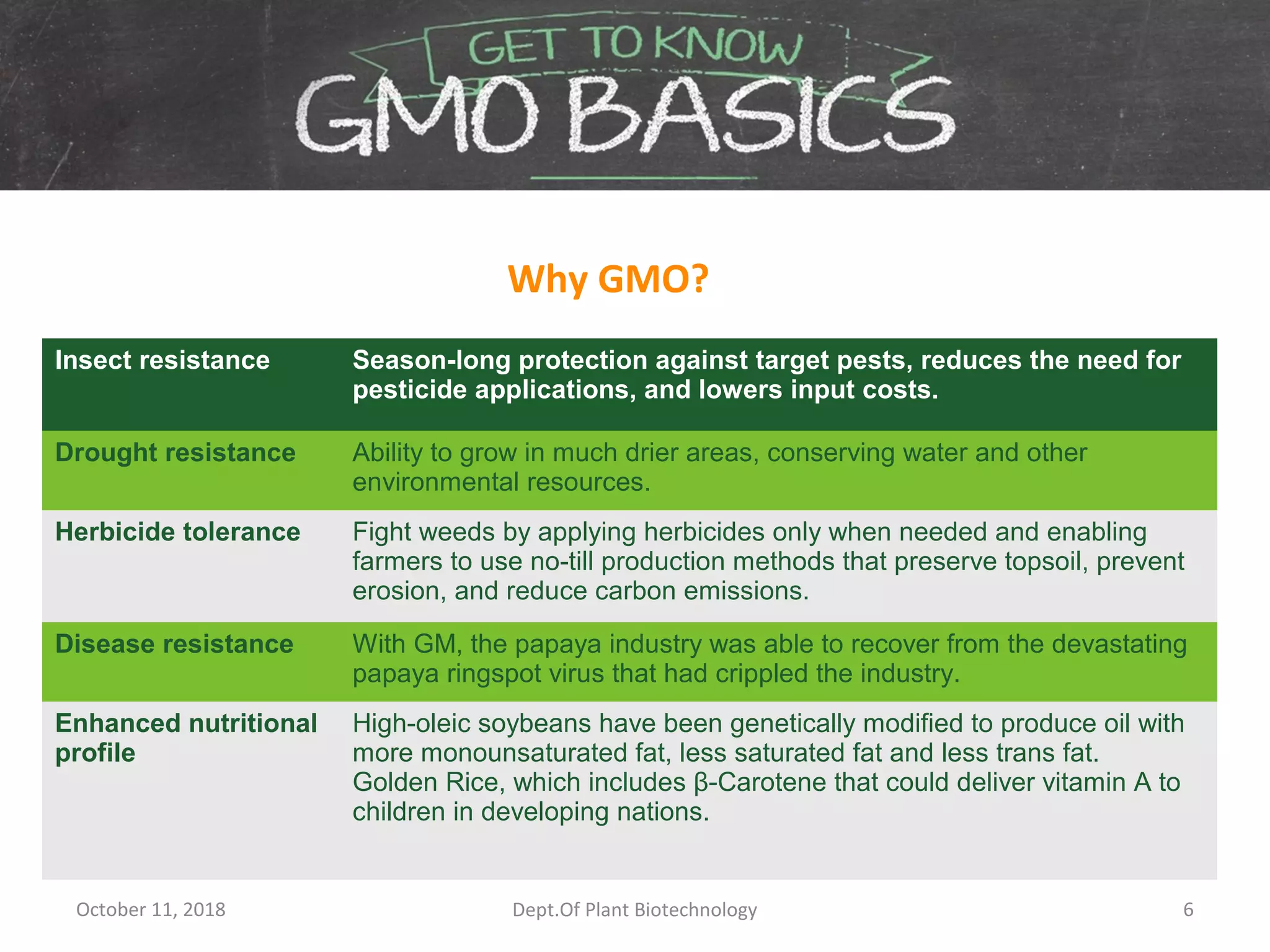
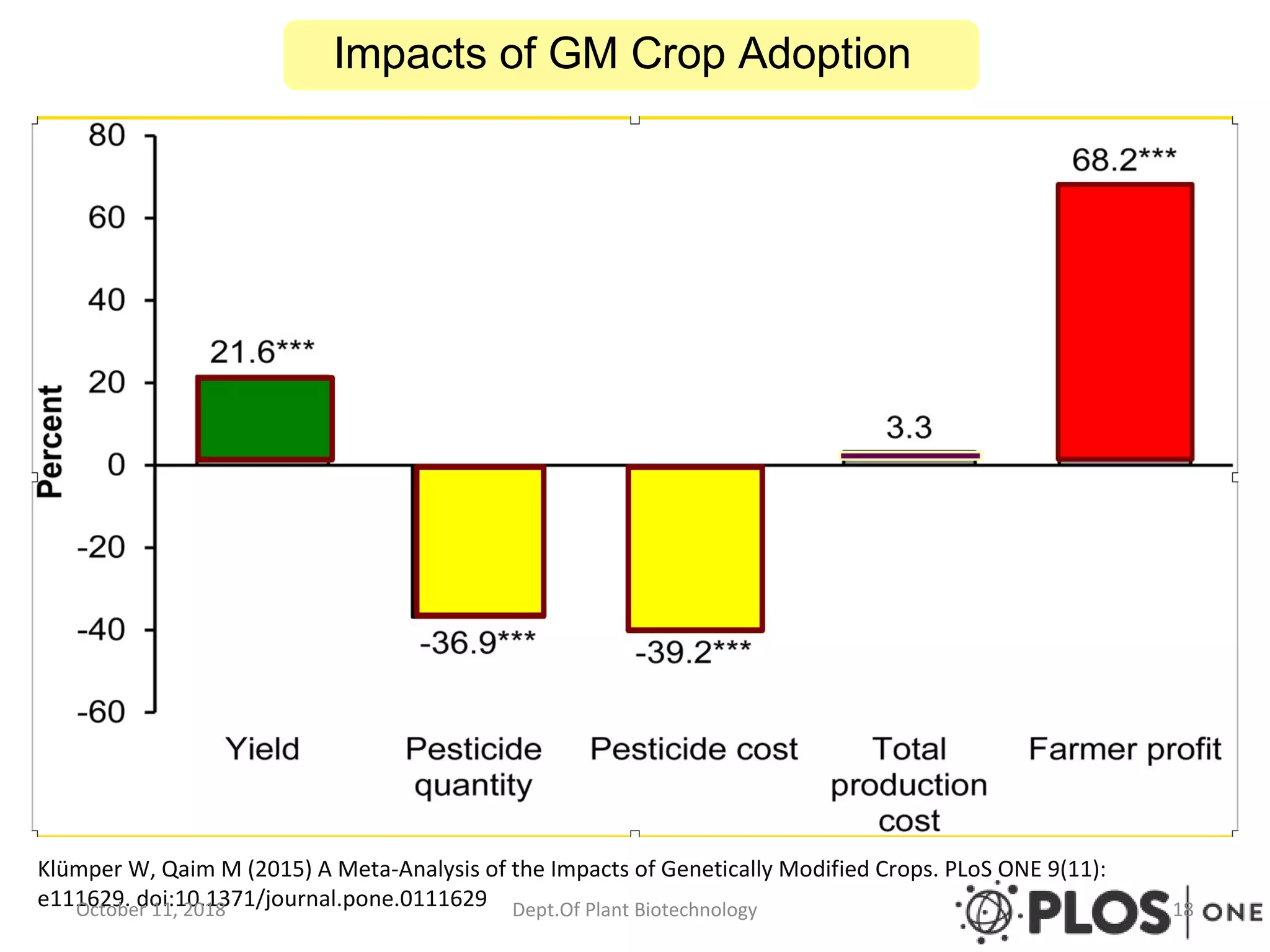
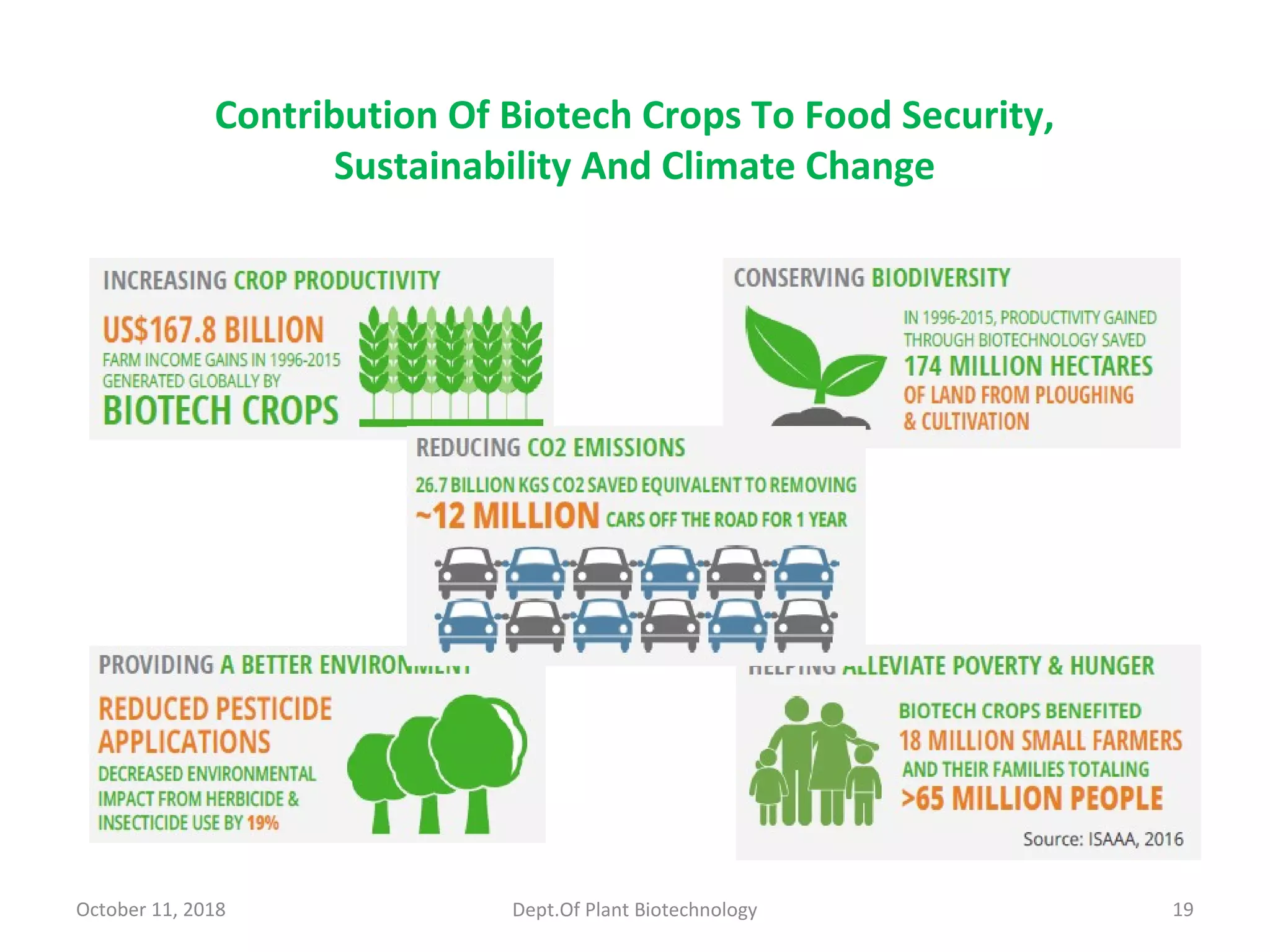
This document discusses the pros and cons of transgenic crops from both national and international perspectives. It provides examples of the benefits of transgenic crops, such as insect resistance, drought tolerance, disease resistance, and enhanced nutritional profiles. However, it also outlines some controversies, including potential human health impacts, environmental hazards like gene transfer to other species, and issues around intellectual property and corporate control. The document examines both sides of the transgenic crop debate through multiple sections and references.














![Cont..
4. Access and intellectual property
– Domination of world food production by companies.
– Increasing dependence on industrialized nations by developing countries.
– Bio piracy, or foreign exploitation of natural resources .
5. Labelling
– Mandatory in India (2013), not mandatory in some countries
(e.g. United States).
– Mixing GM crops with non-GM products confounds labeling attempts.
6. Society
– New advances may be skewed to interests of rich countries.
October 11, 2018 Dept.Of Plant Biotechnology 23
Parsai G. Centre makes labelling of GM foods mandatory. [Online] Available from http://www.thehindu.com/news/national/article
3551679.ece. [Accessed October, 2013].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prosconsofgmo-181011060812/75/Pros-and-cons-of-Transgenic-crops-current-scenario-23-2048.jpg)


































![ReferencesReferences
• Google search & Newspaper articles on GM crops.
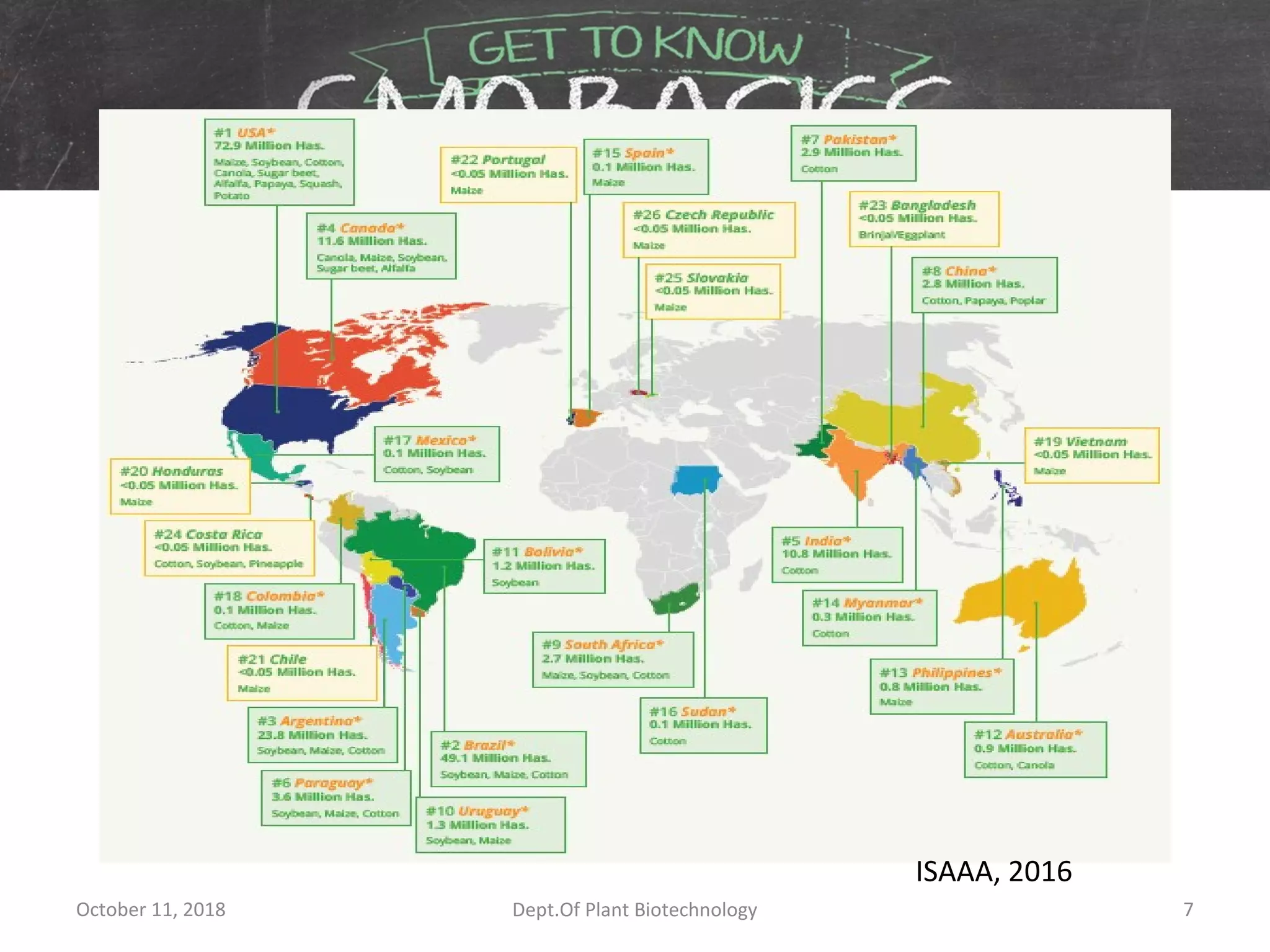
• ISAAA. 2016. Global Status of Commercialized Biotech/GM Crops: 2016. ISAAA
Brief No. 52. ISAAA: Ithaca, NY.
• Manas Ranjan Panda, Research Asst. DLAP (OUAT),Phulbani ,Odisha review
(2016).
• www.Greenpeace.org
• Whitman DB. (2015). Genetically modified foods: harmful or helpful. [Online]
Available from www.csa.com/discoveryguides/gmfood/ overview.php.
[Accessed October, 2012].
• ISAAA 2013 Annual Report Executive Summary, Global Status of Commercialized
Biotech/GM Crops: 2013 ISAAA Brief 46-2013, Retrieved 6 August 2014.
• Ian Berry, “Pesticides Make a Comeback,” The Wall Street Journal, May 21, 2013.
• GM crops: public perception and scientific solutions (Trends in Plant Science, Vol
4, No 12, pp 467-469,Dec 2015).
October 11, 2018 63Dept.Of Plant Biotechnology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/prosconsofgmo-181011060812/75/Pros-and-cons-of-Transgenic-crops-current-scenario-63-2048.jpg)
