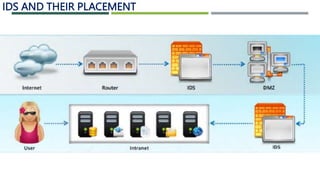
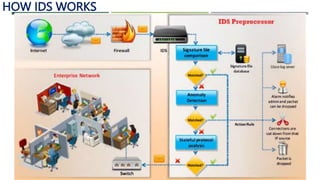
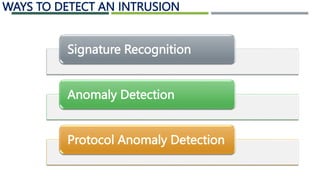
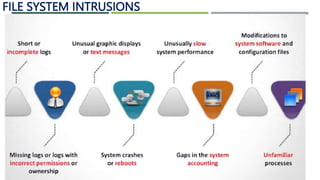
An intrusion detection system (IDS) monitors network traffic and system activities for malicious activities or policy violations. An IDS uses signature-based detection to compare events against known intrusion signatures. It also uses anomaly detection to identify deviations from a baseline of normal user behavior. A network-based IDS monitors all network traffic while a host-based IDS analyzes the activities on an individual system. Other types of IDS include log file monitoring, file integrity checking, and system integrity verification. An IDS helps identify intrusions by detecting anomalies, protocol violations, and unauthorized changes to systems or files.