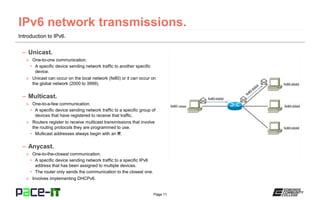
The document provides an overview of IPv6, highlighting its significance as the successor to IPv4, addressing the limitations of the latter and offering a much larger address space of over 340 undecillion addresses. It explains the structure of IPv6 addresses, including local and global formats, and discusses various types of communications such as unicast, multicast, and anycast. Additionally, the document touches on auto-configuration capabilities and the compatibility of IPv6 with IPv4 through methods like dual stack configuration and tunneling.