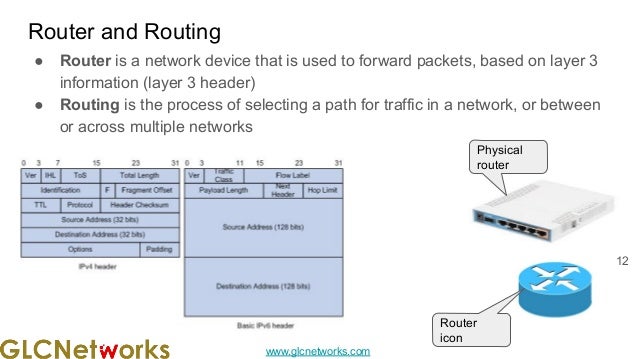
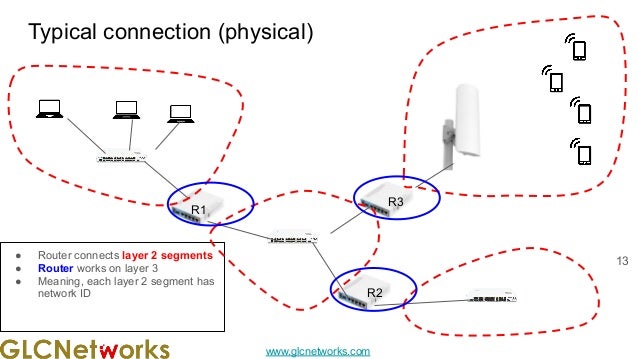
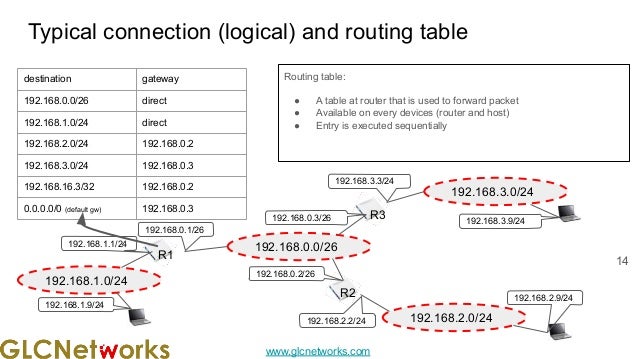
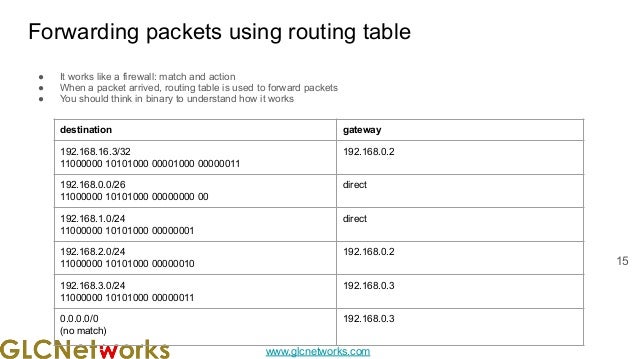
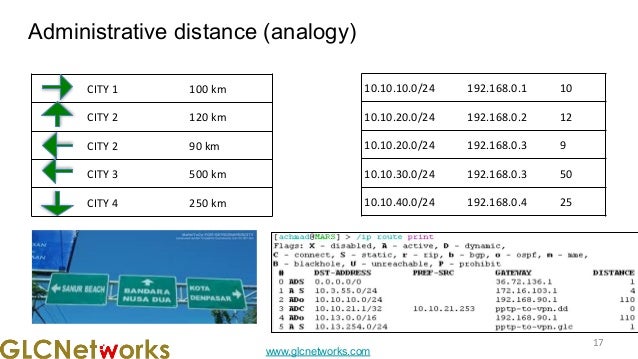
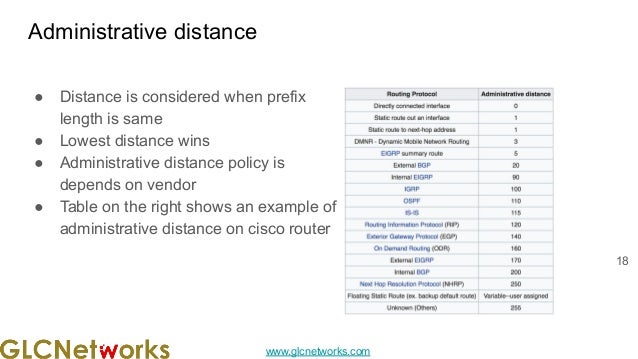
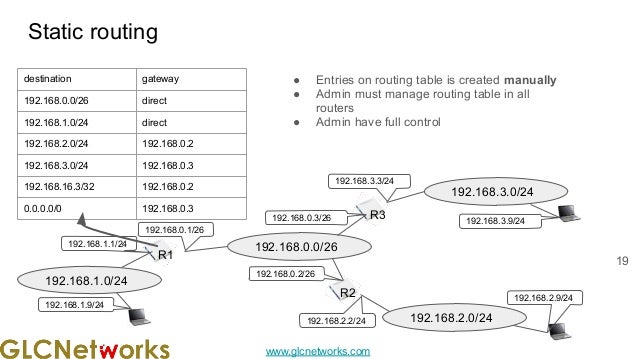
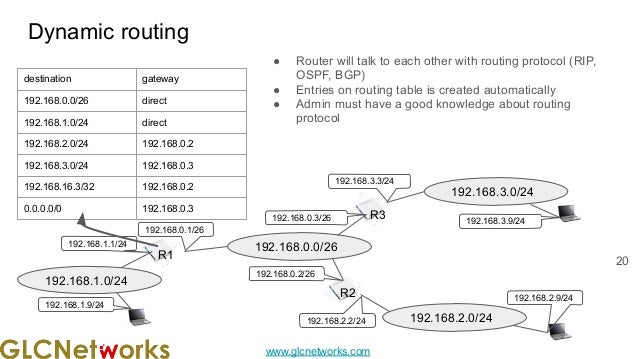
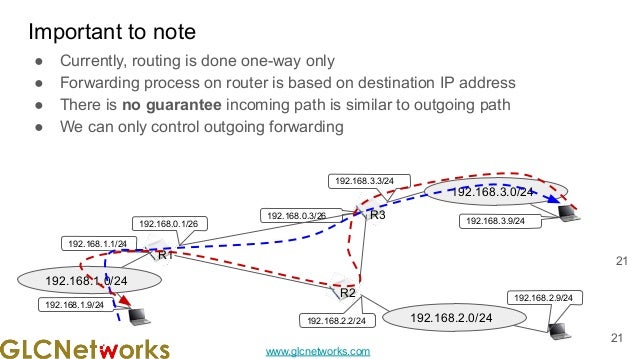
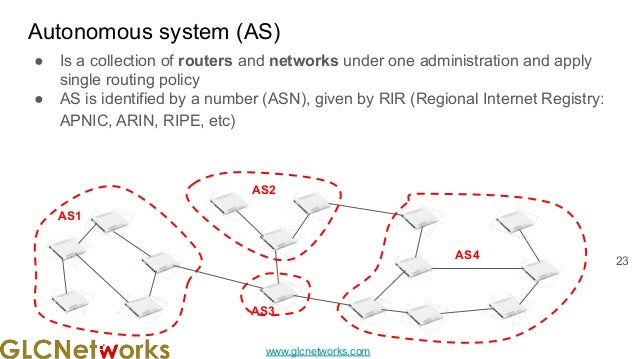
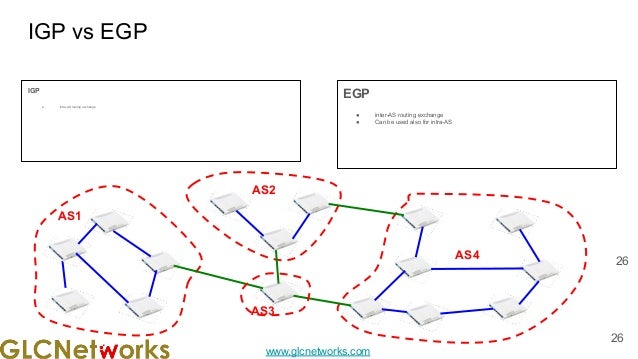
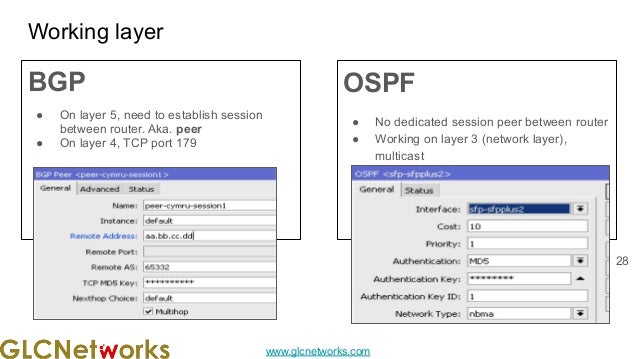
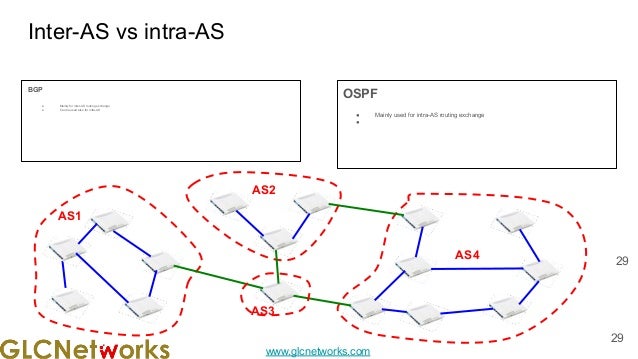
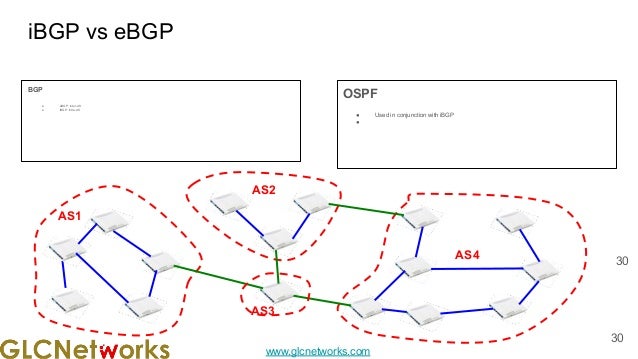
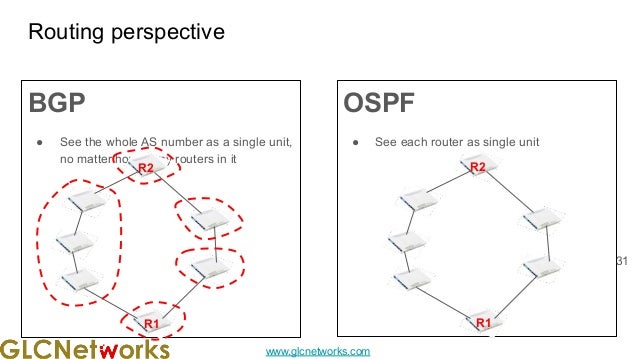
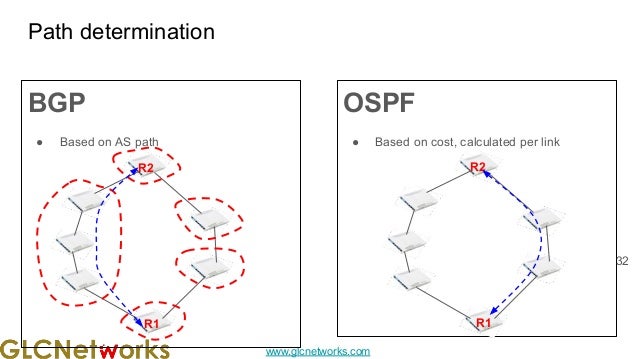
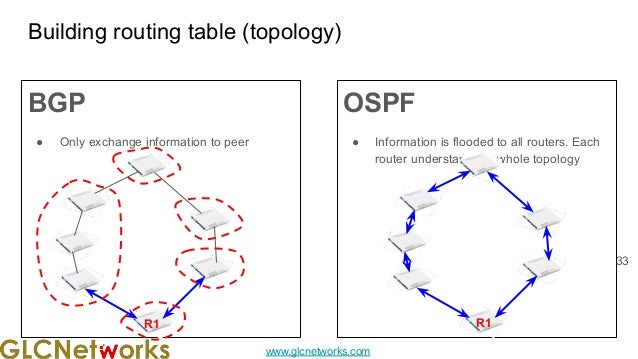
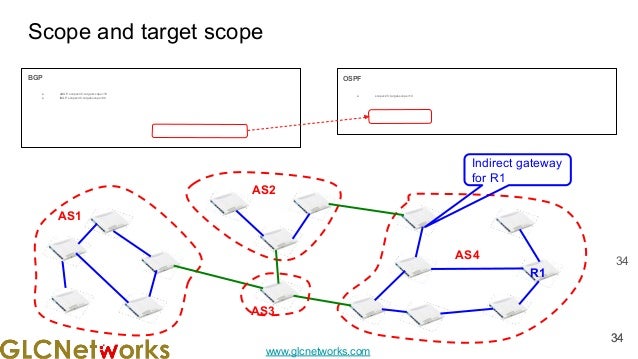
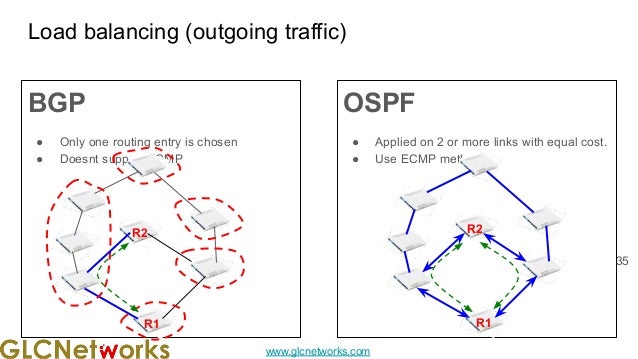
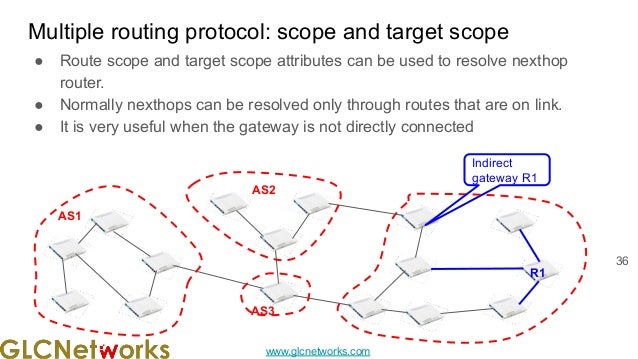
The document presents a webinar on policy-based routing with indirect BGP hosted by GLC Networks, led by trainer Achmad Mardiansyah. It covers essential networking concepts, router functions, routing techniques (both static and dynamic), and the differences between interior and exterior gateway protocols, specifically focusing on BGP and OSPF. Additionally, it invites participants to engage in live practices and Q&A sessions while promoting GLC's training opportunities and resources.