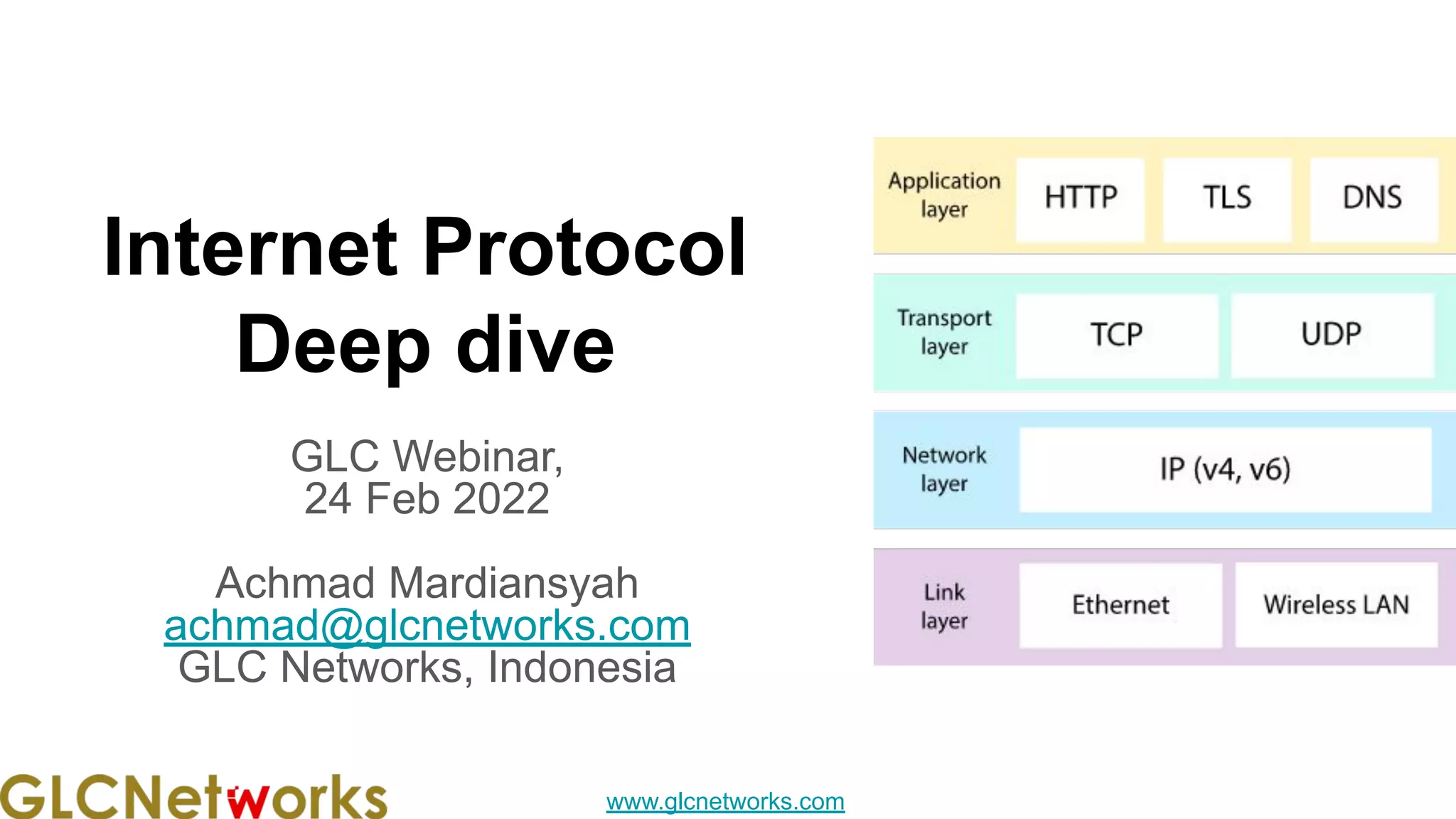
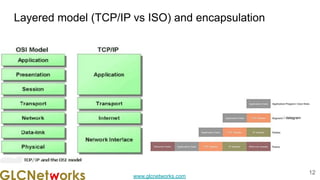
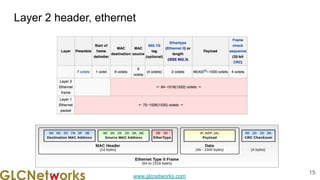
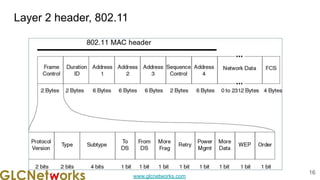
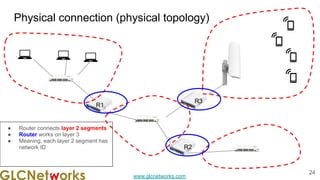
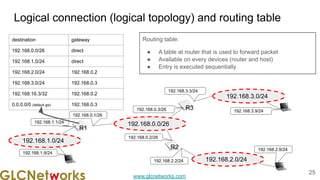
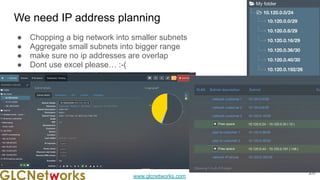
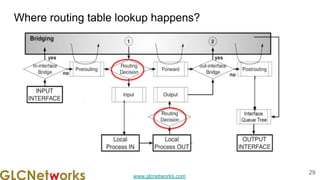
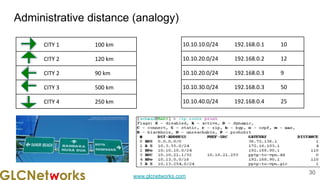
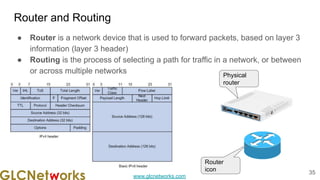
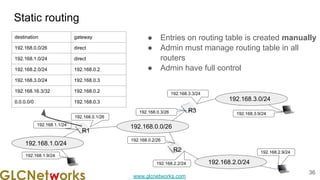
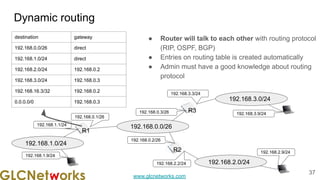
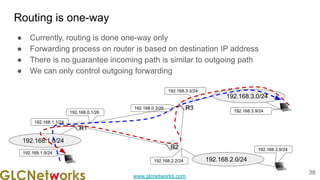
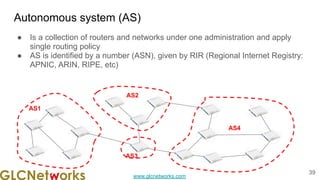
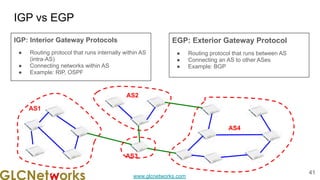
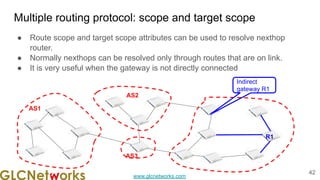
The document outlines the GLC Networks webinar on Internet Protocol, led by trainer Achmad Mardiansyah, covering topics such as OSI layers, IP addressing, routing, and troubleshooting techniques. Key aspects include a review of prerequisite knowledge, introduction to GLC Networks and its offerings, as well as a live practice session. Participants are encouraged to engage in Q&A and share their experiences during the webinar.