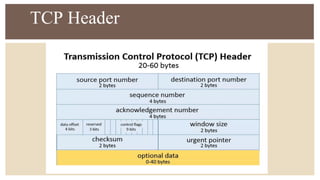
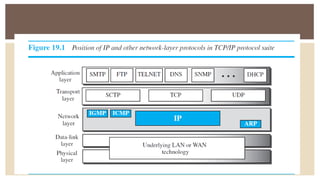
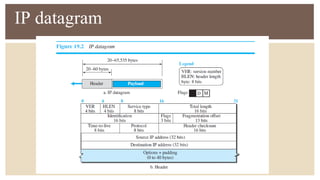
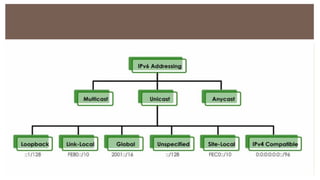
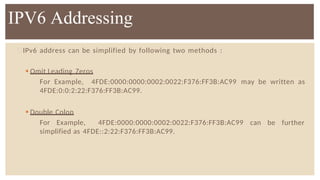
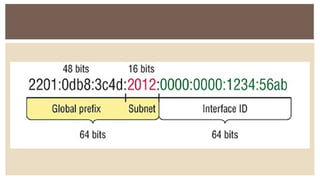
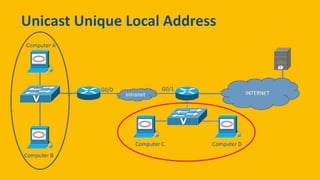
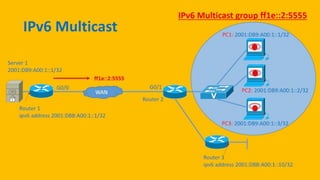
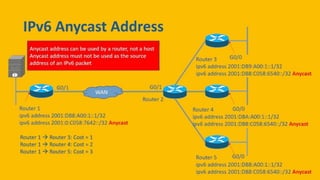
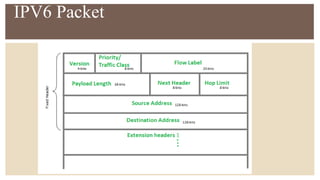
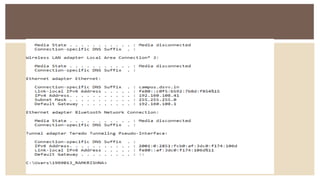
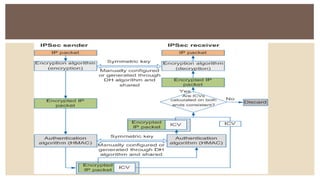
IPv6 was developed by IETF to address the problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, as IPv4 addresses were running out. IPv6 addresses are 128 bits, vastly larger than the 32-bit IPv4 addresses, providing trillions more available addresses. IPv6 was intended to replace IPv4 as the new internet protocol standard, providing features like built-in security, larger address space, and more efficient routing.