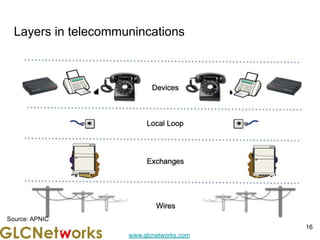
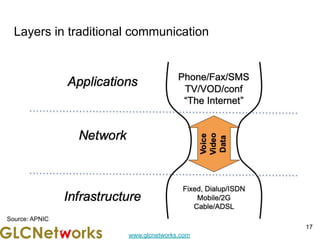
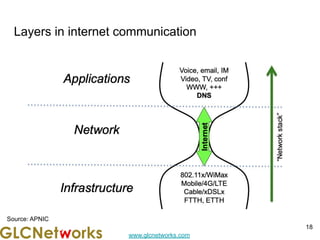
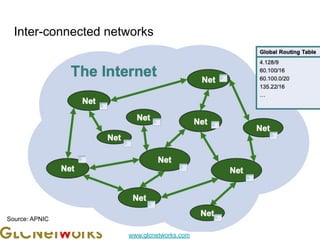
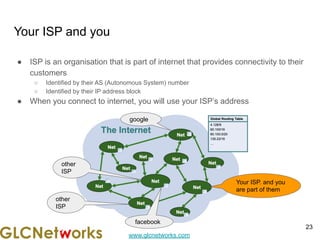
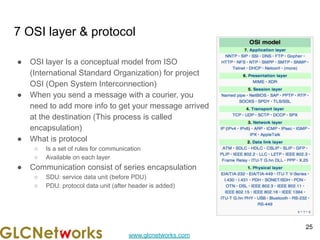
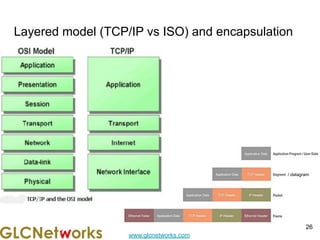
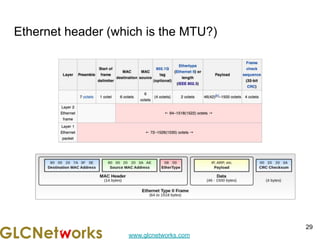
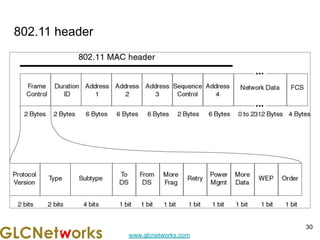
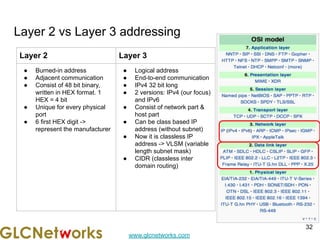
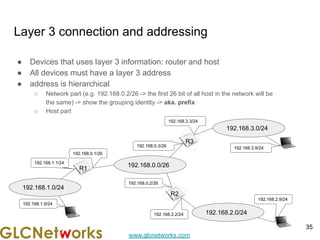
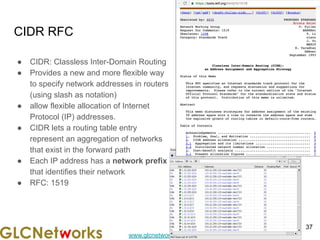
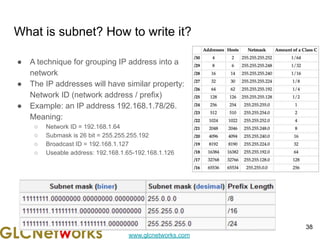
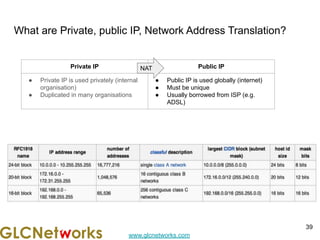
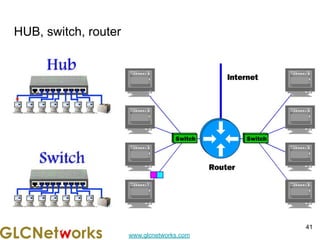
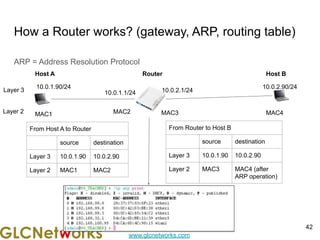
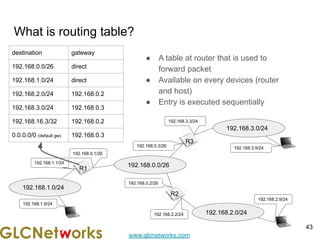
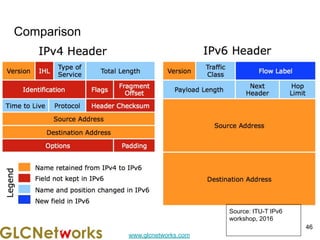
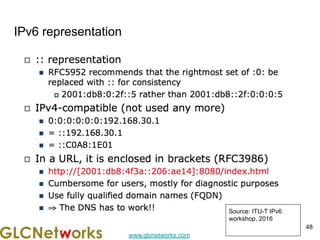
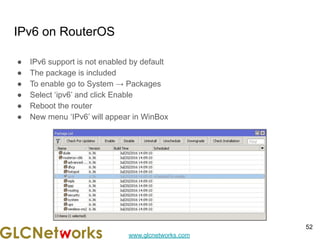
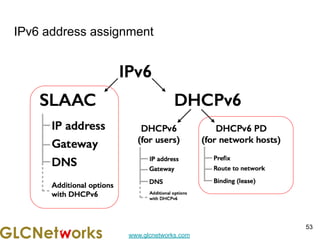
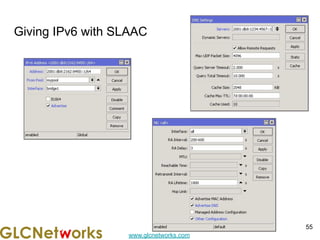
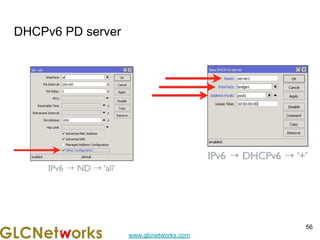
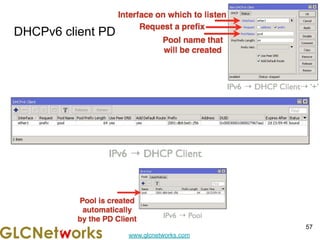
The document is a presentation for a webinar on IPv6 and MikroTik by Achmad Mardiansyah from GLC Networks, covering basic networking concepts, the differences between IPv4 and IPv6, and practical implementation on MikroTik routers. It includes an introduction, prerequisites, live practice sessions, and a Q&A segment, encouraging attendees to share their experiences. The session aims at enhancing understanding of internet protocols and their applications in modern networking.