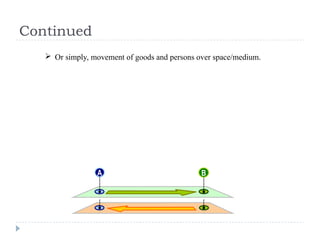
This document provides an overview of transportation engineering. It defines transportation engineering as the application of technology and scientific principles to planning, designing, operating, and managing facilities for transporting people and goods. It discusses the importance of transportation for a country's development and economy. It also outlines the major modes of transportation, including roads, railways, waterways, and airways, describing their key characteristics. The document focuses on the characteristics of road transportation and its importance as the most accessible mode. It concludes by discussing factors that influence the choice of transportation mode.