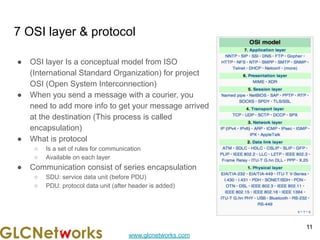
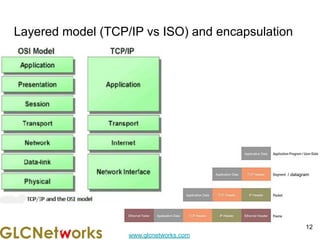
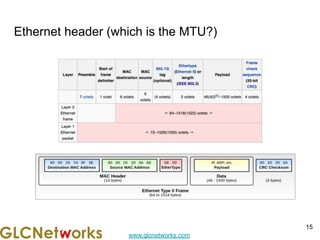
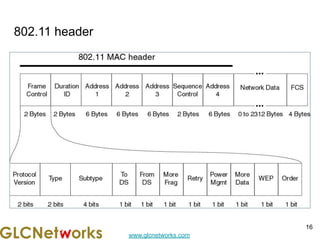
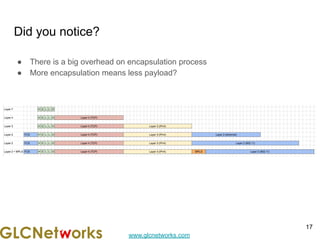
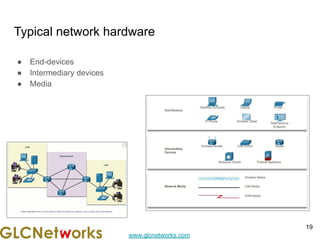
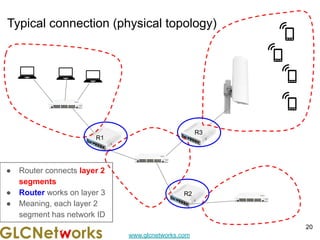
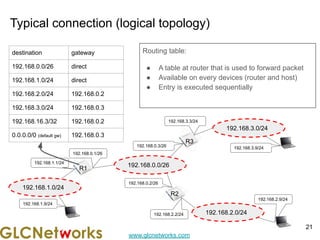
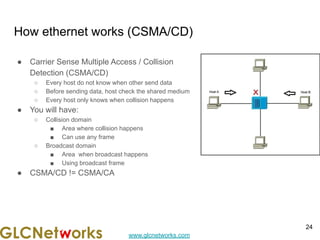
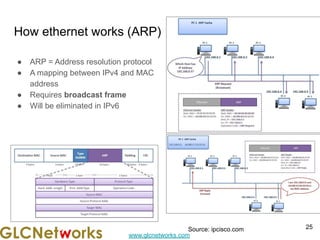
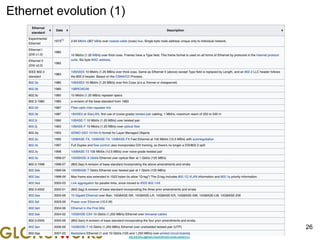
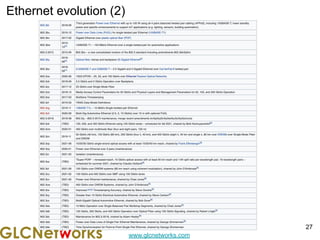
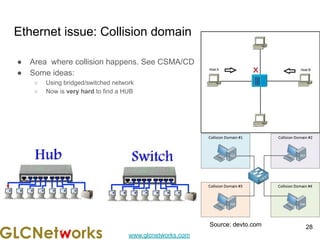
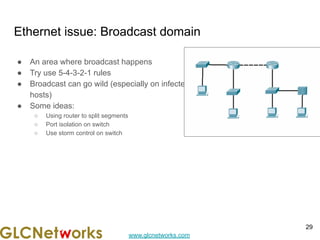
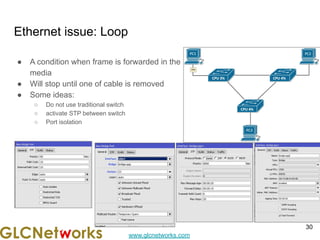
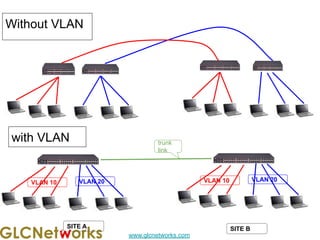
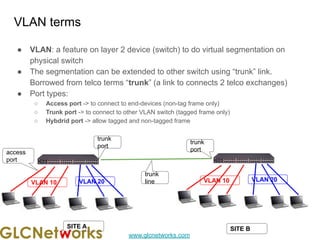
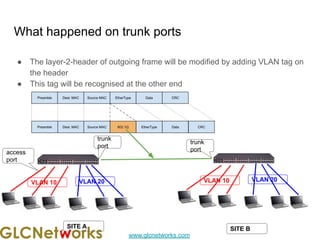
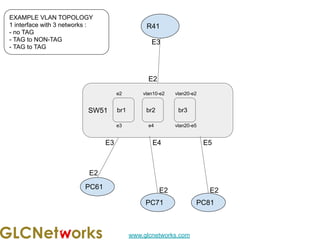
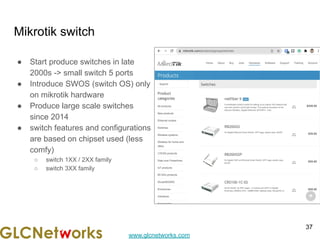
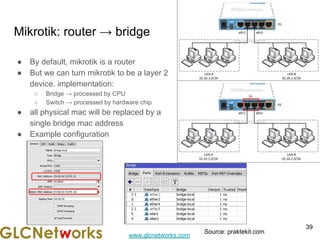
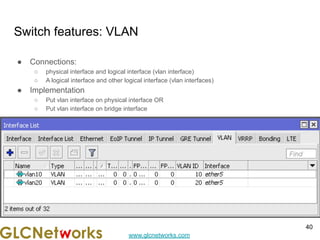
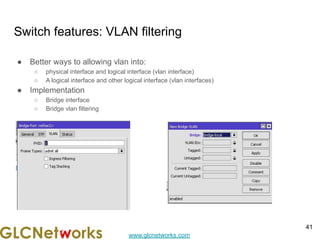
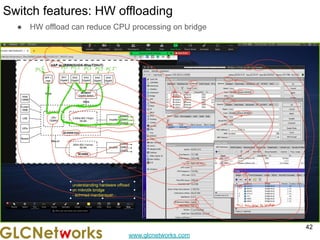
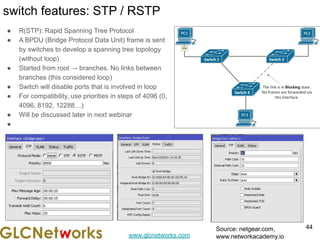
The document outlines a webinar by GLC Networks, focusing on Mikrotik switch features to enhance network performance, led by trainer Achmad Mardiansyah. It covers topics such as switch technology, layering protocols, and various switch functionalities, including VLAN, HW offloading, and loop protection. The session includes live practice and a Q&A segment, along with an invitation for participants to engage and share their knowledge.