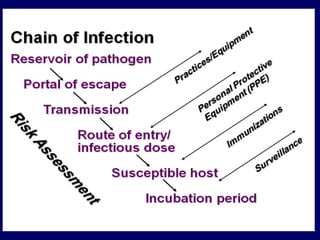
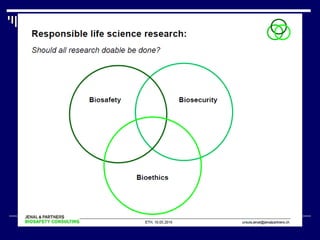
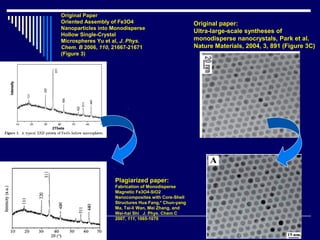
The document discusses biosafety and bioethics, emphasizing methods such as containment and personal protective equipment to ensure safety in laboratories handling infectious agents. It highlights common challenges including inadequate training, poor waste management, and lack of regulations, along with the ethical considerations necessary for conducting research responsibly. Additionally, it addresses the importance of maintaining ethical standards to foster trust and accountability in scientific work.