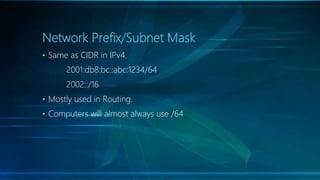
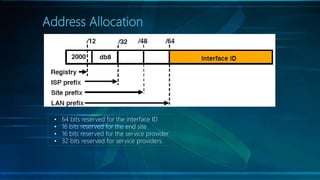
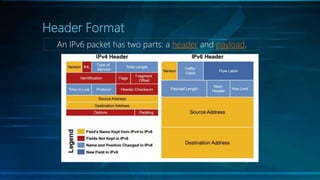
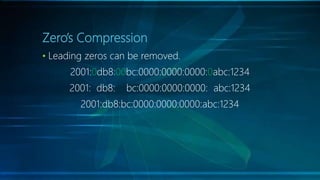
IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol, designed to replace IPv4 due to address exhaustion issues, providing an extensive 128-bit address space. It simplifies address representation through zero compression and offers auto-configuration features for new devices. Key elements include multicast addressing, absence of traditional broadcasts, and a structured allocation scheme for network prefixes.





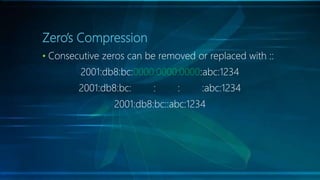


![Ports
• [IPv6 address]: port
• [2001:db8:bc::abc:1234]:91
• http:// [2001:db8:bc::abc:1234]:91](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipv6-190507175133/85/IPv6-basic-introduction-11-320.jpg)