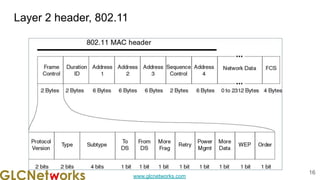
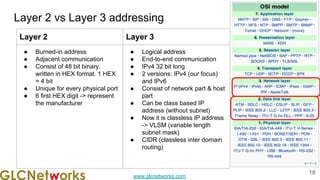
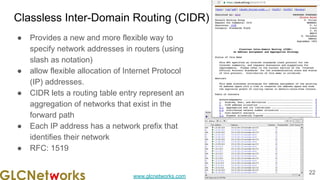
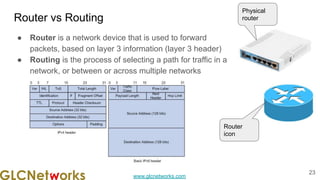
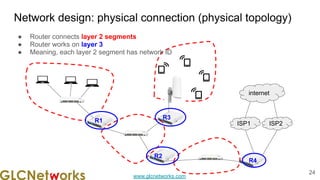
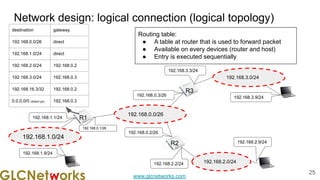
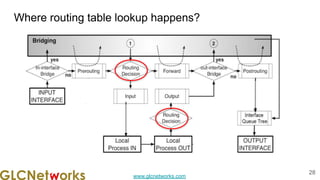
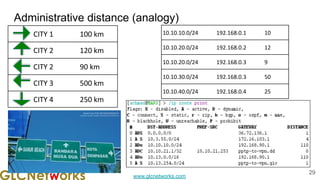
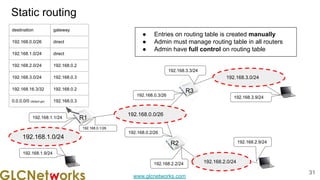
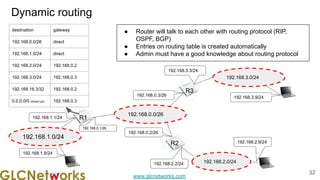
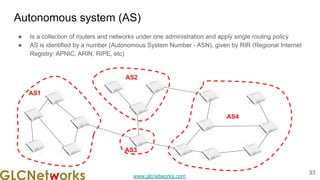
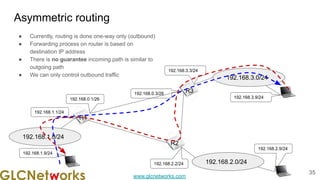
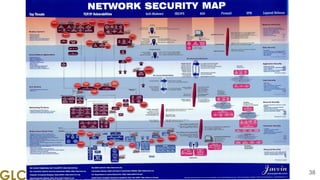
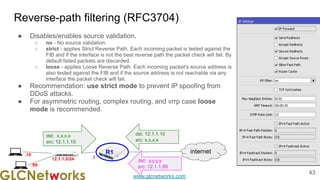
The document is a presentation from a webinar hosted by GLC Networks on the best current practice (BCP 38) for ingress filtering aimed at enhancing network security. It includes foundational knowledge about networking, protocols, and various routing techniques, alongside practical recommendations for mitigating network attacks like IP spoofing and DDoS. The presentation emphasizes the importance of employing strict mode for reverse-path filtering and highlights the role of GLC Networks as an IT training and consulting entity in Indonesia.