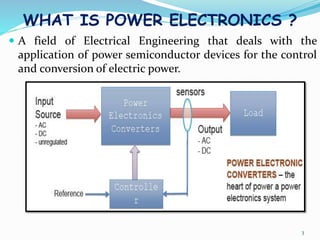
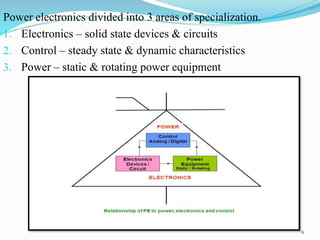
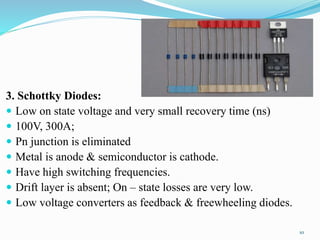
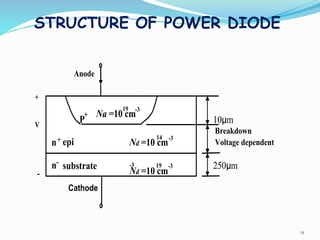
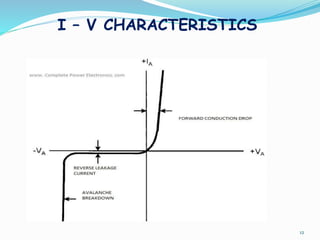
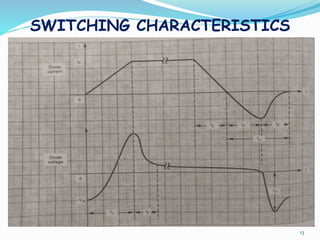
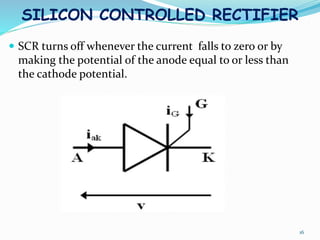
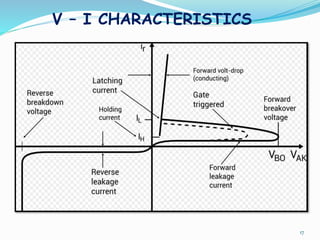
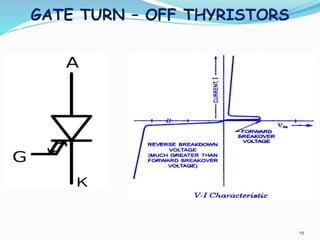
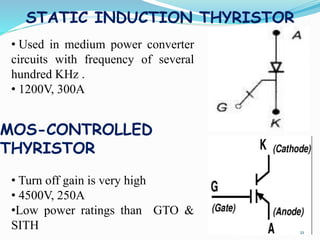
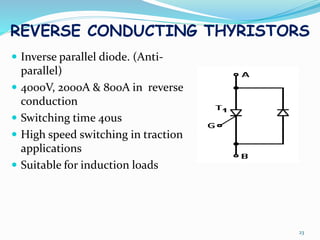
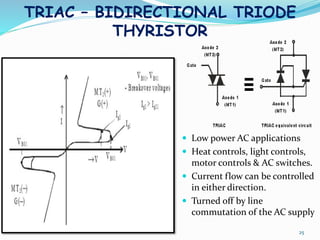
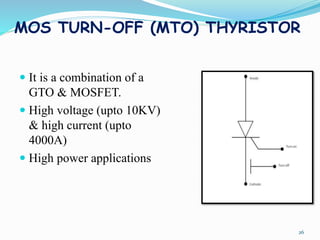
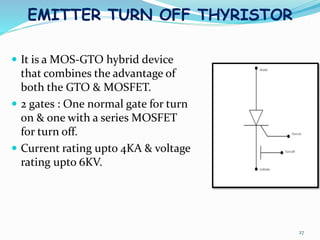
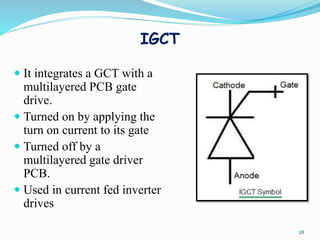
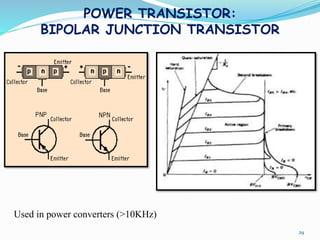
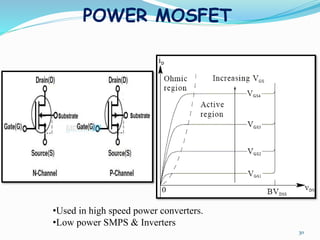
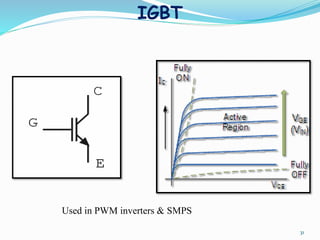
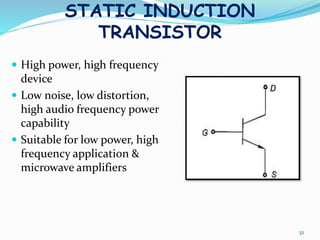
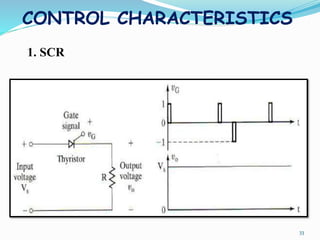
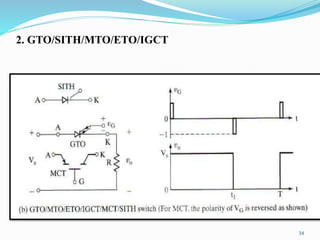
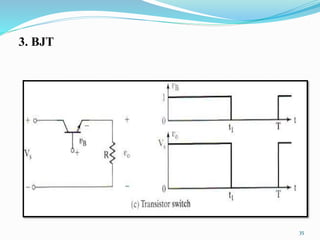
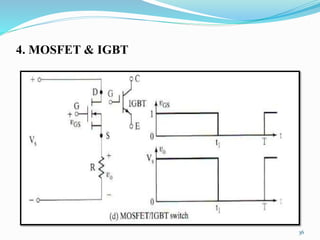
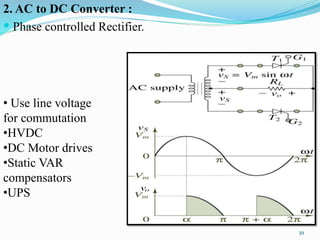
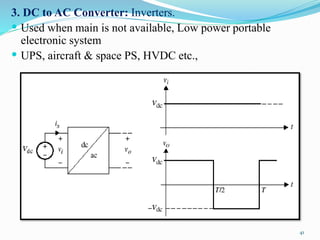
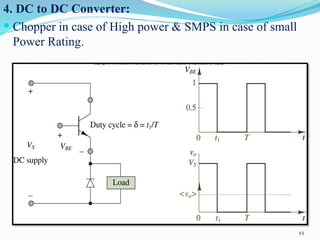
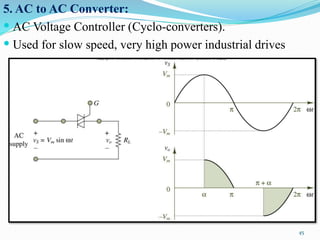
The document presents an overview of power electronics, focusing on the application of power semiconductor devices for electric power control and conversion. It covers various types of semiconductor devices including thyristors, transistors, and diodes, along with their characteristics, applications, and different power electronic circuits. Additionally, it discusses the classification of devices based on their operational characteristics and highlights peripheral effects associated with power converters.