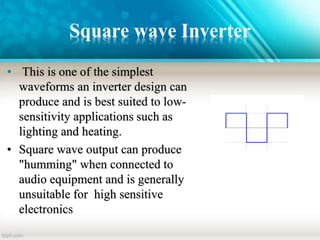
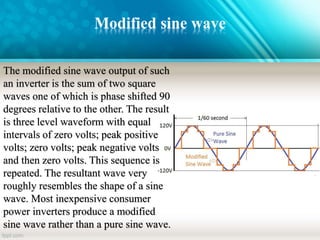
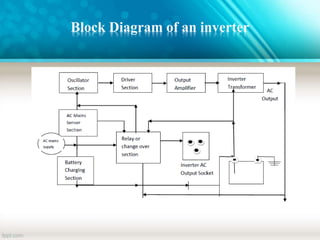
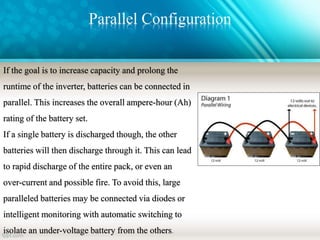
An inverter is a device that converts DC power from batteries into AC power. It allows appliances that run on AC power to operate from a DC power source. There are different types of inverters based on their output waveform: square wave, modified sine wave, and pure sine wave. Square wave inverters are the cheapest but produce a less stable output. Modified sine wave inverters produce a three-step waveform and are suitable for basic appliances. Pure sine wave inverters have the best waveform quality but are the most expensive. Inverters are commonly used in UPS systems, with solar panels, for backup power, and in HVDC transmission.